Difference between revisions of "Major Histocompatability Complexes"
| (93 intermediate revisions by 6 users not shown) | |||
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
| − | {{ | + | {{OpenPagesTop}} |
| − | | | + | [[Image:MHC.jpg|thumb|right|250px|Major Histocompatibility Complexes - B. Catchpole, RVC 2008]] |
| − | | | + | ==Introduction== |
| − | | | + | T-cells rely on Major Histocompatability Complexes (MHC), which are molecules manufactured within cells for the purpose of presenting antigen fragments so that they can be detected by the immune system. MHC has evolved to form two classes for antigen presentation: '''MHC I''' presents digested fragments from antigen in '''cellular cytoplasm''', and '''MHC II''' presents digested fragments from antigen in the '''tissue fluid''' (extracellular). MHC I tends to bind slightly smaller peptides (~9 amino acids) than MHC II (~15 amino acids). |
| − | | | ||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| + | ==MHC I== | ||
===Structure=== | ===Structure=== | ||
| + | [[Image:MHC I Structure.jpg|thumb|right|200px| Structure of MHC I molecule - Copyright Prof Dirk Werling DrMedVet PhD MRCVS]] | ||
| − | + | MHC class I is expressed on virtually all nucleated cells (so, for example, it is not expressed on erythrocytes), although quantity varies betweeen cell types, and consists of a membrane-associated heavy chain bound non-covalently with a secreted light chain. The heavy chain is made up of three distinct extracellular protein domains - α1, α2 and α3. The heavy chain C - terminus is cytoplasmic. | |
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | + | The light chain is known as β2-microglobulin and is similar in structure to one of the heavy chain domains. It is not membrane associated but binds to the α3-domain of the heavy chain. | |
| + | The MHC class I domains are structurally and genetically related to immunoglobulin and TcR domains; the outer domains (α1 and α2) are like the variable domains and the α3 domain and β2m are like the constant domains. | ||
| − | + | MHC class I molecules are folded to form specific 3-dimensional structures. The α1 and α2 domains are folded to produce an antigen-binding groove which can bind molecules of a limited size only (8-10 amino acids). This limits the size of epitope seen by the T-cell receptors. | |
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| + | ===Presentation Pathway=== | ||
| + | [[Image:MHC I processing.jpg|thumb|200px|left|'''MHC I presentation pathway, courtesy of B. Catchpole, 2008''']] | ||
| + | MHC I presents '''endogenous''' (intracellular) peptides. Viral proteins are broken down to peptides by the proteasome and transferred to the endoplasmic reticulum (ER) via transporters associated with antigen processing (TAP) molecules. In the ER peptides are processed with empty MHC I molecules and exported to the cell surface for presentation to the T-cell receptors of [[T_cells#Cytotoxic_CD8.2B|CD8<sup>+</sup> T-cells]]. The purpose of presentation in this manner is to kill the cell to prevent viral replication. Activation of the cell with '''Interferon''' enhances expression of MHC class I molecules as part of the [[Innate Immunity to Viruses|innate immunity]] to viruses. | ||
| − | == | + | ==MHC II== |
| + | [[Image:MHC II Structure.jpg|thumb|right|200px| Structure of MHC II molecule - Copyright Prof Dirk Werling DrMedVet PhD MRCVS]] | ||
===Structure=== | ===Structure=== | ||
| + | MHC class II is expressed mainly on [[Macrophages|macrophages]], [[T cell differentiation#Antigen Presentation by Dendritic Cells|dendritic cells]] and [[B cells|B-lymphocytes]]. MHC class II consists of membrane-associated α and β chains with each chain being a transmembrane glycoprotein. The extracellular parts of each chain have two Ig-like domains - α1 and α2, β1 and β2. The β2 domain is responsible for the activation of [[T cells|T helper cells]] through the interaction with the CD4<sup>+</sup> on the cell surface of the T helper cells. The outer domains (α1 and β1) are variable and the inner domains (α2 and β2) are constant. | ||
| + | |||
| + | The 3-dimensional structure of MHC class II is similar to MHC class I; the outer domains of the α and β chains fold in a similar way to the α1 and α2 domains of class I to produce the antigen-binding groove. | ||
| + | |||
| + | ===Presentation Pathway=== | ||
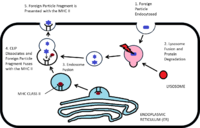
| + | [[File:MHC Class II Presentation.png|thumb|left|200px|MHC Class II Presentation pathway - RJ Francis, RVC, 2012]] | ||
| + | MHC II presents '''exogenous''' (Extracellular fluid - ECF) peptides. Endocytosed antigen interacts with MHC II in the cytoplasm to form a complex: | ||
| + | *Antigen is endoycotsed from the ECF | ||
| + | *Lysosomes fuse with primary endosomes to digest the antigen to peptides | ||
| + | *MHC II is meanwhile being produced by the endoplasmic reticulum, along with an invariant chain chaperone | ||
| + | *These pathways (endoytotic and secretory) merge to allow interaction between the antigen and MHC II and the invariant chain is digested, leaving a CLIP peptide in the binding groove. | ||
| + | *Foreign antigen then replaces the CLIP peptide | ||
| + | *The MHC II-antigen complex is then secreted to the cell surface for presentation to [[T_cells#Helper_CD4.2B|CD4<sup>+</sup> T-cells]] | ||
| + | |||
| + | ==Antigen/MHC Interaction== | ||
| + | MHC molecules do not recognise specific amino acid sequences of antigens, rather they recognise particular motifs of amino acids. The association of any MHC allele with a peptide may be determined by the presence of as few as two amino acids, however these determinants must be present in a particular array. The actual identity of the amino acids is not important for MHC binding, but the physical and chemical characteristics of the amino acid are vitally important. | ||
| + | |||
| + | Interactions of individual amino acids at the head and tail of the peptide-binding groove control the binding of peptides. The amino acids are mainly positioned at the floor of the antigen-binding groove, or within the helices facing into the groove. MHC amino acids associate with the amino acids near the ends of the peptides and the intervening stretch of peptide folds into a helix within the groove. | ||
| − | + | MHC molecules have the capacity to bind to trillions of different peptides. They adopt a flexible, floppy conformation until peptide binding when the molecules fold around the peptide to increase the stability of the complex. A small number of anchor residues then tether the peptide. This configuration allows different sequences between anchors, and also allows peptides of different lengths to bind. | |
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | == | + | ==TCR-MHC Interaction== |
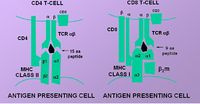
| + | [[Image:MHC T cell Interaction.jpg|thumb|right|200px|Molecules of T lymphocyte recognition - Copyright Prof Dirk Werling DrMedVet PhD MRCVS]] | ||
| + | Only peptide associated with MHC will interact with and activate [[T cells]]. T cells therefore cannot be directly activated by a peptide on a foreign organism. | ||
| − | + | T cells will react against foreign MHC molecules (e.g. from a different person) and this is the basis of graft rejection, for example in Heart transplants. | |
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | == | + | ==MHC Genetics (Polymorphism)== |
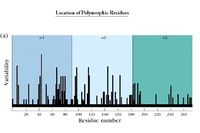
| + | [[Image:Location of Polymorphic Residues 1.jpg|thumb|right|200px|Location of Polymorphic Residues - Copyright Prof Dirk Werling DrMedVet PhD MRCVS]] | ||
| + | Each individual has 6 types of MHC; MHC molecules are co-dominantly expressed. The combination of alleles in a chromosome is called an '''MHC Haplotype'''. | ||
| − | + | Different individuals have different critical amino acids within the MHC i.e. different amino acids that determine peptide binding. This variation is termed '''MHC polymorphism'''. | |
| − | + | *Each polymorphic variant is called an '''allele''' | |
| − | + | Both type I and type II MHC molecules are highly polymorphic - the most polymorphic regions of class I are in the alpha 1 and alpha 2 domains. The most polymorphic regions of class II are in the alpha 1 and beta 1 domains. | |
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | * | ||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | + | Most polymorphisms are point mutations and there are millions of variations in [[Immunoglobulins|antibodies]] and TCRs; however, with MHC there is very limited variation between molecules. Allelic variation within the MHC molecule occurs at the peptide binding site and on the top or sides of the binding cleft. Polymorphisms and polygenism in the MHC provides protection from pathogens evading the immune system. | |
| + | * MHC polymorphism has been best studied in the human | ||
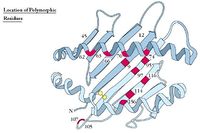
| + | [[Image:Location of Polymorphic Residues 2.jpg|thumb|right|200px|Location of Polymorphic Residues - Copyright Prof Dirk Werling DrMedVet PhD MRCVS]] | ||
| − | + | ===MHC Polymorphism In People=== | |
| − | * | + | * There are three types (loci) of MHC class I molecules known as human leukocyte antigen (HLA) - A, B, and C |
| − | * | + | * Equally there are three loci of MHC class II molecules - HLAs DP, DQ and DR |
| − | + | In the entire human population there are only approximately 50 different variants (alleles) at each MHC class I and class II locus. | |
| − | + | The variation within MHC class I is entirely based on the class I heavy chain (the β2m is invariant). The variation within MHC class II is mainly within the β chains. Every individual has two alleles at each MHC locus inherited one from each parent. Any individual will therefore express two variants at most at each locus. | |
| + | This gives a maximum variability for an individual of: | ||
| + | * 6 different variants of MHC class I (2 each of HLA - A, B and C) | ||
| + | * 6 different variants of MHC class II (2 each of HLA - DP, DQ and DR) | ||
| + | Many animal species have fewer loci than the human e.g. ruminants have no MHC class II DP. | ||
| − | + | ==MHC and the Disease Process== | |
| − | + | Antigen from a pathogen has to be seen by the host MHC before an efficient immune response can occur so inevitably there is a constant evolutionary battle between the host and potential pathogens. Specifically, there is selective pressure on the pathogen to evolve proteins that do not interact with the host MHC and equally a selective pressure on the host to continue to be able to recognize the pathogen. | |
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | + | One consequence of this parallel evolution is that host-pathogen relationships can lead to the selection of particular MHC variants, for example: | |
| + | * MHC class II alleles DR13/DR1*1301 are prevalent in Central and Western Africa and impart resistance to malaria. | ||
| + | * MHC-DRB1 is prevalent in Western Europe, but rare in the Inuit populations of North America, and is associated with the clearance of hepatitis B infection in Western Europe, and so, perhaps unsuprisingly, Inuits have the highest incidence of hepatitis B in the world. | ||
| − | + | In humans there are also strong associations between certain alleles and some autoimmune diseases, for example: | |
| − | + | * [[Diabetes Mellitus|Diabetes mellitus]] | |
| − | + | * Ankylosing spondylitis | |
| − | + | * Rheumatoid arthritis | |
| − | + | <br><br> | |
| − | + | {{Jim Bee 2007}} | |
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | * | ||
| − | * | ||
| − | * | ||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | + | {{OpenPages}} | |
| − | + | [[Category:Adaptive Immune System]] | |
| − | + | [[Category:Lymphocytes]] | |
| − | + | [[Category:Image Review]] | |
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
Latest revision as of 16:19, 2 July 2012
Introduction
T-cells rely on Major Histocompatability Complexes (MHC), which are molecules manufactured within cells for the purpose of presenting antigen fragments so that they can be detected by the immune system. MHC has evolved to form two classes for antigen presentation: MHC I presents digested fragments from antigen in cellular cytoplasm, and MHC II presents digested fragments from antigen in the tissue fluid (extracellular). MHC I tends to bind slightly smaller peptides (~9 amino acids) than MHC II (~15 amino acids).
MHC I
Structure
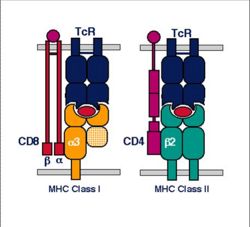
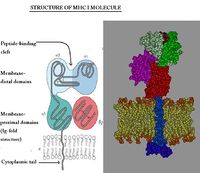
MHC class I is expressed on virtually all nucleated cells (so, for example, it is not expressed on erythrocytes), although quantity varies betweeen cell types, and consists of a membrane-associated heavy chain bound non-covalently with a secreted light chain. The heavy chain is made up of three distinct extracellular protein domains - α1, α2 and α3. The heavy chain C - terminus is cytoplasmic.
The light chain is known as β2-microglobulin and is similar in structure to one of the heavy chain domains. It is not membrane associated but binds to the α3-domain of the heavy chain. The MHC class I domains are structurally and genetically related to immunoglobulin and TcR domains; the outer domains (α1 and α2) are like the variable domains and the α3 domain and β2m are like the constant domains.
MHC class I molecules are folded to form specific 3-dimensional structures. The α1 and α2 domains are folded to produce an antigen-binding groove which can bind molecules of a limited size only (8-10 amino acids). This limits the size of epitope seen by the T-cell receptors.
Presentation Pathway
MHC I presents endogenous (intracellular) peptides. Viral proteins are broken down to peptides by the proteasome and transferred to the endoplasmic reticulum (ER) via transporters associated with antigen processing (TAP) molecules. In the ER peptides are processed with empty MHC I molecules and exported to the cell surface for presentation to the T-cell receptors of CD8+ T-cells. The purpose of presentation in this manner is to kill the cell to prevent viral replication. Activation of the cell with Interferon enhances expression of MHC class I molecules as part of the innate immunity to viruses.
MHC II
Structure
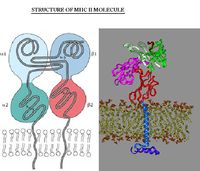
MHC class II is expressed mainly on macrophages, dendritic cells and B-lymphocytes. MHC class II consists of membrane-associated α and β chains with each chain being a transmembrane glycoprotein. The extracellular parts of each chain have two Ig-like domains - α1 and α2, β1 and β2. The β2 domain is responsible for the activation of T helper cells through the interaction with the CD4+ on the cell surface of the T helper cells. The outer domains (α1 and β1) are variable and the inner domains (α2 and β2) are constant.
The 3-dimensional structure of MHC class II is similar to MHC class I; the outer domains of the α and β chains fold in a similar way to the α1 and α2 domains of class I to produce the antigen-binding groove.
Presentation Pathway
MHC II presents exogenous (Extracellular fluid - ECF) peptides. Endocytosed antigen interacts with MHC II in the cytoplasm to form a complex:
- Antigen is endoycotsed from the ECF
- Lysosomes fuse with primary endosomes to digest the antigen to peptides
- MHC II is meanwhile being produced by the endoplasmic reticulum, along with an invariant chain chaperone
- These pathways (endoytotic and secretory) merge to allow interaction between the antigen and MHC II and the invariant chain is digested, leaving a CLIP peptide in the binding groove.
- Foreign antigen then replaces the CLIP peptide
- The MHC II-antigen complex is then secreted to the cell surface for presentation to CD4+ T-cells
Antigen/MHC Interaction
MHC molecules do not recognise specific amino acid sequences of antigens, rather they recognise particular motifs of amino acids. The association of any MHC allele with a peptide may be determined by the presence of as few as two amino acids, however these determinants must be present in a particular array. The actual identity of the amino acids is not important for MHC binding, but the physical and chemical characteristics of the amino acid are vitally important.
Interactions of individual amino acids at the head and tail of the peptide-binding groove control the binding of peptides. The amino acids are mainly positioned at the floor of the antigen-binding groove, or within the helices facing into the groove. MHC amino acids associate with the amino acids near the ends of the peptides and the intervening stretch of peptide folds into a helix within the groove.
MHC molecules have the capacity to bind to trillions of different peptides. They adopt a flexible, floppy conformation until peptide binding when the molecules fold around the peptide to increase the stability of the complex. A small number of anchor residues then tether the peptide. This configuration allows different sequences between anchors, and also allows peptides of different lengths to bind.
TCR-MHC Interaction
Only peptide associated with MHC will interact with and activate T cells. T cells therefore cannot be directly activated by a peptide on a foreign organism.
T cells will react against foreign MHC molecules (e.g. from a different person) and this is the basis of graft rejection, for example in Heart transplants.
MHC Genetics (Polymorphism)
Each individual has 6 types of MHC; MHC molecules are co-dominantly expressed. The combination of alleles in a chromosome is called an MHC Haplotype.
Different individuals have different critical amino acids within the MHC i.e. different amino acids that determine peptide binding. This variation is termed MHC polymorphism.
- Each polymorphic variant is called an allele
Both type I and type II MHC molecules are highly polymorphic - the most polymorphic regions of class I are in the alpha 1 and alpha 2 domains. The most polymorphic regions of class II are in the alpha 1 and beta 1 domains.
Most polymorphisms are point mutations and there are millions of variations in antibodies and TCRs; however, with MHC there is very limited variation between molecules. Allelic variation within the MHC molecule occurs at the peptide binding site and on the top or sides of the binding cleft. Polymorphisms and polygenism in the MHC provides protection from pathogens evading the immune system.
- MHC polymorphism has been best studied in the human
MHC Polymorphism In People
- There are three types (loci) of MHC class I molecules known as human leukocyte antigen (HLA) - A, B, and C
- Equally there are three loci of MHC class II molecules - HLAs DP, DQ and DR
In the entire human population there are only approximately 50 different variants (alleles) at each MHC class I and class II locus.
The variation within MHC class I is entirely based on the class I heavy chain (the β2m is invariant). The variation within MHC class II is mainly within the β chains. Every individual has two alleles at each MHC locus inherited one from each parent. Any individual will therefore express two variants at most at each locus. This gives a maximum variability for an individual of:
- 6 different variants of MHC class I (2 each of HLA - A, B and C)
- 6 different variants of MHC class II (2 each of HLA - DP, DQ and DR)
Many animal species have fewer loci than the human e.g. ruminants have no MHC class II DP.
MHC and the Disease Process
Antigen from a pathogen has to be seen by the host MHC before an efficient immune response can occur so inevitably there is a constant evolutionary battle between the host and potential pathogens. Specifically, there is selective pressure on the pathogen to evolve proteins that do not interact with the host MHC and equally a selective pressure on the host to continue to be able to recognize the pathogen.
One consequence of this parallel evolution is that host-pathogen relationships can lead to the selection of particular MHC variants, for example:
- MHC class II alleles DR13/DR1*1301 are prevalent in Central and Western Africa and impart resistance to malaria.
- MHC-DRB1 is prevalent in Western Europe, but rare in the Inuit populations of North America, and is associated with the clearance of hepatitis B infection in Western Europe, and so, perhaps unsuprisingly, Inuits have the highest incidence of hepatitis B in the world.
In humans there are also strong associations between certain alleles and some autoimmune diseases, for example:
- Diabetes mellitus
- Ankylosing spondylitis
- Rheumatoid arthritis
| Originally funded by the RVC Jim Bee Award 2007 |
Error in widget FBRecommend: unable to write file /var/www/wikivet.net/extensions/Widgets/compiled_templates/wrt69749fce00e5a7_27788701 Error in widget google+: unable to write file /var/www/wikivet.net/extensions/Widgets/compiled_templates/wrt69749fce0ed077_53779761 Error in widget TwitterTweet: unable to write file /var/www/wikivet.net/extensions/Widgets/compiled_templates/wrt69749fce192859_85126081
|
| WikiVet® Introduction - Help WikiVet - Report a Problem |