Difference between revisions of "Aquaporins of the Kidney and Water Homeostasis - Anatomy & Physiology"
| (44 intermediate revisions by 3 users not shown) | |||
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
| − | {{ | + | {{OpenPagesTop}} |
| − | + | ==The Ability of the Kidney To Alter the Water Content of the Body== | |
| − | + | ||
| − | + | * Take a dog which weighs 20kg and is drinking normally. It will produce 0.5l of urine per 24 hours. | |
| − | + | * If the dog drinks excessively it can produce 8ml urine/min to compensate meaning a total of 11 litres per 24 hours | |
| − | | | + | * If a dog is denied water the production drops to a tiny 0.15 litres per 24 hours |
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
| + | The reabsorption of water can occur paracellulary - the main method in the proximal tubule or transcellulary - the main method in the distal tubule and collecting duct. | ||
| + | * Contrary to popular belief diffusion of water across lipid bilayers (transcellulary) is too slow for most physiological processes | ||
| + | * Aquaporins solve this problem | ||
| + | |||
| + | * '''The reabsorption in the proximal tubule and loop of henle occurs as water follows the reabsorbed sodium via osmosis.''' | ||
| + | * The protein osmotic pressure coupled with the hydrostatic pressure of the [[Glomerular Apparatus and Filtration - Anatomy & Physiology#Pressure in the Peritubular Capillaries#Pressure in the Peritubular Capillaries|'''peritubular capillaries]]''' effects the volume of water excreted or conserved also. | ||
| + | |||
==What are Aquaporins== | ==What are Aquaporins== | ||
* Family of membrane channel proteins | * Family of membrane channel proteins | ||
* Over a dozen homologous water transporting proteins make up this family in mammals | * Over a dozen homologous water transporting proteins make up this family in mammals | ||
| − | * Allow rapid transport of substances | + | * Allow rapid transport of substances across membranes |
* Found in all life forms | * Found in all life forms | ||
* Commonly abbreviated to '''AQP''' | * Commonly abbreviated to '''AQP''' | ||
* Ones found in the kidneys are: | * Ones found in the kidneys are: | ||
** <Font Color="#669933">'''AQP1'''</Font> - Tubules | ** <Font Color="#669933">'''AQP1'''</Font> - Tubules | ||
| − | ** <Font Color="#669933">'''AQP2'''</Font> - [[Collecting Duct - Anatomy & Physiology| Collecting duct]] | + | ** <Font Color="#669933">'''AQP2'''</Font> - [[Reabsorption and Secretion Along the Distal Tubule and Collecting Duct - Anatomy & Physiology| Collecting duct]] |
| − | ** <Font Color="#CC6633">'''AQP3'''</Font> - [[Collecting Duct - Anatomy & Physiology| Collecting duct]] | + | ** <Font Color="#CC6633">'''AQP3'''</Font> - [[Reabsorption and Secretion Along the Distal Tubule and Collecting Duct - Anatomy & Physiology| Collecting duct]] |
| − | ** <Font Color="#669933">'''AQP4'''</Font> - [[Collecting Duct - Anatomy & Physiology| Collecting duct]] | + | ** <Font Color="#669933">'''AQP4'''</Font> - [[Reabsorption and Secretion Along the Distal Tubule and Collecting Duct - Anatomy & Physiology| Collecting duct]] |
| − | ** <Font Color="#660000">'''AQP6'''</Font> - [[Collecting Duct - Anatomy & Physiology| Collecting duct (intercalated cells)]] | + | ** <Font Color="#660000">'''AQP6'''</Font> - [[Reabsorption and Secretion Along the Distal Tubule and Collecting Duct - Anatomy & Physiology| Collecting duct (intercalated cells)]] |
| − | ** <Font Color="#CC6633">'''AQP7'''</Font> - [[Proximal Tubule - Anatomy & Physiology| Proximal tubule]] | + | ** <Font Color="#CC6633">'''AQP7'''</Font> - [[Reabsorption and Secretion Along the Proximal Tubule - Anatomy & Physiology| Proximal tubule]] |
** <Font Color="#9900ff">'''AQP11'''</Font> - Kidney | ** <Font Color="#9900ff">'''AQP11'''</Font> - Kidney | ||
* They are colour coded according to their function | * They are colour coded according to their function | ||
| Line 27: | Line 34: | ||
** <Font Color="#9900ff">'''Function Unknown'''</Font> | ** <Font Color="#9900ff">'''Function Unknown'''</Font> | ||
| − | |||
* They allow the reabsorption of water, glycerol and chlorine from the filtrate | * They allow the reabsorption of water, glycerol and chlorine from the filtrate | ||
| − | * Without | + | * Without them producing concentrated urine would be impossible |
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | == | + | ==[[Pituitary Gland - Anatomy & Physiology #Posterior Pituitary Gland| ADH]] and the [[Reabsorption and Secretion Along the Distal Tubule and Collecting Duct - Anatomy & Physiology#Collecting Duct|Collecting Duct]]== |
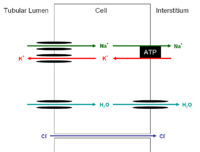
| − | + | [[Image:collductexch.jpg|right|thumb|200px|<small><center>Exchange in the Principal Cells of the Collecting Duct</center></small>]] | |
| − | + | The membrane of the [[Reabsorption and Secretion Along the Distal Tubule and Collecting Duct - Anatomy & Physiology#Collecting Duct|Collecting Duct]] is practically impermeable to water. Therefore in order for water reabsorption from this part of the nephron to occur it is vital that aquaporins are inserted. This is the role of [[Pituitary Gland - Anatomy & Physiology #Posterior Pituitary Gland| ADH]]. These channels are always present on the basolateral membrane of the epithelial cells but their presence and concentration on the apical membrane is reliant on the concentration of ADH in the blood. ADH works by binding to '''V<sub>2</sub>''' receptors on the basolateral membranes of the cells and activates adenyl cyclase creating '''cyclicAMP''' (cAMP) this in turn activates '''protein kinase A''' which causes '''protein phosphorylation'''. This causes vesicles with ready made glycoprotein '''AQP2''' aquaporins in their membranes to move to the apical cell membrane and insert the aquaporins via exocytosis. This rapidly increases the water permeability and allowing reabsorption | |
| − | + | {{OpenPages}} | |
| − | + | [[Category:Water Balance and Homeostasis]][[Category:Bullet Points]] | |
Latest revision as of 14:30, 5 July 2012
The Ability of the Kidney To Alter the Water Content of the Body
- Take a dog which weighs 20kg and is drinking normally. It will produce 0.5l of urine per 24 hours.
- If the dog drinks excessively it can produce 8ml urine/min to compensate meaning a total of 11 litres per 24 hours
- If a dog is denied water the production drops to a tiny 0.15 litres per 24 hours
The reabsorption of water can occur paracellulary - the main method in the proximal tubule or transcellulary - the main method in the distal tubule and collecting duct.
- Contrary to popular belief diffusion of water across lipid bilayers (transcellulary) is too slow for most physiological processes
- Aquaporins solve this problem
- The reabsorption in the proximal tubule and loop of henle occurs as water follows the reabsorbed sodium via osmosis.
- The protein osmotic pressure coupled with the hydrostatic pressure of the peritubular capillaries effects the volume of water excreted or conserved also.
What are Aquaporins
- Family of membrane channel proteins
- Over a dozen homologous water transporting proteins make up this family in mammals
- Allow rapid transport of substances across membranes
- Found in all life forms
- Commonly abbreviated to AQP
- Ones found in the kidneys are:
- AQP1 - Tubules
- AQP2 - Collecting duct
- AQP3 - Collecting duct
- AQP4 - Collecting duct
- AQP6 - Collecting duct (intercalated cells)
- AQP7 - Proximal tubule
- AQP11 - Kidney
- They are colour coded according to their function
- Water channels
- Glycerol channels
- Intracellular chloride channels
- Function Unknown
- They allow the reabsorption of water, glycerol and chlorine from the filtrate
- Without them producing concentrated urine would be impossible
ADH and the Collecting Duct
The membrane of the Collecting Duct is practically impermeable to water. Therefore in order for water reabsorption from this part of the nephron to occur it is vital that aquaporins are inserted. This is the role of ADH. These channels are always present on the basolateral membrane of the epithelial cells but their presence and concentration on the apical membrane is reliant on the concentration of ADH in the blood. ADH works by binding to V2 receptors on the basolateral membranes of the cells and activates adenyl cyclase creating cyclicAMP (cAMP) this in turn activates protein kinase A which causes protein phosphorylation. This causes vesicles with ready made glycoprotein AQP2 aquaporins in their membranes to move to the apical cell membrane and insert the aquaporins via exocytosis. This rapidly increases the water permeability and allowing reabsorption
Error in widget FBRecommend: unable to write file /var/www/wikivet.net/extensions/Widgets/compiled_templates/wrt66349a22651db7_62290474 Error in widget google+: unable to write file /var/www/wikivet.net/extensions/Widgets/compiled_templates/wrt66349a2268f128_50291586 Error in widget TwitterTweet: unable to write file /var/www/wikivet.net/extensions/Widgets/compiled_templates/wrt66349a2272c6f7_62108604
|
| WikiVet® Introduction - Help WikiVet - Report a Problem |