Difference between revisions of "Soft Palate"
Jump to navigation
Jump to search
Fiorecastro (talk | contribs) |
|||
| (21 intermediate revisions by 4 users not shown) | |||
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
| − | + | {{toplink | |
| + | |linkpage =Alimentary - Anatomy & Physiology | ||
| + | |linktext =Alimentary System | ||
| + | |maplink = | ||
| + | }} | ||
| + | <br> | ||
==Introduction== | ==Introduction== | ||
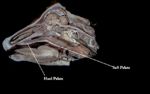
| − | The soft palate (velum palatine) is located caudally to the [[Hard Palate|hard palate]] | + | The soft palate (velum palatine) is located caudally to the [[Hard Palate - Anatomy & Physiology|hard palate]]. It is comprised of muscle and is involved in tasting food and in [[deglutition]]. |
| − | [[Image:Hard and Soft Palate Anatomy.jpg|thumb|right| | + | [[Image:Hard and Soft Palate Anatomy.jpg|thumb|right|150px|Soft Palate - Copyright Nottingham 2008]] |
==Structure and Function== | ==Structure and Function== | ||
| − | + | *Muscle | |
| + | |||
| + | *Contacts [[Epiglottis|epiglottis]] caudally | ||
| − | [[Image:Soft Palate XS.jpg|thumb|right| | + | *Very folded mucosa |
| + | |||
| + | *Striated palatine muscle | ||
| + | [[Image:Soft Palate XS.jpg|thumb|right|150px|Soft Palate Cross-section - Copyright RVC]] | ||
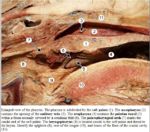
==Musculature and Innervation== | ==Musculature and Innervation== | ||
| − | + | *Sensation and taste from glossopharyngeal ([[Cranial Nerves - Anatomy & Physiology|CN IX]]) | |
| − | + | *Palatine muscle | |
| − | + | **Origin: hard palate transeverse ridges | |
| + | **Insertion: soft palate | ||
| + | **Shortens palate | ||
| + | **Major innervation from vagus nerve ([[Cranial Nerves - Anatomy & Physiology|CN X]]) | ||
| + | **Minor from glossopgaryngeal nerve ([[Cranial Nerves - Anatomy & Physiology|CN IX]]) | ||
| − | + | *Tensor velli palatini | |
| − | + | **Origin: near tympanic bulla on [[Skull and Facial Muscles - Anatomy & Physiology#Temporal Bone (os temporale)|temporal bone]] | |
| − | [[Image:Pharynx Anatomy.jpg|thumb|right| | + | **Insertion: lateral aponeurosis |
| + | **Pharyngeal arch 1 | ||
| + | **Mandibular of trigeminal ([[Cranial Nerves - Anatomy & Physiology|CN V3]]) | ||
| + | **Tenses soft palate | ||
| + | [[Image:Pharynx Anatomy.jpg|thumb|right|150px|Soft palate - Copyright C.Clarkson and T.F.Fletcher University of Minnesota]] | ||
| + | *Levator velli palatini | ||
| + | **Origin: near tympanic bulla on [[Skull and Facial Muscles - Anatomy & Physiology#Temporal Bone (os temporale)|temporal bone]] | ||
| + | **Insertion: lateral aponeurosis | ||
| + | **Raises soft palate | ||
| + | **Major innervation from vagus nerve ([[Cranial Nerves - Anatomy & Physiology|CN X]]) | ||
| + | **Minor from glossopgaryngeal nerve ([[Cranial Nerves - Anatomy & Physiology|CN IX]]) | ||
| − | + | *Palatopharyngeus | |
| − | + | **closes palatopharyngeal arch and therefore lift soft palate | |
| + | **Major innervation from vagus nerve ([[Cranial Nerves - Anatomy & Physiology|CN X]]) | ||
| + | **Minor from glossopgaryngeal nerve ([[Cranial Nerves - Anatomy & Physiology|CN IX]]) | ||
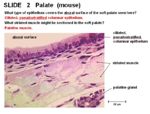
| − | === | + | ==Histology== |
| − | |||
| − | + | [[Image:Soft Palate Mouse.jpg|thumb|right|150px|Soft Palate (Mouse) - Copyright RVC 2008]] | |
| − | [[Image:Soft Palate Mouse.jpg|thumb|right| | + | *Respiratory mucosa - ciliated pseudostratified columnar epithelium on aboral surface |
| − | + | ||
| + | *Stratified squamous epithelium on oral surface | ||
| + | |||
| + | *[[Palatine Gland - Anatomy & Physiology|Palatine]] salivary glands | ||
==Species Differences== | ==Species Differences== | ||
===Porcine=== | ===Porcine=== | ||
| − | + | *Soft palate does not contact the [[Epiglottis|epiglottis]] as the porcine soft palate is raised higher in the [[Oral Cavity Overview - Anatomy & Physiology|oral cavity ]] than in other species | |
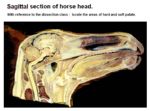
===Equine=== | ===Equine=== | ||
| − | + | *Tight laryngeal cuff around the laryngeal entrance therefore the soft palate cannot be raised for long periods of time and thus horses are nasal breathers | |
| + | |||
| + | *Laryngeal cuffing prevents [[control of Feeding - Anatomy & Physiology#The Vomit Reflex|vomiting]] | ||
===Canine=== | ===Canine=== | ||
| − | As brachiocephalic breeds have a shortened skull length, the soft palate | + | *As brachiocephalic breeds have a shortened skull length, the soft palate often obstruct air flow into the [[Larynx - Anatomy & Physiology|larynx]] causing breathing difficulties |
===Avian=== | ===Avian=== | ||
| − | Birds lack a soft palate | + | *Birds lack a soft palate |
| + | |||
| + | ==Test yourself with the Soft Palate & Facial Muscle flashcards== | ||
| + | |||
| + | [[Oral Cavity - Anatomy & Physiology - Flashcards#Soft Palate Flashcards|Soft Palate Flashcards]] | ||
| + | |||
| + | [[Facial_Muscles_-_Musculoskeletal_-_Flashcards|Facial Muscle Flashcards]] | ||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | [[Category: | + | [[Category:Alimentary System]] |
Revision as of 12:42, 31 August 2010
|
|
Introduction
The soft palate (velum palatine) is located caudally to the hard palate. It is comprised of muscle and is involved in tasting food and in deglutition.
Structure and Function
- Muscle
- Contacts epiglottis caudally
- Very folded mucosa
- Striated palatine muscle
Musculature and Innervation
- Sensation and taste from glossopharyngeal (CN IX)
- Palatine muscle
- Tensor velli palatini
- Origin: near tympanic bulla on temporal bone
- Insertion: lateral aponeurosis
- Pharyngeal arch 1
- Mandibular of trigeminal (CN V3)
- Tenses soft palate
- Levator velli palatini
- Origin: near tympanic bulla on temporal bone
- Insertion: lateral aponeurosis
- Raises soft palate
- Major innervation from vagus nerve (CN X)
- Minor from glossopgaryngeal nerve (CN IX)
- Palatopharyngeus
Histology
- Respiratory mucosa - ciliated pseudostratified columnar epithelium on aboral surface
- Stratified squamous epithelium on oral surface
- Palatine salivary glands
Species Differences
Porcine
- Soft palate does not contact the epiglottis as the porcine soft palate is raised higher in the oral cavity than in other species
Equine
- Tight laryngeal cuff around the laryngeal entrance therefore the soft palate cannot be raised for long periods of time and thus horses are nasal breathers
- Laryngeal cuffing prevents vomiting
Canine
- As brachiocephalic breeds have a shortened skull length, the soft palate often obstruct air flow into the larynx causing breathing difficulties
Avian
- Birds lack a soft palate