Difference between revisions of "Dental Indices and Criteria"
Volkswagen (talk | contribs) |
|||
| (10 intermediate revisions by 2 users not shown) | |||
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
| + | {{OpenPagesTop}} | ||
==Introduction== | ==Introduction== | ||
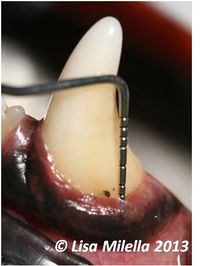
[[File:Periodontal probe in situ.jpg|right|200px|thumb|Periodontal probe used to measure gingival sulcus depth and feel for attachment loss. Here the probing depth is 2mm and considered normal on a canine tooth<small>''© Lisa Milella 2013''</small>]] | [[File:Periodontal probe in situ.jpg|right|200px|thumb|Periodontal probe used to measure gingival sulcus depth and feel for attachment loss. Here the probing depth is 2mm and considered normal on a canine tooth<small>''© Lisa Milella 2013''</small>]] | ||
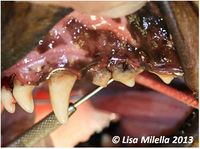
[[File:Periodontal probe and furcation.jpg|right|200px|thumb|Periodontal probe used to check for furcation exposure. The probe is passed horizontally between the roots. The probe extends from the palatal aspect through to the buccal aspect, indicating that there is complete bone loss between the roots, a grade 3 furcation exposure.<small>''© Lisa Milella 2013''</small>]] | [[File:Periodontal probe and furcation.jpg|right|200px|thumb|Periodontal probe used to check for furcation exposure. The probe is passed horizontally between the roots. The probe extends from the palatal aspect through to the buccal aspect, indicating that there is complete bone loss between the roots, a grade 3 furcation exposure.<small>''© Lisa Milella 2013''</small>]] | ||
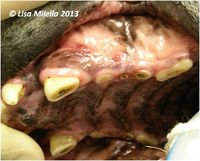
| − | [[File:Worn dog teeth.jpg|right|200px|thumb|Severely worn maxillary canine and premolars. The canine and 2nd premolar have pulp exposure (black spot) and draining fistulae just above the mucogingival junction. The first and 3rd premolars are worn with tertiary (or reparative) [[ | + | [[File:Worn dog teeth.jpg|right|200px|thumb|Severely worn maxillary canine and premolars. The canine and 2nd premolar have pulp exposure (black spot) and draining fistulae just above the mucogingival junction. The first and 3rd premolars are worn with tertiary (or reparative) [[Tooth - Anatomy & Physiology#Dentin|dentine]] (tan colour).<small>''© Lisa Milella 2013''</small>]] |
The following indices and criteria should be evaluated for each tooth: | The following indices and criteria should be evaluated for each tooth: | ||
#Gingivitis and gingival index | #Gingivitis and gingival index | ||
| Line 14: | Line 15: | ||
==Gingivitis and Gingival Index== | ==Gingivitis and Gingival Index== | ||
| − | The presence and degree of '''[[gingivitis]]''' (inflammation of the [[gingiva]]) is assessed based on a combination of redness and swelling, as well as presence or absence of '''bleeding''' on gentle probing of the '''gingival sulcus'''. An index which relies on both visual inspection and bleeding, namely the '''modified Löe and Silness gingival index''' < | + | The presence and degree of '''[[gingivitis]]''' (inflammation of the [[gingiva]]) is assessed based on a combination of redness and swelling, as well as presence or absence of '''bleeding''' on gentle probing of the '''gingival sulcus'''. An index which relies on both visual inspection and bleeding, namely the '''modified Löe and Silness gingival index''' <ref>Loe. H (1967) '''The gingival Index, the plaque index and the retention index system.''''' Journal of Periodontology'' 38: 610-616</ref>, can also be used: |
<br> | <br> | ||
:'''Gingival index 0''' - Clinically healthy gingiva | :'''Gingival index 0''' - Clinically healthy gingiva | ||
| Line 20: | Line 21: | ||
:'''Gingival index 2''' - Moderate gingivitis: the gingival margin is red and swollen; gentle probing of the gingival sulcus results in bleeding | :'''Gingival index 2''' - Moderate gingivitis: the gingival margin is red and swollen; gentle probing of the gingival sulcus results in bleeding | ||
:'''Gingival index 3''' - Severe gingivitis: the gingival margin is very swollen with a red or bluish-red color; there is spontaneous hemorrhage and/or ulceration of the gingival margin | :'''Gingival index 3''' - Severe gingivitis: the gingival margin is very swollen with a red or bluish-red color; there is spontaneous hemorrhage and/or ulceration of the gingival margin | ||
| − | <br><br> | + | <br><br> |
| + | |||
==Periodontal Probing Depth (PPD)== | ==Periodontal Probing Depth (PPD)== | ||
| − | The depth of the sulcus can be assessed by gently inserting a graduated [[Periodontal Probe|periodontal probe]] '''until resistance is encountered at the base of the sulcus'''. The depth from the free [[Gingiva|gingival margin]] to the base of the sulcus is measured in mm at several locations around the whole circumference of the [[:Category:Teeth - Anatomy & Physiology|tooth]]. The probe is moved gently horizontally, walking along the floor of the sulcus. The '''gingival sulcus is normally 1–3 mm deep in the dog''' and '''0.5–1 mm in the cat'''. Measurements in excess of these values usually indicate [[Periodontal Disease|periodontal disease]], when the [[ | + | The depth of the sulcus can be assessed by gently inserting a graduated [[Periodontal Probe|periodontal probe]] '''until resistance is encountered at the base of the sulcus'''. The depth from the free [[Gingiva|gingival margin]] to the base of the sulcus is measured in mm at several locations around the whole circumference of the [[:Category:Teeth - Anatomy & Physiology|tooth]]. The probe is moved gently horizontally, walking along the floor of the sulcus. The '''gingival sulcus is normally 1–3 mm deep in the dog''' and '''0.5–1 mm in the cat'''. Measurements in excess of these values usually indicate [[Periodontal Disease|periodontal disease]], when the [[Tooth - Anatomy & Physiology#Periodontal Ligament|periodontal ligament]] has been destroyed and [[Tooth - Anatomy & Physiology#Alveolar Bone|alveolar bone]] resorbed, thus allowing the probe to be inserted to a greater depth. The term used to describe this is '''periodontal pocketing'''. All sites with periodontal pocketing should be accurately recorded. Gingival inflammation resulting in swelling or hyperplasia of the free [[gingiva]] will, of course, also result in measuring sulcus depths in excess of normal values. In these situations, the term '''pseudopocketing''' is used, as the periodontal ligament and bone are intact (i.e.there is no evidence of [[periodontitis]]) and the increase in PPD is due to swelling or [[Gingival Hyperplasia|hyperplasia of the gingiva]]. |
<br><br> | <br><br> | ||
==Gingival Recession== | ==Gingival Recession== | ||
| − | Gingival recession is also measured using a [[Periodontal Probe|periodontal probe]]. It is the '''distance (in mm) from the [[ | + | Gingival recession is also measured using a [[Periodontal Probe|periodontal probe]]. It is the '''distance (in mm) from the [[Tooth - Anatomy & Physiology|cemento-enamel]] junction to the free [[Gingiva|gingival margin]]'''. At sites with gingival recession, [[#Periodontal Probing Depth (PPD)|PPD]] may be within normal values despite loss of [[Tooth - Anatomy & Physiology#Alveolar Bone|alveolar bone]] due to [[periodontitis]]. |
<br><br> | <br><br> | ||
==Furcation Involvement== | ==Furcation Involvement== | ||
| − | Furcation involvement refers to the situation where the '''bone between the roots of multirooted teeth is destroyed''' due to [[periodontitis]] | + | Furcation involvement refers to the situation where the '''bone between the roots of multirooted teeth is destroyed''' due to [[periodontitis]]. The furcation sites of multirooted teeth should be examined with either a '''[[Periodontal Probe|periodontal probe]]''' . Furcation involvement is graded as follows: |
<br> | <br> | ||
:'''Grade 0''' - No furcation involvement | :'''Grade 0''' - No furcation involvement | ||
| Line 52: | Line 54: | ||
==Crown Abnormalities== | ==Crown Abnormalities== | ||
| − | Any '''surface defect of the [[ | + | Any '''surface defect of the [[Tooth - Anatomy & Physiology#Crown|crown]]''' needs to be identified and recorded. Surface defects are diagnosed using the [[Dental Explorer|explorer probe]] – the sharp point is run across the crown to identify any catches. Crown defects such as [[Radiographic Interpretation of Dental Developmental Abnormalities - Small Animal#Abnormal Tooth Shape or Structure|enamel dysplasia]], fractured teeth (with or without pulp exposure), worn teeth, [[Dental Caries|caries lesions]] or [[Feline Odontoclastic Resorptive Lesions|odontoclastic resorptive lesions]] are noted on the [[Dental Recording|chart]] and treated appropriately. |
| + | |||
| + | ==References== | ||
| + | <references /> | ||
| + | Gorrel, C. (2004) '''Oral examination and recording.''' In : Veterinary Dentistry for the general practitioner. ''Saunders'', Chpt 6, pp47-55 | ||
| + | |||
| + | Robinson, J, Gorrel, C. (1995) '''Oral Examination and radiography.''' In : Crossley, D.A & Penman, S (eds) ''Manual of Small Animal Dentistry''. Cheltenham, UK, BSAVA Chpt 5 pp35-49 | ||
| + | |||
| + | {{Lisa Milella written | ||
| + | |date = 20 October 2014}} | ||
| − | {{ | + | {{Waltham}} |
| + | {{OpenPages}} | ||
[[Category:Oral Examination]] | [[Category:Oral Examination]] | ||
| − | [[Category: | + | [[Category:Waltham reviewed]] |
| − | |||
| − | |||
Latest revision as of 13:15, 8 February 2017
Introduction
The following indices and criteria should be evaluated for each tooth:
- Gingivitis and gingival index
- Periodontal probing depth
- Gingival recession
- Furcation involvement
- Mobility
In animals with large accumulations of dental deposits (plaque and calculus) on the teeth, it may be necessary to remove these to assess periodontal status accurately. Care must be taken not to damage the gingival tissues whilst removing the calculus.
Gingivitis and Gingival Index
The presence and degree of gingivitis (inflammation of the gingiva) is assessed based on a combination of redness and swelling, as well as presence or absence of bleeding on gentle probing of the gingival sulcus. An index which relies on both visual inspection and bleeding, namely the modified Löe and Silness gingival index [1], can also be used:
- Gingival index 0 - Clinically healthy gingiva
- Gingival index 1 - Mild gingivitis: slight reddening and swelling of the gingival margin; no bleeding on gentle probing of the gingival sulcus
- Gingival index 2 - Moderate gingivitis: the gingival margin is red and swollen; gentle probing of the gingival sulcus results in bleeding
- Gingival index 3 - Severe gingivitis: the gingival margin is very swollen with a red or bluish-red color; there is spontaneous hemorrhage and/or ulceration of the gingival margin
Periodontal Probing Depth (PPD)
The depth of the sulcus can be assessed by gently inserting a graduated periodontal probe until resistance is encountered at the base of the sulcus. The depth from the free gingival margin to the base of the sulcus is measured in mm at several locations around the whole circumference of the tooth. The probe is moved gently horizontally, walking along the floor of the sulcus. The gingival sulcus is normally 1–3 mm deep in the dog and 0.5–1 mm in the cat. Measurements in excess of these values usually indicate periodontal disease, when the periodontal ligament has been destroyed and alveolar bone resorbed, thus allowing the probe to be inserted to a greater depth. The term used to describe this is periodontal pocketing. All sites with periodontal pocketing should be accurately recorded. Gingival inflammation resulting in swelling or hyperplasia of the free gingiva will, of course, also result in measuring sulcus depths in excess of normal values. In these situations, the term pseudopocketing is used, as the periodontal ligament and bone are intact (i.e.there is no evidence of periodontitis) and the increase in PPD is due to swelling or hyperplasia of the gingiva.
Gingival Recession
Gingival recession is also measured using a periodontal probe. It is the distance (in mm) from the cemento-enamel junction to the free gingival margin. At sites with gingival recession, PPD may be within normal values despite loss of alveolar bone due to periodontitis.
Furcation Involvement
Furcation involvement refers to the situation where the bone between the roots of multirooted teeth is destroyed due to periodontitis. The furcation sites of multirooted teeth should be examined with either a periodontal probe . Furcation involvement is graded as follows:
- Grade 0 - No furcation involvement
- Grade 1 - Initial furcation involvement: the furcation can be felt with the probe/explorer, but horizontal tissue destruction is less than 1/3 of the horizontal width of the furcation
- Grade 2 - Partial furcation involvement: it is possible to explore the furcation but the probe/explorer cannot be passed through it from buccal to palatal/lingual; horizontal tissue destruction is more than 1/3 of the horizontal width of the furcation
- Grade 3 - Total furcation involvement: the probe/explorer can be passed through the furcation from the buccal to palatal/lingual aspect of the mouth
Tooth Mobility
The extent of tooth mobility should be assessed using a suitable instrument, e.g. the blunt end of the handle of a dental mirror or probe. It should not be assessed using fingers directly, since the yield of the soft tissues of the fingers will mask the extent of tooth mobility. Tooth mobility is graded as follows:
- Grade 0 - No mobility
- Grade 1 - Horizontal movement of 1 mm or less
- Grade 2 - Horizontal movement of more than 1 mm. Note that multirooted teeth are scored more severely and a horizontal mobility in excess of 1 mm is usually considered a Grade 3 even in the absence of vertical movement.
- Grade 3 - Vertical as well as horizontal movement
Crown Abnormalities
Any surface defect of the crown needs to be identified and recorded. Surface defects are diagnosed using the explorer probe – the sharp point is run across the crown to identify any catches. Crown defects such as enamel dysplasia, fractured teeth (with or without pulp exposure), worn teeth, caries lesions or odontoclastic resorptive lesions are noted on the chart and treated appropriately.
References
- ↑ Loe. H (1967) The gingival Index, the plaque index and the retention index system. Journal of Periodontology 38: 610-616
Gorrel, C. (2004) Oral examination and recording. In : Veterinary Dentistry for the general practitioner. Saunders, Chpt 6, pp47-55
Robinson, J, Gorrel, C. (1995) Oral Examination and radiography. In : Crossley, D.A & Penman, S (eds) Manual of Small Animal Dentistry. Cheltenham, UK, BSAVA Chpt 5 pp35-49
| This article was written by Lisa Milella BVSc DipEVDC MRCVS. Date reviewed: 20 October 2014 |
| Endorsed by WALTHAM®, a leading authority in companion animal nutrition and wellbeing for over 50 years and the science institute for Mars Petcare. |
Error in widget FBRecommend: unable to write file /var/www/wikivet.net/extensions/Widgets/compiled_templates/wrt69a3db555c0dc8_32997681 Error in widget google+: unable to write file /var/www/wikivet.net/extensions/Widgets/compiled_templates/wrt69a3db55632495_14940497 Error in widget TwitterTweet: unable to write file /var/www/wikivet.net/extensions/Widgets/compiled_templates/wrt69a3db556886c1_26091473
|
| WikiVet® Introduction - Help WikiVet - Report a Problem |