Difference between revisions of "Mite Life Cycle"
Fiorecastro (talk | contribs) |
|||
| (4 intermediate revisions by one other user not shown) | |||
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
| − | {{ | + | {{review}} |
| − | |||
[[File:mite egg.jpg|thumb|150px|right|Red Palm Mite Egg. E. Erbe unknown date, wikimedia commons]] | [[File:mite egg.jpg|thumb|150px|right|Red Palm Mite Egg. E. Erbe unknown date, wikimedia commons]] | ||
| − | [[File:larva.jpg|thumb|150px|right|Mite larva of either family ''Trombidiidae'' or ''Erythraeidae''. Pudding4brains 2008, wikimedia commons]] | + | [[File:larva.jpg|thumb|150px|right|Mite larva of either family ''Trombidiidae'' or ''Erythraeidae''. Pudding4brains 2008, wikimedia commons]][[File:nymph.jpg|thumb|150px|right|Rhinonyssid mite nymph. Lajos.Rozsa. 1988, wikimedia commons]] |
The life cycle length of a mite varies between species, but is approximately 3 weeks on average. The ''[[Psoroptes]]'' mite has a lifecycle of 10 days, whereas the ''[[Demodex]]'' mite has a 21 day lifecycle. | The life cycle length of a mite varies between species, but is approximately 3 weeks on average. The ''[[Psoroptes]]'' mite has a lifecycle of 10 days, whereas the ''[[Demodex]]'' mite has a 21 day lifecycle. | ||
| Line 16: | Line 15: | ||
Once nymphs have emerged from the larval stage, the nymphs moult finally into adult mites. These adult mites can be [[Burrowing Mites|burrowing mites]] or [[:Category:Non-Burrowing Mites|surface mites]] depending on their species. | Once nymphs have emerged from the larval stage, the nymphs moult finally into adult mites. These adult mites can be [[Burrowing Mites|burrowing mites]] or [[:Category:Non-Burrowing Mites|surface mites]] depending on their species. | ||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
==References== | ==References== | ||
Durden, Lance A. (2002). Medical and veterinary entomology (3rd ed.). Academic Press. | Durden, Lance A. (2002). Medical and veterinary entomology (3rd ed.). Academic Press. | ||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| + | [[Category:To_Do_-_AimeeHicks]] | ||
[[Category:Expert_Review]][[Category:Mites|E]] | [[Category:Expert_Review]][[Category:Mites|E]] | ||
Revision as of 11:06, 23 July 2010
| This article has been peer reviewed but is awaiting expert review. If you would like to help with this, please see more information about expert reviewing. |
The life cycle length of a mite varies between species, but is approximately 3 weeks on average. The Psoroptes mite has a lifecycle of 10 days, whereas the Demodex mite has a 21 day lifecycle.
Eggs
The female mite lays eggs on the host. The number of eggs varies between species.
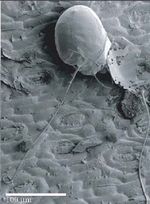
Larvae
The mite's eggs hatch into hexapod larvae. Larvae often only feed on skin cells, not blood at this stage. In some mites the larval stage is the only parasitic stage of their life cycle, for example Trombicula autumnalis. This stage of the mite's life cycle usually lasts around 3-4 days.
Nymphs
The larvae remain dormant for 24 hours and moult into nymphs. There are two nymphal stages recognised. This stage in the mite's life cycle also lasts around 3-4 days.
Adults
Once nymphs have emerged from the larval stage, the nymphs moult finally into adult mites. These adult mites can be burrowing mites or surface mites depending on their species.
References
Durden, Lance A. (2002). Medical and veterinary entomology (3rd ed.). Academic Press.