Difference between revisions of "Pulp and Periapical Disease"
| Line 48: | Line 48: | ||
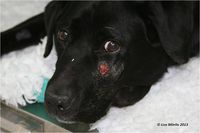
An untreated periapical abscess can lead to complications such as [[osteomyelitis]] and cellulitis through spread of the infection. A fistulous tract opening on the skin or oral mucosa may develop. | An untreated periapical abscess can lead to complications such as [[osteomyelitis]] and cellulitis through spread of the infection. A fistulous tract opening on the skin or oral mucosa may develop. | ||
| − | ==Combined [[Periodontal Conditions|Periodontic]] and Endodontic Lesions== | + | ==Combined [[Periodontal Conditions|Periodontic]] and [[Endodontic Conditions - Small Animal|Endodontic Lesions]]== |
There are possible pathways of communication between the pulp and the periodontium. These are denuded dentine tubules, lateral and/or accessory pulp canals, and at the apical foramen. Consequently, a periapical lesion may have a periodontal origin and a periodontal type lesion may originate from the pulp. Another possibility is that a lesion is the result of a combination of endodontic and periodontal pathology. The lesions are classified according to aetiology as follows: | There are possible pathways of communication between the pulp and the periodontium. These are denuded dentine tubules, lateral and/or accessory pulp canals, and at the apical foramen. Consequently, a periapical lesion may have a periodontal origin and a periodontal type lesion may originate from the pulp. Another possibility is that a lesion is the result of a combination of endodontic and periodontal pathology. The lesions are classified according to aetiology as follows: | ||
Revision as of 16:54, 14 August 2014
Pulpitis
Trauma to a tooth (mechanical, chemical, thermal, infective) often results in pulpal inflammation (pulpitis).
Depending on the type of trauma, its severity and duration, the pulpitis may be reversible, but often this is not the case and the inflammation becomes irreversible. The result of untreated irreversible pulpitis is pulp necrosis, followed by the spread of inflammation to affect the apical periodontium (apical periodontitis) and the periapical bone, resulting in bone destruction around the apex of the root (periapical disease).
A tooth affected by pulp and periapical diseases should always be treated, it cannot just be ignored. There are two available treatment options, namely to extract the tooth or to perform endodontic treatment and retain the tooth.
It is also possible that the infection originates from a circulating pyaemia producing pulpitis.
Pulpal Reactions
Crown fracture very often involves exposure of the pulp in the young and older animal as the pulp chamber follows the contour of the crown. As the animal gets older there is normally a reduction in the size of the pulp cavity, which is associated with continued deposition of secondary dentine. There are conditions that accelerate the rate of deposition of secondary dentine, thus prematurely reducing the size of the pulp cavity. Attrition and abrasion are two common conditions resulting in a narrow pulp cavity. Injury, orthodontic force and disease can all alter and decrease the pulp chamber and canals. In extreme cases, injury to a tooth will result in the complete obliteration of the pulp chamber and root canals. Less commonly, the obliteration is partial, with the pulp chamber retaining the size and shape it had at the time of the injury, and the root canals becoming completely obliterated. On the other hand, injuries that cause inflammation and degeneration/necrosis of the pulp also account for many abnormally large pulp cavities, as dentine production ceases when the pulp is chronically inflamed or necrotic.
Periapical Lesions
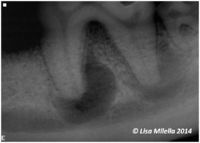
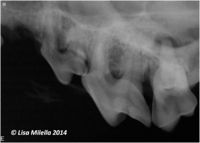
Pathology in the area surrounding the apex of a root, i.e. periapical pathology, is most commonly a sequel to chronic pulpitis or pulp necrosis. Initially there is inflammation of the apical periodontal ligament. If untreated, the apical periodontitis progresses to involve the surrounding bone, resulting in destruction of the bone, which is replaced by soft tissue. This is evident as an apical rarefaction on a radiograph. The soft tissue may be granulation tissue (periapical granuloma), cyst (periapical or radicular cyst) or abscess (periapical abscess).
Clinical Signs
Periapical lesions may be entirely asymptomatic or excruciatingly painful. The clinical signs indicative of periapical pathology are often insidious and not noticed by the owner. It is often only after completion of treatment that the owner reports a dramatic improvement in the animal’s general demeanour. Consequently, periapical lesions confirmed by radiography should be treated even if the animal is not showing obvious signs of pain or discomfort. Similarly, discoloured teeth with a necrotic pulp need to be treated before periapical pathology develops.
Diagnosis of Endodontic Disease
It is important to determine whether the pulp is exposed or not. If there is an obvious pulp exposure this can be diagnosed clinically by visual inspection of the tooth. Occasionally it may not be obvious and examination under general anaesthesia using a dental explorer probe or path finder needs to be performed. This should NEVER be done in the conscious animal as an exposed pulp will be very sensitive.
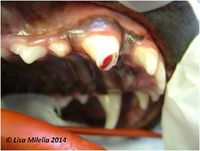
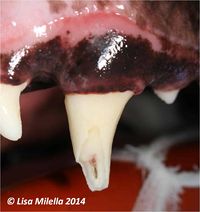
A red or black spot usually indicates that the pulp is exposed. The red spot indicates a fresh/vital/inflamed pulp, whilst a black spot usually indicates that the pulp has started to become necrotic and the black colour results from degradation of haemoglobin. Whether the pulp is vital or not, the tooth will still require treatment.
In cases of caries decay, a brown discolouration is seen on the occlusal surface. Due to the demineralization of the enamel and dentine, this brown discolouration is soft and the explorer probe sticks in the carious dentine.
Radiography may help determine whether a root fracture is present, the nature of the fracture (crown-root/vertical fracture) and whether perapical pathology is present. Radiographs also help determine whether teeth with uncomplicated crown fractures need treatment or not. Radiographs do not confirm that the pulp itself is exposed. See radiographic interpretation of endodontic disease.
Treatment
Treatment for all three entities is the same, i.e. endodontic therapy or if there are complicating factors, e.g. advanced periodontitis, then extraction.
An untreated periapical abscess can lead to complications such as osteomyelitis and cellulitis through spread of the infection. A fistulous tract opening on the skin or oral mucosa may develop.
Combined Periodontic and Endodontic Lesions
There are possible pathways of communication between the pulp and the periodontium. These are denuded dentine tubules, lateral and/or accessory pulp canals, and at the apical foramen. Consequently, a periapical lesion may have a periodontal origin and a periodontal type lesion may originate from the pulp. Another possibility is that a lesion is the result of a combination of endodontic and periodontal pathology. The lesions are classified according to aetiology as follows:
- A Class I lesion, or endodontic–periodontic lesion, is endodontic in origin, i.e. pathology begins in the pulp and progresses to involve the periodontium.
- A Class II lesion, or periodontic–endodontic lesion, is periodontic in origin, i.e. pathology begins in the periodontium and progresses to involve the pulp.
- A Class III lesion, or true combined lesion, is a fusion of independent periodontic and endodontic lesions.