Difference between revisions of "Immunoglobulin G"
m (Text replace - 'Immunoglobulin G - WikiBlood' to 'Immunoglobulin G') |
|||
| (12 intermediate revisions by 5 users not shown) | |||
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
| − | {{ | + | {{OpenPagesTop}} |
| − | + | ==Overview== | |
| − | [[Image:LH IgG.png|thumb| | + | [[Image:LH IgG.png|thumb|250px|right|'''IgG''']] |
| − | [[Image:IgG.jpg|thumb|right| | + | [[Image:IgG.jpg|thumb|right|250px|IgG - B. Catchpole, RVC 2008]] |
| − | + | ||
| + | ''Shortened to IgG'' | ||
| + | |||
| + | IgG is the major antibody in blood plasma, and constitutes at least 80% of all antibodies in the body. It is the smallest immunoglobulin, so can readily leave the blood plasma and enter tissues. They can also cross the placenta, providing adaptive immunity to the foetus when the mother is under attack. IgG is also present in breast milk. | ||
| + | |||
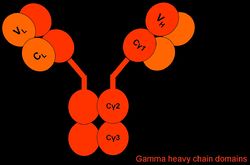
==Structure== | ==Structure== | ||
| − | + | ||
| − | + | IgG is Y-shaped, with three constant regions and a heavy chain subunit type γ. There are several different IgG subclasses, depending on the species coded for by the IGHG gene. | |
| − | + | ||
| − | + | '''Ruminants''' | |
| − | + | ||
| − | + | Have three subclasses, G1-G3. IgG1 is the major antibody in ruminant mucosal secretions and colostrum. | |
| − | + | ||
| − | + | '''Dogs, rodents and cats''' | |
| − | + | ||
| − | + | Have four subclasses. Dogs: G1-G4; Rodents: G1, G2a, G2b, G3. Cats are unknown. | |
| − | + | ||
| + | '''Pigs''' | ||
| + | |||
| + | Have five subclasses, G1-G4 (G2a, G2b). | ||
| + | |||
| + | '''Horses''' | ||
| + | |||
| + | Have six subclasses, G1-G6. | ||
| + | |||
==Production== | ==Production== | ||
| − | + | ||
| + | IgG is produced by [[B cell differentiation|plasma cells]] in the spleen, bone marrow and lymph nodes. | ||
| + | |||
==Function== | ==Function== | ||
| − | + | ||
| − | + | Some IgG subclasses can activate complement via the classical pathway. Some subclasses act as targets for [[Macrophages|macrophages]], [[Eosinophils|eosinophils]] and [[Neutrophils|neutrophils]]. It is therefore the major antibody in tissue fluids and lymph. IgG specifically binds to antigens on bacteria, causing agglutination and opsonisation. | |
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ==Links== | |
| − | + | ||
| − | + | [[Immunoglobulins|Immunoglobulins]] | |
| − | + | ||
| − | + | [[Immunoglobulin A|Immunoglobulin A]] | |
| − | + | ||
| + | [[Immunoglobulin D|Immunoglobulin D]] | ||
| + | |||
| + | [[Immunoglobulin E|Immunoglobulin E]] | ||
| + | |||
| + | [[Immunoglobulin M|Immunoglobulin M]] | ||
| + | |||
| + | <br><br> | ||
| + | {{Jim Bee 2007}} | ||
| + | |||
| + | {{OpenPages}} | ||
| + | |||
| + | [[Category:Immunoglobulins]] | ||
| + | [[Category:A&P Done]] | ||
Latest revision as of 16:09, 2 July 2012
Overview
Shortened to IgG
IgG is the major antibody in blood plasma, and constitutes at least 80% of all antibodies in the body. It is the smallest immunoglobulin, so can readily leave the blood plasma and enter tissues. They can also cross the placenta, providing adaptive immunity to the foetus when the mother is under attack. IgG is also present in breast milk.
Structure
IgG is Y-shaped, with three constant regions and a heavy chain subunit type γ. There are several different IgG subclasses, depending on the species coded for by the IGHG gene.
Ruminants
Have three subclasses, G1-G3. IgG1 is the major antibody in ruminant mucosal secretions and colostrum.
Dogs, rodents and cats
Have four subclasses. Dogs: G1-G4; Rodents: G1, G2a, G2b, G3. Cats are unknown.
Pigs
Have five subclasses, G1-G4 (G2a, G2b).
Horses
Have six subclasses, G1-G6.
Production
IgG is produced by plasma cells in the spleen, bone marrow and lymph nodes.
Function
Some IgG subclasses can activate complement via the classical pathway. Some subclasses act as targets for macrophages, eosinophils and neutrophils. It is therefore the major antibody in tissue fluids and lymph. IgG specifically binds to antigens on bacteria, causing agglutination and opsonisation.
Links
| Originally funded by the RVC Jim Bee Award 2007 |
Error in widget FBRecommend: unable to write file /var/www/wikivet.net/extensions/Widgets/compiled_templates/wrt67f237025cd0f2_95488768 Error in widget google+: unable to write file /var/www/wikivet.net/extensions/Widgets/compiled_templates/wrt67f2370263d6e4_75184416 Error in widget TwitterTweet: unable to write file /var/www/wikivet.net/extensions/Widgets/compiled_templates/wrt67f237026a3728_90219010
|
| WikiVet® Introduction - Help WikiVet - Report a Problem |