Difference between revisions of "Nephron Microscopic Anatomy"
Fiorecastro (talk | contribs) |
|||
| (31 intermediate revisions by 6 users not shown) | |||
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | ==Glomerulus== | + | ==The Renal Corpuscle== |
| + | ===Glomerulus=== | ||
[[Image:normcorpusclekidapx.jpg|right|thumb|250px|<small><center>Histology section of a normal renal corpuscle (© RVC 2008)</center></small>]] | [[Image:normcorpusclekidapx.jpg|right|thumb|250px|<small><center>Histology section of a normal renal corpuscle (© RVC 2008)</center></small>]] | ||
[[Image:normcorpusclekidap2.jpg|right|thumb|250px|<small><center>Histology section of a normal renal corpuscle (© RVC 2008)</center></small>]] | [[Image:normcorpusclekidap2.jpg|right|thumb|250px|<small><center>Histology section of a normal renal corpuscle (© RVC 2008)</center></small>]] | ||
| Line 18: | Line 11: | ||
* These capillaries do not connect to venules as with other capillaries | * These capillaries do not connect to venules as with other capillaries | ||
* Blood flows into these capillaries through a wide afferent arteriole and leaves through a narrower efferent arteriole | * Blood flows into these capillaries through a wide afferent arteriole and leaves through a narrower efferent arteriole | ||
| − | * The flow from the efferant arteriole enters the [[ | + | * The flow from the efferant arteriole enters the [[Glomerular Apparatus and Filtration - Anatomy & Physiology#Pressure in the Peritubular Capillaries|peritubular capillaries]] surrounding the proximal tubule |
* This change in diameter maintains a high filtration pressure which is essential for filtration | * This change in diameter maintains a high filtration pressure which is essential for filtration | ||
* Also the blood entering the afferent arteriole is at very high pressure already as it from the renal artery | * Also the blood entering the afferent arteriole is at very high pressure already as it from the renal artery | ||
| − | * The pressure actually forces molecules through the '''glomerular filtration barrier''' which is responsible for selectively filtering the blood forming the glomerular filtrate. | + | * The pressure actually forces molecules through the [[Glomerular Apparatus and Filtration - Anatomy & Physiology#Glomerular Filtration|'''glomerular filtration barrier''']] which is responsible for selectively filtering the blood forming the glomerular filtrate. |
* As well as the the cells in the blood vessels the other component of the glomerulus are the mesangial cells: | * As well as the the cells in the blood vessels the other component of the glomerulus are the mesangial cells: | ||
** These give support to the glomerulus | ** These give support to the glomerulus | ||
** Maintain glomerular basal lamina | ** Maintain glomerular basal lamina | ||
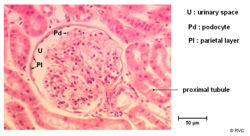
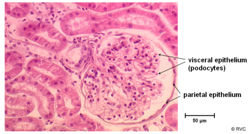
| − | ==Bowmans Capsule== | + | ===The Bowmans Capsule=== |
* Surrounds the capillaries of the glomerulus | * Surrounds the capillaries of the glomerulus | ||
| − | * Has two layers | + | * Has two layers separated by the '''urinary space''' |
** Inner visceral layer - Podocytes | ** Inner visceral layer - Podocytes | ||
** Outer parietal layer | ** Outer parietal layer | ||
* It is here where the filtrate is collected before entering the proximal tubule | * It is here where the filtrate is collected before entering the proximal tubule | ||
| + | |||
| + | ===The Physiology of the Renal Corpuscle=== | ||
| + | |||
| + | Details of the physiology of the renal corpuscle can be found [[Glomerular Apparatus and Filtration - Anatomy & Physiology#Glomerular Filtration|here]] | ||
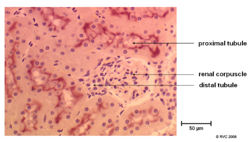
==Proximal Tubule== | ==Proximal Tubule== | ||
| Line 44: | Line 41: | ||
** Lots of mitochondria to provide energy for exchange | ** Lots of mitochondria to provide energy for exchange | ||
** Lots of Na<sup>+</sup> / K<sup>+</sup> ATPases to maintain ion levels in cells at right level to allow efficient take up of ions from lumen | ** Lots of Na<sup>+</sup> / K<sup>+</sup> ATPases to maintain ion levels in cells at right level to allow efficient take up of ions from lumen | ||
| + | |||
| + | ===The Physiology of the Proximal Tubule=== | ||
| + | Details of the physiology of the proximal tubule can be found [[Reabsorption and Secretion Along the Proximal Tubule - Anatomy & Physiology|here]] | ||
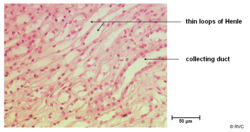
==The Loop of Henle== | ==The Loop of Henle== | ||
| − | The loop of henle basically consists of two parallel limbs which descend from the cortex into the medulla. They are joined at the bottom and as such the flow moves down one limb and up the other in opposite directions. This sets up a counter current | + | The loop of henle basically consists of two parallel limbs which descend from the cortex into the medulla. They are joined at the bottom and as such the flow moves down one limb and up the other in opposite directions. This sets up a counter current exchange and allows the loop of henle to be the major site of water reabsorption along the nephron. It has three parts; the thin decsending limb, the thin ascending limb and the thick ascending limb |
| − | ==The | + | ===The Physiology of the Loop of Henle=== |
| − | + | Details of the physiology of the loop of henle can be found [[Reabsorption and Secretion Along the Loop of Henle - Anatomy & Physiology|here]] | |
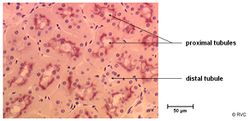
==The Distal Tubule== | ==The Distal Tubule== | ||
| Line 58: | Line 58: | ||
** Straight part - connects the thick ascending limb of the loop of henle to the convoluted distal tubule | ** Straight part - connects the thick ascending limb of the loop of henle to the convoluted distal tubule | ||
** Convoluted part - connects the straight part to the connecting duct | ** Convoluted part - connects the straight part to the connecting duct | ||
| − | * No brush border - very few micro villi (compared to the | + | * No brush border - very few micro villi (compared to the proximal tubule) |
* The basal lamina is striated to increase the surface area for reabsorption | * The basal lamina is striated to increase the surface area for reabsorption | ||
| + | |||
| + | ===The Physiology of the Distal Tubule=== | ||
| + | |||
| + | Details of the physiology of the distal tubule can be found [[Reabsorption and Secretion Along the Distal Tubule and Collecting Duct - Anatomy & Physiology#Distal Tubule|here]] | ||
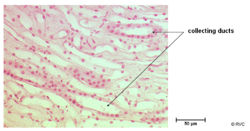
==Collecting Duct== | ==Collecting Duct== | ||
| Line 67: | Line 71: | ||
* The collecting duct has 2 cell types | * The collecting duct has 2 cell types | ||
** Intercalated cells | ** Intercalated cells | ||
| − | ** Principal | + | ** Principal cells |
* The cells are flat to cylindrical | * The cells are flat to cylindrical | ||
* Have clearly visible cell borders | * Have clearly visible cell borders | ||
| + | |||
| + | ===The Physiology of the Collecting Duct=== | ||
| + | |||
| + | Details of the physiology of the collecting duct can be found [[Reabsorption and Secretion Along the Distal Tubule and Collecting Duct - Anatomy & Physiology#Collecting Duct|here]] | ||
| + | |||
| + | ==Blood Supply to the Nephron== | ||
| + | |||
| + | The blood enters the glomerulus through the afferent arteriole. It is filtered by the glomerulus and what remains in the blood vessels leaves this structure via the efferent arteriole. The vessel then winds around the proximal tubule and is thus called a peritubular capillary. As it works its way along the tubule it collects the reabsorbed substances which it originally lost in the glomerulus. As the tubule descends into the medulla and becomes the Loop of Henle the blood vessel follows it and becomes what is known as the vasa recta. Upon its exit from the the medulla it wraps itself around the distal tubule. | ||
| + | |||
| + | ===The Vasa Recta=== | ||
| + | |||
| + | Vasa Recta is the name given to blood vessels supplying the medullary region of the kidney. They are arranged in a U configuration but flow is opposite to that of the [[Reabsorption and Secretion Along the Loop of Henle - Anatomy & Physiology| Loop of Henle]]. The blood vessels descend from the cortex down into the medulla. It supplies the nutrients and oxygen the [[Reabsorption and Secretion Along the Loop of Henle - Anatomy & Physiology| Loop of Henle]] needs. | ||
| + | |||
| + | The physiology of the vasa recta can be found [[Reabsorption and Secretion Along the Loop of Henle - Anatomy & Physiology#Vasa Recta Physiology|here]] | ||
| + | |||
| + | ==Revision== | ||
| + | |||
| + | Use the [[Microscopic Anatomy of the Nephron - Renal Flash Cards - Anatomy & Physiology|flash card revision resource]] for this section to test yourself. | ||
| + | |||
| + | |||
| + | [[Category:Nephron]] | ||
| + | [[Category:Bullet Points]] | ||
Latest revision as of 16:11, 6 January 2023
The Renal Corpuscle
Glomerulus
- Made up of many parallel capillaries
- These capillaries do not connect to venules as with other capillaries
- Blood flows into these capillaries through a wide afferent arteriole and leaves through a narrower efferent arteriole
- The flow from the efferant arteriole enters the peritubular capillaries surrounding the proximal tubule
- This change in diameter maintains a high filtration pressure which is essential for filtration
- Also the blood entering the afferent arteriole is at very high pressure already as it from the renal artery
- The pressure actually forces molecules through the glomerular filtration barrier which is responsible for selectively filtering the blood forming the glomerular filtrate.
- As well as the the cells in the blood vessels the other component of the glomerulus are the mesangial cells:
- These give support to the glomerulus
- Maintain glomerular basal lamina
The Bowmans Capsule
- Surrounds the capillaries of the glomerulus
- Has two layers separated by the urinary space
- Inner visceral layer - Podocytes
- Outer parietal layer
- It is here where the filtrate is collected before entering the proximal tubule
The Physiology of the Renal Corpuscle
Details of the physiology of the renal corpuscle can be found here
Proximal Tubule
- This is the piece of nephron which starts at the Bowmans capsule and ends in the loop of henle
- Consists of two parts which differ in cell morphology and function
- Pars convoluter - joins the urinary pole of the Bowmans capsule
- Pars recta (straight part) - links the pars convoluter to the descending thin limb of the loop of henle
- Has a brush border of densely packed microvilli to increase surface area
- The basal lamina is striated to increase the surface area for reabsorption
- Typical of actively ion transporting epithelial cells
- Lots of mitochondria to provide energy for exchange
- Lots of Na+ / K+ ATPases to maintain ion levels in cells at right level to allow efficient take up of ions from lumen
The Physiology of the Proximal Tubule
Details of the physiology of the proximal tubule can be found here
The Loop of Henle
The loop of henle basically consists of two parallel limbs which descend from the cortex into the medulla. They are joined at the bottom and as such the flow moves down one limb and up the other in opposite directions. This sets up a counter current exchange and allows the loop of henle to be the major site of water reabsorption along the nephron. It has three parts; the thin decsending limb, the thin ascending limb and the thick ascending limb
The Physiology of the Loop of Henle
Details of the physiology of the loop of henle can be found here
The Distal Tubule
- Consists of two parts
- Straight part - connects the thick ascending limb of the loop of henle to the convoluted distal tubule
- Convoluted part - connects the straight part to the connecting duct
- No brush border - very few micro villi (compared to the proximal tubule)
- The basal lamina is striated to increase the surface area for reabsorption
The Physiology of the Distal Tubule
Details of the physiology of the distal tubule can be found here
Collecting Duct
- This structure links the distal tubule to the area cribosa of the papilla into the renal pelvis
- Here the final concentration of the urine occurs as the collecting duct makes the transition from the isotonic cortex to the hypertonic medulla the increasing osmolarity of the interstial fluid causes more and more water to be reabsorbed.
- The collecting duct has 2 cell types
- Intercalated cells
- Principal cells
- The cells are flat to cylindrical
- Have clearly visible cell borders
The Physiology of the Collecting Duct
Details of the physiology of the collecting duct can be found here
Blood Supply to the Nephron
The blood enters the glomerulus through the afferent arteriole. It is filtered by the glomerulus and what remains in the blood vessels leaves this structure via the efferent arteriole. The vessel then winds around the proximal tubule and is thus called a peritubular capillary. As it works its way along the tubule it collects the reabsorbed substances which it originally lost in the glomerulus. As the tubule descends into the medulla and becomes the Loop of Henle the blood vessel follows it and becomes what is known as the vasa recta. Upon its exit from the the medulla it wraps itself around the distal tubule.
The Vasa Recta
Vasa Recta is the name given to blood vessels supplying the medullary region of the kidney. They are arranged in a U configuration but flow is opposite to that of the Loop of Henle. The blood vessels descend from the cortex down into the medulla. It supplies the nutrients and oxygen the Loop of Henle needs.
The physiology of the vasa recta can be found here
Revision
Use the flash card revision resource for this section to test yourself.