Difference between revisions of "Hepatic Lipidosis"
Fiorecastro (talk | contribs) |
|||
| (15 intermediate revisions by 5 users not shown) | |||
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
| + | {{unfinished}} | ||
| − | Also known as: '''''Lipid Mobilisation Syndrome ''''' | + | Also known as: '''''Lipid Mobilisation Syndrome''''' |
| − | == | + | ==Description== |
| + | Hepatic lipidosis describes a syndrome caused by derangements in lipid and protein metabolism. It occurs in both cats and dogs but it produces a more important clinical syndrome in cats. Similar phenomena occur in horses, donkeys, cattle and sheep when they are exposed to periods of metabolic stress. Hepatic lipidosis may be '''primary''' (or idiopathic) or it may be '''secondary''' to another disease. | ||
| − | + | ===Primary Lipidosis=== | |
| + | '''Primary or idiopathic hepatic lipidosis''' is most commonly recognised in obese indoor cats following a period of anorexia or stress. It is the most common hepatic disease of cats in North America but it is becoming more common in Europe. It occurs due to the accumulation of large amounts of lipid in hepatocytes, altering the morphology of the cells and producing an acute hepatopathy. The mortality rate of this disease is high unless it is treated aggressively. | ||
| − | + | The lipid that accumulates within hepatocytes is composed of triglyceride which is synthesised from circulating fatty acids in the liver. Circulating fatty acid concentrations are regulated by a number of hormonal factors that act on the enzymes hormone-sensitive lipase (HSL) and lipoprotein lipase (LPL). HSL is responsible for releasing fatty acids from adipose tissue and its action is stimulated by catecholamines, glucagon, corticosteroids and thyroid hormones but inhibited by insulin. LPL degrades circulating lipoprotein complexes allowing fatty acids to be taken back up into adipose stores. The liver and other tissues usually oxidise fatty acids via the Krebs cycle within mitochondria but this pathway is downregulated in animals that receive excessive dietary calories. Additionally, hepatocytes are able to package fatty acids into very low lipoprotein complexes (VLDLs) that are released back into the circulation. If the apolipoproteins that partly constitute the VLDLs are deficient, fatty acids may not be dispatched from the liver. The accumulation of triglycerides in the liver reflects an imbalance between the processes that cause lipid mobilisation, those that lead to fatty acid oxidation and dispatch and those that encourage storage in adipose tissue. Oneore more of the following mechanisms may be involved: | |
| + | *Increased activation of HSL by '''catecholamines''' released in response to stress. | ||
| + | *Failure to produce sufficient '''insulin''' (in [[Diabetes Mellitus|diabetes mellitus]]) results in uncontrolled HSL activity. | ||
| + | *Excessive lipid mobilisation induced by '''anorexia''', '''starvation''' or '''illness''', partly under the influence of glucagon on HSL. | ||
| + | *'''Deficiency of dietary proteins''' and other nutrients, which reduces the capacity of the liver to produce lipid transport (apolipo-)proteins and to metabolise fat. Recognised micronutrient deficiencies include '''arginine''', '''carnitine''', '''taurine''' and '''methionine'''. Carnitine has a vital role in carrying fatty acids across the inner mitochondrial membrane. | ||
| + | *Disturbances in the neural and hormonal mechanisms that control '''appetite''' and satiety resulting in inappropriate anorexia. | ||
| − | ''' | + | ===Secondary Lipidosis=== |
| + | '''Secondary hepatic lipidosis''' is a neuroendocrine response to other diseases, including [[Pancreatitis - Dog and Cat|pancreatitis]], [[Diabetes Mellitus|diabetes mellitus]], [[Inflammatory Bowel Disease|inflammatory bowel disease]] and primary hypertriglyceridaemia. Secondary hepatic lipidosis is therefore less closely associated with obesity and it may be seen in normal or even thin cats. In dogs, this secondary lipid accumulation rarely contributes to the clinical syndrome but in cats, it may greatly exacerbate the disease suffered by the affected animal. Secondary lipidosis is much more common than primary in cats in the UK. | ||
| − | + | ==Signalment== | |
| + | Indoor and obese cats are more prone to the development of primary hepatic lipidosis during periods of stress or anorexia. Most cases occur in middle-aged cats with no apparent breed predisposition. | ||
| − | === | + | ==Diagnosis== |
| + | ===Clinical Signs=== | ||
| + | [[File:Jaundiced cat.jpg|thumb|Image of a jaundiced cat that was suffering from hepatic lipidosis. Note the icteric pinnae.<br><small>Copyright Sabar 2007 Wikimedia Commons]]</small> | ||
| + | Clinical signs may appear to be non-specific at first and they include: | ||
| + | *Severe persistent '''anorexia''' with lethargy. Cats may lose weight and have an unkempt appearance. | ||
| + | *[[Icterus|'''Jaundice''']] may or may not occur. It is a form of intra-hepatic icterus as the swollen hepatocytes partially obstruct the flow of bile in the canaliculi. | ||
| + | *[[Hepatic Encephalopathy|'''Hepatic encephalopathy''']] may manifest mainly as depression and hypersalivation. | ||
| + | *[[Diarrhoea|'''Diarrhoea''']] and [[Vomiting|'''vomiting''']] do not occur with all cases of hepatic lipidosis. | ||
| + | *'''Palpable hepatomegaly''' may be appreciable as the liver enlarges with the storage of lipid in hepatocytes. | ||
| + | *'''Coagulopathies''' sometimes occur in affected animals and may manifest as spontaneous subcutaneous, intra-articular or intra-cavitatory haemorrhage. The syndrome develops due to reduced absorption of vitamin K or failure to reclaim vitamin K in the liver due to diffuse hepatic disease. | ||
| − | ''' | + | ===Laboratory Tests=== |
| + | ====Haematology==== | ||
| + | Affected animals may have red blood cells of varying morphology ('''poikilocytosis''') and this may be related to alterations in erythrocyte membrane lipid content. Cats with hepatic lipidosis are also prone to the development of Heinz body '''anaemia''' and haemolysis due to hypophosphataemia. | ||
| − | == | + | ====Biochemistry==== |
| + | Cholestatic enzymes are usually elevated due to intra-hepatic cholestasis but the exact pattern observed varies between species. In cats, an elevated concentration of '''ALP''' is more sensitive for the detection of hepatic lipidosis and this enzyme is often greatly elevated while the level of GGT remains normal. In dogs, an elevated serum concentration of '''GGT''' is more sensitive than ALP for the detection of hepatic lipidosis. | ||
| − | + | [[Bilirubin|'''Hyperbilirubinaemia''']] often occurs and this may be clinically evident as [[Icterus|icterus]]. | |
| − | + | Animals that have been inappetant for some time or which have vomited recently are likely to be '''hypokalaemic''' and it is important that this deficiency is treated for the patient to regain voluntary intake of food. Animals with hepatic lipidosis often become '''hypophosphataemic''' but this may only occur with refeeding as the blood concentrations of glucose and insulin rise, driving phosphate intracellularly. A similar phenomenon occur when animals with [[Diabetes Mellitus|diabetic ketoacidosis]] are first treated with insulin. | |
| − | == | + | ====Other Tests==== |
| − | + | Where this is available, proteins produced in the absence of vitamin K (PIVKAs) and '''clotting times''' may be measured to determine whether the animal has a coagulopathy. | |
| − | |||
| − | + | Urinalysis may reveal '''bilirubinuria''' as the serum bilirubin concentration is increased as in any cholestatic disease. | |
| − | + | Cats with hepatic lipidosis often become deficient for vitamin B12 (cyanocobalamin), especially if they concurrent [[Inflammatory Bowel Disease|inflammatory bowel disease]] of [[Pancreatitis - Dog and Cat|pancreatitis]]. | |
| − | ==== | + | ===Diagnostic Imaging=== |
| + | ====Radiography==== | ||
| + | '''Plain radiographs of the abdomen''' usually show only marked hepatomegaly with a right shift of the gastric axis when viewed on a right lateral film. The borders of the liver lobes will be rounded and extensive intra-abdominal fat reserves may be evident in obese cats giving excellent serosal detail. | ||
| − | + | ====Ultrasonography==== | |
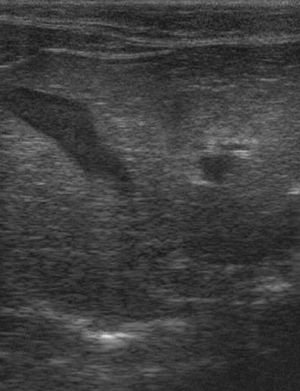
| + | [[File:Sono Hepatische Lipidose Katze 0.jpg|thumb|Ultrasonographic image of a feline liver affected by hepatic lipidosis. The liver has a similar echogenicity to the surrounding fat.<br><small>Copyright Kalumet 2009 Wikimedia Commons]]</small> | ||
| + | An abdominal ultrasound scan will reveal an enlarged and '''diffusely hyperechoeic''' liver. The underlying cause of the liver disease may also be apparent. | ||
| − | === | + | ===Pathology=== |
| + | Grossly, the liver will appear to be enlarged with rounded edges. The tissue may be white/yellow in colour and the cut surface will be uniform and greasy to handle. | ||
| − | + | ==Histopathology== | |
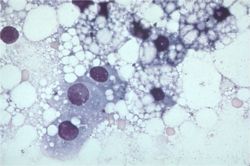
| + | [[Image:Hepatic lipidosis histology.jpg|thumb|right|250px|Histological image of a section of liver with lipidosis. Note the many vacuoles that push the hepatocyte nuclei aside.<br><small>Copyright Karin Allenspach 2008 RVC]]</small> | ||
| + | Fine needle aspiration of the liver (preferably under ultrasound guidance) is often sufficient to make a diagnosis of hepatic lipidosis. Cytological examination of the sample reveals that the hepatcoytes are swollen with lipid which pushes the nuclei aside. Where possible, biopsy of liver tissue and aspiration of bile are indicated to determine the underlying cause of the disease. | ||
| − | [[ | + | ==Treatment== |
| + | Intensive treatment of cats is required as the disease has a high mortality if not managed aggressively. Owners should be warned that long-term nutritional support will be required to achieve a successful outcome. In cases of secondary lipidosis, the underlying cause of disease should be treated. | ||
| + | ===Nutritional Support=== | ||
| + | [[File:FelineHepaticLipidosisEsophagealFeedingTube.jpg|thumb|Image of a cat receving nutritional support via an oesophagostomy tube<br><small>Released into the Public Domain]]</small> | ||
| + | Nutritional support is generally required for a period of 4 - 6 weeks but longer durations may be necessary if the animal fails to eat voluntarily. The two major considerations are the route of feeding and the composition of the diet that is fed. | ||
| + | ====Route of Feeding==== | ||
| + | Naso-oesophageal feeding tubes may be used temporarily to stabilise affected animals but this type of tube is likely to discourage voluntary feeding and it may traumatise the oesophagus. Oesophagostomy tube or gastrostomy tubes are better suited to long-term management of patients with hepatic lipidosis and both may be placed during a short general anaesthetic. Gastrostomy tubes may be placed under endoscopic guidance and these represent the best option if the animal has evidence of [[Oesophagitis|oesophagitis]] or chronic [[Vomiting|vomiting]]. | ||
| − | + | ====Composition of the Diet==== | |
| + | The fat content of the diet should be restricted to limit post-prandial hypertriglyceridaemia and the carbohydrate content should be limited as high concentrations will reduce the oxidation of fatty acids. In cats, a diet of the '''highest possible protein content''' is indicated unless the animal is showing signs of hepatic encephalopathy. Even in this situation, it is preferable to attempt to manage the signs of encephalopathy medically while continuing to feed a diet with a moderate protein content. | ||
| − | + | Specific nutrients such as arginine, taurine, or carnitine may also be added and there is some evidence to suggest that carnitine supplementation may be beneficial in cats with hepatic lipidosis. B vitamins, particularly B12 in cats, should be supplemented if they are thought to be deficient. Antioxidants (including s-adenosyl methionine (SAMe) and vitamin E can be added to the diet to limit oxidative Heinz body anaemia that occurs with hepatic lipidosis and to limit inflammatory liver pathology. | |
| − | + | ===[[Hepatic Encephalopathy #Medical Management|Hepatic Encephalopathy]]=== | |
| + | This syndrome should be treated specifically if it occurs. | ||
| − | + | ===Gastro-intestinal Drugs=== | |
| + | Episodes of vomiting may cause dehydration and electrolyte imbalances and it is therefore important that this is prevented. '''Maropitant''' (an NK1 receptor antagonist) is often used as an anti-emetic as it has both central and peripheral actions and this is often combined with [[Gastroprotective Drugs #Histamine (H2) Receptor Antagonists|'''ranitidine''']] which acts as a gastric acid secretory inhibitor and a prokinetic (by preventing the degradation of intestinal acetylcholine). Ranitidine or [[Drugs Acting on the Intestines#Drugs Acting on 5-HT4 Receptors|'''metoclopromide''']] may also be appropriate if the vomiting is thought to result from delayed gastric emptying or intestinal ileus. | ||
| − | + | ===Fluid Therapy=== | |
| + | Intravenous fluid therapy is often warranted in the early stages of disease when the patient is likely to be dehydrated and to have marked electrolyte imbalances. Blood glucose concentration should be monitored but supplementation with dextrose solutions should be sparing as this is likely to inhibit fatty acid oxidation. Of the electrolytes, potassium and chloride are most likely to be deficient at presentation and potassium should be supplemented if its concentration can be measured regularly. As feeding is introduced, hypophosphataemia may occur as part of a '''refeeding syndrome''' and this should be supplemented as necessary. | ||
| − | === | + | ===Coagulopathy=== |
| + | Supplementation with '''vitamin K''' may be required by subcutaneous injection if the coagulopathy is significant. | ||
| − | ==== | + | ==Prognosis== |
| + | This is dependent on the underlying cause and the way in which the patient is managed. If treated appropriately, 85% of severely affected animals will recover. | ||
| − | ''' | + | See also: |
| + | '''Hyperlipaemia''' in [[Hyperlipaemia - Horse|'''horses''']] and [[Hyperlipaemia - Donkey|'''donkeys''']]<br> | ||
| + | '''[[Fatty Liver Syndrome]]''' in '''cattle'''<br> | ||
| + | '''[[White Liver Disease - Sheep|White liver disease]]''' and '''[[Pregnancy Toxaemia|pregnancy toxaemia]]''' in '''sheep''' | ||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | == | + | ==References== |
| − | + | *Ettinger, S.J. and Feldman, E. C. (2000) '''Textbook of Veterinary Internal Medicine Diseases of the Dog and Cat Volume 2''' (Fifth Edition) ''W.B. Saunders Company''. | |
| − | + | *Hall, E.J, Simpson, J.W. and Williams, D.A. (2005) '''BSAVA Manual of Canine and Feline Gastroenterology (2nd Edition)''' ''BSAVA'' | |
| + | *Nelson, R.W. and Couto, C.G. (2009) '''Small Animal Internal Medicine (Fourth Edition)''' ''Mosby Elsevier''. | ||
| + | *Tilley, L. P. & Smith, F. W. K. (2007) '''Blackwell's Five-minute Veterinary Consult: Canine & Feline (Fourth Edition)''' ''Blackwell Publishing'' | ||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | === | + | ====Feline==== |
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | + | *Survival rate is only 50-60% | |
| + | *Pathophysiology: | ||
| + | **Incompletely understood | ||
| + | **Obese cats that lose 30-40% of body weight exhibit a similar syndrome to naturally occurring hepatic lipidosis | ||
| + | **But many causative factors for naturally occurring hepatic lipidosis: | ||
| + | ***Peripheral lipolysis secondary to absolute or relative lack of insulin | ||
| + | ***Protein-calories malnutrition | ||
| + | ***Amino acid deficiencies – inability to synthesize apolipoproteins necessary to mobilize hepatic fat | ||
| + | ***Deficiency of lipotrophic compounds | ||
| + | ***Error of fatty acid oxidation | ||
| + | ***Hepatic perioxosomal damage due to oxidative stress | ||
| + | *Cats with hepatic lipidosis have higher nonesterified fatty acids (NEFAs) compared to controls and those with cholangiohepatitis | ||
| + | **NEFAs are derived from lipolysis of fat stores and enter the [[Liver - Anatomy & Physiology|liver]] | ||
| + | **They are oxidized in the [[Liver - Anatomy & Physiology|liver]] for energy or converted to phospholipids or cholesterol or reesterified to triglycerides | ||
| + | **Limited increase in lipoprotein synthesis and secretion of triglycerides in VLDLs | ||
| + | **Capacity for increase in oxidation by mitochondria and ketone body synthesis is low | ||
| + | **Rate of fatty acid esterification to triglycerides is not limited so can lead to a marked increase in the accumulation of stored hepatic triglycerides | ||
| + | *Also all triglyceride accumulation in hepatocytes in these cats comes from mobilized peripheral adipose stores during nutritional stress | ||
| + | **high levels of triglyceride concentrations in the [[Liver - Anatomy & Physiology|liver]] will cause: | ||
| + | ***severe periacinar necrosis | ||
| + | ***jaundice | ||
| + | ***hepatic encephalopathy | ||
| + | ***high mortality rate | ||
| + | *Lipolysis – under control of hormone-sensitive lipase hydrolyses triglycerides to NEFAs and glycerol | ||
| + | **Insulin – inhibits it | ||
| + | *Catecholamines (eg: released in stress, etc – neural input), glucocorticoids, thyroxine, GH and glucagons all promote lipolysis | ||
| + | *Lower insulin levels in cats with hepatic lipidosis or cholangiohepatitis compared to controls; and lower glucogon:insulin ratio in diseased cats | ||
| + | **But as not lipidosis specific, not likely to be the main factor involved | ||
| + | *Higher serum triglycerides in lipidotic cats compared to controls | ||
| − | == | + | ==Test yourself with the Liver Pathology Flashcards== |
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | + | [[Liver_Flashcards_-_Pathology|Liver Pathology Flashcards]] | |
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | + | [[Category:Liver_-_Degenerative_Pathology]][[Category:Liver Diseases - Cat]] | |
| − | + | [[Category:To_Do_-_Clinical]] | |
| − | + | [[Category:Liver Diseases - Dog]] | |
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | [[Category:Liver_-_Degenerative_Pathology]] [[Category: | ||
| − | [[Category: | ||
Revision as of 10:50, 21 December 2010
| This article is still under construction. |
Also known as: Lipid Mobilisation Syndrome
Description
Hepatic lipidosis describes a syndrome caused by derangements in lipid and protein metabolism. It occurs in both cats and dogs but it produces a more important clinical syndrome in cats. Similar phenomena occur in horses, donkeys, cattle and sheep when they are exposed to periods of metabolic stress. Hepatic lipidosis may be primary (or idiopathic) or it may be secondary to another disease.
Primary Lipidosis
Primary or idiopathic hepatic lipidosis is most commonly recognised in obese indoor cats following a period of anorexia or stress. It is the most common hepatic disease of cats in North America but it is becoming more common in Europe. It occurs due to the accumulation of large amounts of lipid in hepatocytes, altering the morphology of the cells and producing an acute hepatopathy. The mortality rate of this disease is high unless it is treated aggressively.
The lipid that accumulates within hepatocytes is composed of triglyceride which is synthesised from circulating fatty acids in the liver. Circulating fatty acid concentrations are regulated by a number of hormonal factors that act on the enzymes hormone-sensitive lipase (HSL) and lipoprotein lipase (LPL). HSL is responsible for releasing fatty acids from adipose tissue and its action is stimulated by catecholamines, glucagon, corticosteroids and thyroid hormones but inhibited by insulin. LPL degrades circulating lipoprotein complexes allowing fatty acids to be taken back up into adipose stores. The liver and other tissues usually oxidise fatty acids via the Krebs cycle within mitochondria but this pathway is downregulated in animals that receive excessive dietary calories. Additionally, hepatocytes are able to package fatty acids into very low lipoprotein complexes (VLDLs) that are released back into the circulation. If the apolipoproteins that partly constitute the VLDLs are deficient, fatty acids may not be dispatched from the liver. The accumulation of triglycerides in the liver reflects an imbalance between the processes that cause lipid mobilisation, those that lead to fatty acid oxidation and dispatch and those that encourage storage in adipose tissue. Oneore more of the following mechanisms may be involved:
- Increased activation of HSL by catecholamines released in response to stress.
- Failure to produce sufficient insulin (in diabetes mellitus) results in uncontrolled HSL activity.
- Excessive lipid mobilisation induced by anorexia, starvation or illness, partly under the influence of glucagon on HSL.
- Deficiency of dietary proteins and other nutrients, which reduces the capacity of the liver to produce lipid transport (apolipo-)proteins and to metabolise fat. Recognised micronutrient deficiencies include arginine, carnitine, taurine and methionine. Carnitine has a vital role in carrying fatty acids across the inner mitochondrial membrane.
- Disturbances in the neural and hormonal mechanisms that control appetite and satiety resulting in inappropriate anorexia.
Secondary Lipidosis
Secondary hepatic lipidosis is a neuroendocrine response to other diseases, including pancreatitis, diabetes mellitus, inflammatory bowel disease and primary hypertriglyceridaemia. Secondary hepatic lipidosis is therefore less closely associated with obesity and it may be seen in normal or even thin cats. In dogs, this secondary lipid accumulation rarely contributes to the clinical syndrome but in cats, it may greatly exacerbate the disease suffered by the affected animal. Secondary lipidosis is much more common than primary in cats in the UK.
Signalment
Indoor and obese cats are more prone to the development of primary hepatic lipidosis during periods of stress or anorexia. Most cases occur in middle-aged cats with no apparent breed predisposition.
Diagnosis
Clinical Signs
Clinical signs may appear to be non-specific at first and they include:
- Severe persistent anorexia with lethargy. Cats may lose weight and have an unkempt appearance.
- Jaundice may or may not occur. It is a form of intra-hepatic icterus as the swollen hepatocytes partially obstruct the flow of bile in the canaliculi.
- Hepatic encephalopathy may manifest mainly as depression and hypersalivation.
- Diarrhoea and vomiting do not occur with all cases of hepatic lipidosis.
- Palpable hepatomegaly may be appreciable as the liver enlarges with the storage of lipid in hepatocytes.
- Coagulopathies sometimes occur in affected animals and may manifest as spontaneous subcutaneous, intra-articular or intra-cavitatory haemorrhage. The syndrome develops due to reduced absorption of vitamin K or failure to reclaim vitamin K in the liver due to diffuse hepatic disease.
Laboratory Tests
Haematology
Affected animals may have red blood cells of varying morphology (poikilocytosis) and this may be related to alterations in erythrocyte membrane lipid content. Cats with hepatic lipidosis are also prone to the development of Heinz body anaemia and haemolysis due to hypophosphataemia.
Biochemistry
Cholestatic enzymes are usually elevated due to intra-hepatic cholestasis but the exact pattern observed varies between species. In cats, an elevated concentration of ALP is more sensitive for the detection of hepatic lipidosis and this enzyme is often greatly elevated while the level of GGT remains normal. In dogs, an elevated serum concentration of GGT is more sensitive than ALP for the detection of hepatic lipidosis.
Hyperbilirubinaemia often occurs and this may be clinically evident as icterus.
Animals that have been inappetant for some time or which have vomited recently are likely to be hypokalaemic and it is important that this deficiency is treated for the patient to regain voluntary intake of food. Animals with hepatic lipidosis often become hypophosphataemic but this may only occur with refeeding as the blood concentrations of glucose and insulin rise, driving phosphate intracellularly. A similar phenomenon occur when animals with diabetic ketoacidosis are first treated with insulin.
Other Tests
Where this is available, proteins produced in the absence of vitamin K (PIVKAs) and clotting times may be measured to determine whether the animal has a coagulopathy.
Urinalysis may reveal bilirubinuria as the serum bilirubin concentration is increased as in any cholestatic disease.
Cats with hepatic lipidosis often become deficient for vitamin B12 (cyanocobalamin), especially if they concurrent inflammatory bowel disease of pancreatitis.
Diagnostic Imaging
Radiography
Plain radiographs of the abdomen usually show only marked hepatomegaly with a right shift of the gastric axis when viewed on a right lateral film. The borders of the liver lobes will be rounded and extensive intra-abdominal fat reserves may be evident in obese cats giving excellent serosal detail.
Ultrasonography
An abdominal ultrasound scan will reveal an enlarged and diffusely hyperechoeic liver. The underlying cause of the liver disease may also be apparent.
Pathology
Grossly, the liver will appear to be enlarged with rounded edges. The tissue may be white/yellow in colour and the cut surface will be uniform and greasy to handle.
Histopathology
Fine needle aspiration of the liver (preferably under ultrasound guidance) is often sufficient to make a diagnosis of hepatic lipidosis. Cytological examination of the sample reveals that the hepatcoytes are swollen with lipid which pushes the nuclei aside. Where possible, biopsy of liver tissue and aspiration of bile are indicated to determine the underlying cause of the disease.
Treatment
Intensive treatment of cats is required as the disease has a high mortality if not managed aggressively. Owners should be warned that long-term nutritional support will be required to achieve a successful outcome. In cases of secondary lipidosis, the underlying cause of disease should be treated.
Nutritional Support
Nutritional support is generally required for a period of 4 - 6 weeks but longer durations may be necessary if the animal fails to eat voluntarily. The two major considerations are the route of feeding and the composition of the diet that is fed.
Route of Feeding
Naso-oesophageal feeding tubes may be used temporarily to stabilise affected animals but this type of tube is likely to discourage voluntary feeding and it may traumatise the oesophagus. Oesophagostomy tube or gastrostomy tubes are better suited to long-term management of patients with hepatic lipidosis and both may be placed during a short general anaesthetic. Gastrostomy tubes may be placed under endoscopic guidance and these represent the best option if the animal has evidence of oesophagitis or chronic vomiting.
Composition of the Diet
The fat content of the diet should be restricted to limit post-prandial hypertriglyceridaemia and the carbohydrate content should be limited as high concentrations will reduce the oxidation of fatty acids. In cats, a diet of the highest possible protein content is indicated unless the animal is showing signs of hepatic encephalopathy. Even in this situation, it is preferable to attempt to manage the signs of encephalopathy medically while continuing to feed a diet with a moderate protein content.
Specific nutrients such as arginine, taurine, or carnitine may also be added and there is some evidence to suggest that carnitine supplementation may be beneficial in cats with hepatic lipidosis. B vitamins, particularly B12 in cats, should be supplemented if they are thought to be deficient. Antioxidants (including s-adenosyl methionine (SAMe) and vitamin E can be added to the diet to limit oxidative Heinz body anaemia that occurs with hepatic lipidosis and to limit inflammatory liver pathology.
Hepatic Encephalopathy
This syndrome should be treated specifically if it occurs.
Gastro-intestinal Drugs
Episodes of vomiting may cause dehydration and electrolyte imbalances and it is therefore important that this is prevented. Maropitant (an NK1 receptor antagonist) is often used as an anti-emetic as it has both central and peripheral actions and this is often combined with ranitidine which acts as a gastric acid secretory inhibitor and a prokinetic (by preventing the degradation of intestinal acetylcholine). Ranitidine or metoclopromide may also be appropriate if the vomiting is thought to result from delayed gastric emptying or intestinal ileus.
Fluid Therapy
Intravenous fluid therapy is often warranted in the early stages of disease when the patient is likely to be dehydrated and to have marked electrolyte imbalances. Blood glucose concentration should be monitored but supplementation with dextrose solutions should be sparing as this is likely to inhibit fatty acid oxidation. Of the electrolytes, potassium and chloride are most likely to be deficient at presentation and potassium should be supplemented if its concentration can be measured regularly. As feeding is introduced, hypophosphataemia may occur as part of a refeeding syndrome and this should be supplemented as necessary.
Coagulopathy
Supplementation with vitamin K may be required by subcutaneous injection if the coagulopathy is significant.
Prognosis
This is dependent on the underlying cause and the way in which the patient is managed. If treated appropriately, 85% of severely affected animals will recover.
See also:
Hyperlipaemia in horses and donkeys
Fatty Liver Syndrome in cattle
White liver disease and pregnancy toxaemia in sheep
References
- Ettinger, S.J. and Feldman, E. C. (2000) Textbook of Veterinary Internal Medicine Diseases of the Dog and Cat Volume 2 (Fifth Edition) W.B. Saunders Company.
- Hall, E.J, Simpson, J.W. and Williams, D.A. (2005) BSAVA Manual of Canine and Feline Gastroenterology (2nd Edition) BSAVA
- Nelson, R.W. and Couto, C.G. (2009) Small Animal Internal Medicine (Fourth Edition) Mosby Elsevier.
- Tilley, L. P. & Smith, F. W. K. (2007) Blackwell's Five-minute Veterinary Consult: Canine & Feline (Fourth Edition) Blackwell Publishing
Feline
- Survival rate is only 50-60%
- Pathophysiology:
- Incompletely understood
- Obese cats that lose 30-40% of body weight exhibit a similar syndrome to naturally occurring hepatic lipidosis
- But many causative factors for naturally occurring hepatic lipidosis:
- Peripheral lipolysis secondary to absolute or relative lack of insulin
- Protein-calories malnutrition
- Amino acid deficiencies – inability to synthesize apolipoproteins necessary to mobilize hepatic fat
- Deficiency of lipotrophic compounds
- Error of fatty acid oxidation
- Hepatic perioxosomal damage due to oxidative stress
- Cats with hepatic lipidosis have higher nonesterified fatty acids (NEFAs) compared to controls and those with cholangiohepatitis
- NEFAs are derived from lipolysis of fat stores and enter the liver
- They are oxidized in the liver for energy or converted to phospholipids or cholesterol or reesterified to triglycerides
- Limited increase in lipoprotein synthesis and secretion of triglycerides in VLDLs
- Capacity for increase in oxidation by mitochondria and ketone body synthesis is low
- Rate of fatty acid esterification to triglycerides is not limited so can lead to a marked increase in the accumulation of stored hepatic triglycerides
- Also all triglyceride accumulation in hepatocytes in these cats comes from mobilized peripheral adipose stores during nutritional stress
- high levels of triglyceride concentrations in the liver will cause:
- severe periacinar necrosis
- jaundice
- hepatic encephalopathy
- high mortality rate
- high levels of triglyceride concentrations in the liver will cause:
- Lipolysis – under control of hormone-sensitive lipase hydrolyses triglycerides to NEFAs and glycerol
- Insulin – inhibits it
- Catecholamines (eg: released in stress, etc – neural input), glucocorticoids, thyroxine, GH and glucagons all promote lipolysis
- Lower insulin levels in cats with hepatic lipidosis or cholangiohepatitis compared to controls; and lower glucogon:insulin ratio in diseased cats
- But as not lipidosis specific, not likely to be the main factor involved
- Higher serum triglycerides in lipidotic cats compared to controls