Difference between revisions of "Anthrax"
| (52 intermediate revisions by 3 users not shown) | |||
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
| − | + | {{OpenPagesTop}} | |
| − | + | {{Factoid link | |
| − | + | |link = Factoid - Anthrax}} | |
| − | + | Also known as: '''''Anthracosis | |
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | [[Category:Cattle]][[Category:Sheep]][[Category: | + | ==Introduction== |
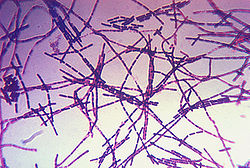
| + | [[File:Bacillus anthracis Gram.jpg|right|thumb|250px|<small><center> photomicrograph of ''Bacillus anthracis'' bacteria using Gram-stain technique. (CDC unknown, Wikimedia commons)</center></small>]] | ||
| + | Anthrax is a serious, often fatal zoonotic disease of wild and domestic mammals caused by the spore-forming bacterium ''[[Bacillus anthracis]]''. The disease has been reported worldwide (particularly in the tropical countries) and often occurs in outbreaks. The disease primarily affects herbivores but humans may be infected via contact with infected animal tissues, exposure to high concentrations of spores or contacted with infected animals. | ||
| + | |||
| + | ==Pathogenesis== | ||
| + | The infected host sheds ''B. anthracis'' bacilli into the environment which sporulate on exposure to air. These spores are highly resistant and can survive in the environment for many years. Grazing animals may become infected if ingestion of a large number of spores occurs. Following inhalation, germination and localised multiplication of the spores takes place. Spread via the lymphatics and blood stream then occurs, leading to massive septicaemia. In addition to the above routes of infection, [[:Category:Biting Flies|biting flies]] appear to have a role in transmission of spores in areas of endemic disease. Inhalation of dust-borne spores may also be of importance in the pathogenesis of the disease. | ||
| + | |||
| + | In general, carnivores are more resistant to disease than herbivores. In herbivores the disease commonly presents as a peracute onset septicaemia with a high mortality rate. In dogs, humans and pigs however, the onset is less acute. | ||
| + | |||
| + | ==Clinical Signs== | ||
| + | ===Ruminants and Horses=== | ||
| + | The incubation period of the disease is approximately three to seven days. Often animals may be '''discovered dead''' in the field before any clinical signs have been observed. In general, in non-immunised ruminants and horses the disease is characterised by sudden death, peracute septicaemia, bleeding from orifices and subcutaneous haemorrhages. Other clinical signs including the following have been described: | ||
| + | |||
| + | * Acute onset severe pyrexia | ||
| + | * Depression | ||
| + | * Neurological signs such as staggering or trembling | ||
| + | * Cyanosis | ||
| + | * Dyspnoea | ||
| + | * Cessation of rumination | ||
| + | * Subcutaneous oedematous swellings | ||
| + | * Congested mucous membranes and petechiae | ||
| + | * Shivering and cramp-like clinical signs | ||
| + | |||
| + | ===Pigs=== | ||
| + | Pigs are relatively resistant to anthrax. The disease in pigs has two manifestations; a pharyngeal and an intestinal form. | ||
| + | |||
| + | The '''pharyngeal''' disease is linked with scavenging or purposeful feeding of infected carcasses and often begins as an oedematous cellulitis of the the neck, head and regional lymph nodes. This may cause death by asphyxia. | ||
| + | |||
| + | The '''intestinal''' form is thought to be associated with contaminated mineral supplements, and may produce less obvious clinical signs including diarrhoea, lethargy and anorexia. Animals affected by the intestinal form frequently recover. | ||
| + | |||
| + | ===Dogs=== | ||
| + | Dogs are rarely affected, but develop a similar disease to that found in pigs. Disease most often occurs due to scavenging of infected sheep or cattle carcasses. Clinical signs include severe inflammation and oedema of the pharyngeal region and the disease is usually not fatal. | ||
| + | |||
| + | ==Diagnosis== | ||
| + | Diagnosis is confirmed in most affected animals (other than pigs) by demonstration of large numbers of rod-shaped ''B. anthracis'' in the blood or tissue. A tissue sample from a fresh carcass may be collected from an incision made in a well vascularised area such as the ear. As pigs with localised disease are rarely bacteraemic, a small piece of lymphatic tissue should be collected aseptically and submitted. Diagnostic tests include '''bacterial culture, PCR''' and '''fluorescent antibody stains''' for demonstration of the bacillus in blood or tissue. | ||
| + | |||
| + | ===Pathology=== | ||
| + | Bloody discharges from body orifices may be observed in carcasses and ''rigor mortis'' is often absent or incomplete in dead animals. Failure of the blood to clot and splenomegaly are other important ''post mortem'' findings. Lymph nodes are often swollen and oedematous. Haemorrhages may be found on the serosal surfaces of the thorax and abdomen as well as the endocardium. | ||
| + | |||
| + | ==Treatment== | ||
| + | '''Penicillin''' and '''Streptomycin''' is the treatment of choice in animals suspected to be suffering from Anthrax. All livestock at risk from infection should be treated with a long-acting antibiotic and moved to uncontaminated pasture. Any suspected contaminated feed should be removed. | ||
| + | |||
| + | ==Control== | ||
| + | Animals in endemic areas should be vaccinated on an annual basis with the '''non-encapsulated Sterne strain vaccine'''. As the vaccine is live, antibiotics should not be administered within one week of vaccination. | ||
| + | |||
| + | {{Learning | ||
| + | |literature review = [http://www.cabdirect.org/search.html?rowId=1&options1=AND&q1=%28%28title%3A%28anthracosis%29%29%29+OR+%28%28title%3A%28Anthrax%29%29%29&occuring1=freetext&rowId=2&options2=AND&q2=&occuring2=freetext&rowId=3&options3=AND&q3=&occuring3=freetext&publishedstart=2000&publishedend=yyyy&calendarInput=yyyy-mm-dd&la=any&it=any&show=all&x=47&y=9 Anthrax publications since 2000] | ||
| + | |full text = [http://www.cabi.org/cabdirect/FullTextPDF/2007/20073085070.pdf ''' Anthrax - the forgotten plague.''' Clark, C.; Western College of Veterinary Medicine, University of Saskatchewan, Saskatoon, Canada, Large Animal Veterinary Rounds, 2006, 6, 10, pp 1-6, 11 ref] | ||
| + | }} | ||
| + | |||
| + | ==References== | ||
| + | * Merck & Co (2008) '''The Merck Veterinary Manual (Eighth Edition)''' ''Merial'' | ||
| + | * Turnbull, P (2007) '''Anthrax in Humans and Animals (Fourth Edition)''' ''World Health Organisation Press'' | ||
| + | * Jones, T. C., Hunt, R. D., King, N. W. (1997) '''Veterinary Pathology''' ''Wiley-Blackwell'' | ||
| + | |||
| + | |||
| + | {{review}} | ||
| + | |||
| + | {{OpenPages}} | ||
| + | [[Category:Alimentary Diseases - Cattle]][[Category:Alimentary Diseases - Pig]][[Category:Alimentary Diseases - Dog]][[Category:Lymphoreticular and Haematopoietic Diseases - Dog]] | ||
| + | [[Category:Alimentary Diseases - Horse]][[Category:Neurological Diseases - Horse]][[Category:Respiratory Diseases - Horse]] | ||
| + | [[Category:Alimentary Diseases - Sheep]][[Category:Neurological Diseases - Sheep]][[Category:Respiratory Diseases - Sheep]] | ||
| + | [[Category:Brian Aldridge reviewing]] | ||
| + | [[Category:Spleen - Pathology]] | ||
Latest revision as of 15:37, 1 July 2013
|
|
Also known as: Anthracosis
Introduction
Anthrax is a serious, often fatal zoonotic disease of wild and domestic mammals caused by the spore-forming bacterium Bacillus anthracis. The disease has been reported worldwide (particularly in the tropical countries) and often occurs in outbreaks. The disease primarily affects herbivores but humans may be infected via contact with infected animal tissues, exposure to high concentrations of spores or contacted with infected animals.
Pathogenesis
The infected host sheds B. anthracis bacilli into the environment which sporulate on exposure to air. These spores are highly resistant and can survive in the environment for many years. Grazing animals may become infected if ingestion of a large number of spores occurs. Following inhalation, germination and localised multiplication of the spores takes place. Spread via the lymphatics and blood stream then occurs, leading to massive septicaemia. In addition to the above routes of infection, biting flies appear to have a role in transmission of spores in areas of endemic disease. Inhalation of dust-borne spores may also be of importance in the pathogenesis of the disease.
In general, carnivores are more resistant to disease than herbivores. In herbivores the disease commonly presents as a peracute onset septicaemia with a high mortality rate. In dogs, humans and pigs however, the onset is less acute.
Clinical Signs
Ruminants and Horses
The incubation period of the disease is approximately three to seven days. Often animals may be discovered dead in the field before any clinical signs have been observed. In general, in non-immunised ruminants and horses the disease is characterised by sudden death, peracute septicaemia, bleeding from orifices and subcutaneous haemorrhages. Other clinical signs including the following have been described:
- Acute onset severe pyrexia
- Depression
- Neurological signs such as staggering or trembling
- Cyanosis
- Dyspnoea
- Cessation of rumination
- Subcutaneous oedematous swellings
- Congested mucous membranes and petechiae
- Shivering and cramp-like clinical signs
Pigs
Pigs are relatively resistant to anthrax. The disease in pigs has two manifestations; a pharyngeal and an intestinal form.
The pharyngeal disease is linked with scavenging or purposeful feeding of infected carcasses and often begins as an oedematous cellulitis of the the neck, head and regional lymph nodes. This may cause death by asphyxia.
The intestinal form is thought to be associated with contaminated mineral supplements, and may produce less obvious clinical signs including diarrhoea, lethargy and anorexia. Animals affected by the intestinal form frequently recover.
Dogs
Dogs are rarely affected, but develop a similar disease to that found in pigs. Disease most often occurs due to scavenging of infected sheep or cattle carcasses. Clinical signs include severe inflammation and oedema of the pharyngeal region and the disease is usually not fatal.
Diagnosis
Diagnosis is confirmed in most affected animals (other than pigs) by demonstration of large numbers of rod-shaped B. anthracis in the blood or tissue. A tissue sample from a fresh carcass may be collected from an incision made in a well vascularised area such as the ear. As pigs with localised disease are rarely bacteraemic, a small piece of lymphatic tissue should be collected aseptically and submitted. Diagnostic tests include bacterial culture, PCR and fluorescent antibody stains for demonstration of the bacillus in blood or tissue.
Pathology
Bloody discharges from body orifices may be observed in carcasses and rigor mortis is often absent or incomplete in dead animals. Failure of the blood to clot and splenomegaly are other important post mortem findings. Lymph nodes are often swollen and oedematous. Haemorrhages may be found on the serosal surfaces of the thorax and abdomen as well as the endocardium.
Treatment
Penicillin and Streptomycin is the treatment of choice in animals suspected to be suffering from Anthrax. All livestock at risk from infection should be treated with a long-acting antibiotic and moved to uncontaminated pasture. Any suspected contaminated feed should be removed.
Control
Animals in endemic areas should be vaccinated on an annual basis with the non-encapsulated Sterne strain vaccine. As the vaccine is live, antibiotics should not be administered within one week of vaccination.
| Anthrax Learning Resources | |
|---|---|
 Full text articles available from CAB Abstract (CABI log in required) |
Anthrax - the forgotten plague. Clark, C.; Western College of Veterinary Medicine, University of Saskatchewan, Saskatoon, Canada, Large Animal Veterinary Rounds, 2006, 6, 10, pp 1-6, 11 ref |
References
- Merck & Co (2008) The Merck Veterinary Manual (Eighth Edition) Merial
- Turnbull, P (2007) Anthrax in Humans and Animals (Fourth Edition) World Health Organisation Press
- Jones, T. C., Hunt, R. D., King, N. W. (1997) Veterinary Pathology Wiley-Blackwell
| This article has been peer reviewed but is awaiting expert review. If you would like to help with this, please see more information about expert reviewing. |
Error in widget FBRecommend: unable to write file /var/www/wikivet.net/extensions/Widgets/compiled_templates/wrt69a899350f4ee1_71582533 Error in widget google+: unable to write file /var/www/wikivet.net/extensions/Widgets/compiled_templates/wrt69a8993517e4c1_55788699 Error in widget TwitterTweet: unable to write file /var/www/wikivet.net/extensions/Widgets/compiled_templates/wrt69a899351e6be3_90630056
|
| WikiVet® Introduction - Help WikiVet - Report a Problem |