Difference between revisions of "Gingival Hyperplasia"
TestStudent (talk | contribs) |
|||
| (5 intermediate revisions by 2 users not shown) | |||
| Line 2: | Line 2: | ||
== Introduction == | == Introduction == | ||
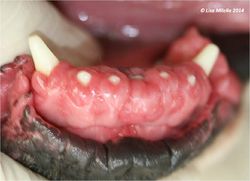
[[File:Gingival hyperplasia.jpg|250px|right|thumb|Gingival hyperplasia]] | [[File:Gingival hyperplasia.jpg|250px|right|thumb|Gingival hyperplasia]] | ||
| − | Gingival hyperplasia often appears as pink, hyperaemic and ulcerated lesions that can be either firm or soft. There can be varying amounts of pigmentation reflecting the normal pigmentation of the oral mucosa. [[ | + | Gingival hyperplasia often appears as pink, hyperaemic and ulcerated lesions that can be either firm or soft. There can be varying amounts of pigmentation reflecting the normal pigmentation of the oral mucosa. [[Enamel Organ#Crown|Crowns]] of teeth are often partially or completely covered by the hyperplastic gingiva forming a potential space or pocket between the [[gingiva]] and the [[Enamel Organ#Crown|crown]] where plaque is able to accumulate. |
Gingival hyperplasia can be described as focal lesions, multiple focal lesions or generalised lesions; or a combination of all of these. | Gingival hyperplasia can be described as focal lesions, multiple focal lesions or generalised lesions; or a combination of all of these. | ||
| Line 35: | Line 35: | ||
== Prognosis == | == Prognosis == | ||
The prognosis following surgical excision and histopathology is good. However, local recurrence is possible but less common if a treatment plan aimed at reducing plaque formation is implemented. A re-examination of the patient should be carried out at least every 6 months to assess for signs of recurrence and the sufficiency of plaque control measures. | The prognosis following surgical excision and histopathology is good. However, local recurrence is possible but less common if a treatment plan aimed at reducing plaque formation is implemented. A re-examination of the patient should be carried out at least every 6 months to assess for signs of recurrence and the sufficiency of plaque control measures. | ||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
==References== | ==References== | ||
| Line 47: | Line 42: | ||
| − | + | {{review}} | |
| − | {{ | ||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
{{OpenPages}} | {{OpenPages}} | ||
| Line 58: | Line 48: | ||
[[Category:Oral_Cavity_-_Proliferative_Pathology]][[Category:Teeth_-_Proliferative_Pathology]][[Category:Expert_Review - Small Animal]] | [[Category:Oral_Cavity_-_Proliferative_Pathology]][[Category:Teeth_-_Proliferative_Pathology]][[Category:Expert_Review - Small Animal]] | ||
[[Category:Oral Diseases - Dog]][[Category:Oral Diseases - Cat]][[Category:Periodontal Conditions]] | [[Category:Oral Diseases - Dog]][[Category:Oral Diseases - Cat]][[Category:Periodontal Conditions]] | ||
| − | [[Category: | + | [[Category:LisaM reviewed]] |
| − | [[Category:Waltham | + | [[Category:Waltham reviewing]] |
Revision as of 17:44, 13 August 2014
Introduction
Gingival hyperplasia often appears as pink, hyperaemic and ulcerated lesions that can be either firm or soft. There can be varying amounts of pigmentation reflecting the normal pigmentation of the oral mucosa. Crowns of teeth are often partially or completely covered by the hyperplastic gingiva forming a potential space or pocket between the gingiva and the crown where plaque is able to accumulate.
Gingival hyperplasia can be described as focal lesions, multiple focal lesions or generalised lesions; or a combination of all of these.
It is thought to be the result of an imbalance in the plaque/host tissue response. There are many factors that can cause this condition. These include drugs such as ciclosporin, phenytoin and calcium channel blockers. Chronic irritation and dental plaque are also causative. Other causes include odontoplastic resorptive lesions, neoplasia and mechanical irritation.
Signalment
This is a common condition in dogs but less common in cats. The following breeds are predisposed: Border Collie, Boxer, German Shepherd (Alsatian), Retriever (Labrador).
Clinical Signs
Signs depend on the severity of gingival hyperplasia and the degree to which the teeth are covered. They include pain on mastication, drooling +/- blood in saliva, haemorrhage of the gingiva, reluctance to eat and dysphagia. The animal may paw its mouth or rub its mouth along the floor.
Diagnosis
Clinical signs are indicative of the condition. A detailed oral examination under sedation will lead to a presumptive diagnosis.
Diagnostic Imaging
Oral radiographs should be taken to rule out concurrent conditions. One such condition is periodontitis which is demonstrated radiographically by alveolar bone loss associated with pocket formation between the tooth crown and gingiva.
Biopsy
Biopsy samples should include those areas of gingiva that show signs of inflammation with a softer than normal texture. Any gingiva with radiographic signs of bone involvement should also be sampled.
Treatment
The suspected cause of the condition should be corrected first. This may include a multimodal treatment plan aimed at controlling plaque formation including teeth brushing and providing the animal with sticks/toys that clean the teeth crowns.
Gingivectomy and gingivoplasty should be carried out under general anaesthetic if significant pseudo-pockets are present between the gingiva and teeth crowns. The aim should be to eliminate the pseudopockets and re-establish the normal anatomy of the gingival margin.
Electrosurgery and laser surgery can be performed. Care must be taken with electrosurgery to avoid contact between the teeth crowns and the electrodes to prevent irreversible heat damage to the pulp.
Prognosis
The prognosis following surgical excision and histopathology is good. However, local recurrence is possible but less common if a treatment plan aimed at reducing plaque formation is implemented. A re-examination of the patient should be carried out at least every 6 months to assess for signs of recurrence and the sufficiency of plaque control measures.
References
Tutt, C., Deeprose, J. and Crossley, D. (2007) BSAVA Manual of Canine and Feline Dentistry (3rd Edition), British Small Animal Veterinary Association.
Merck & Co (2008) The Merck Veterinary Manual, Merial.
| This article has been peer reviewed but is awaiting expert review. If you would like to help with this, please see more information about expert reviewing. |
Error in widget FBRecommend: unable to write file /var/www/wikivet.net/extensions/Widgets/compiled_templates/wrt69a8a9ef6f9ec2_82318609 Error in widget google+: unable to write file /var/www/wikivet.net/extensions/Widgets/compiled_templates/wrt69a8a9ef7e7142_18875715 Error in widget TwitterTweet: unable to write file /var/www/wikivet.net/extensions/Widgets/compiled_templates/wrt69a8a9ef8c0c83_12763288
|
| WikiVet® Introduction - Help WikiVet - Report a Problem |