Difference between revisions of "Gastritis, Acute"
TestStudent (talk | contribs) |
|||
| (36 intermediate revisions by 5 users not shown) | |||
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
| − | {{ | + | {{OpenPagesTop}} |
| + | ==Introduction== | ||
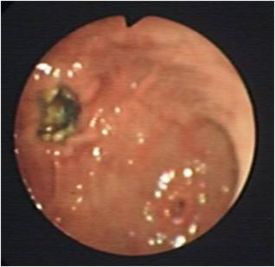
| + | [[Image:Gastric ulceration.jpg|thumb|right|275px|Gastric ulceration - Copyright David Walker RVC]] | ||
| + | Acute inflammation of the stomach is not uncommon, especially in the dog. The cause is usually the ingestion of substances including | ||
| + | [[Gastric Foreign Objects|foreign bodies]], spoiled or contaminated food, toxic plants ,chemicals and drugs (especially [[NSAIDs|non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs]]). | ||
| + | Infectious, viral and bacterial causes are thought to exist in cats and dogs but have not yet been identified. | ||
| − | + | Ingestion of these substances causes disruption of the gastric mucosal barrier. This results in increased permeability, with hydrogen ions and pepsin penetrating the mucosa. An inflammatory response subsequently occurs that may damage blood vessels, resulting in the extravasation of blood and plasma into the gastric lumen. Mucosal erosions can develop due to [[Necrosis - Pathology|necrosis]] of the mucosal epithelial cells. | |
| − | + | ||
| + | Gastritis can cause contraction of gastric smooth muscle which causes spasms and pain. [[Vomiting|Vomiting]] is also a symptom following stimulation of nerve endings that connect with the vomiting centre. | ||
==Signalment== | ==Signalment== | ||
| − | + | Dogs are more commonly affected than cats due to their less selective eating habits. | |
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
==Diagnosis== | ==Diagnosis== | ||
Acute gastritis is a diagnosis of exclusion based on physical examination findings, history of ingestion of causative substances and diagnostic tests. | Acute gastritis is a diagnosis of exclusion based on physical examination findings, history of ingestion of causative substances and diagnostic tests. | ||
| + | |||
===Clinical Signs=== | ===Clinical Signs=== | ||
| − | + | Include acute vomiting (food, bile together with small amounts of blood may be present in the vomitus), anorexia, polydipsia, lethargy, depression and if severely affected dehydration. | |
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
===Abdominal Palpation=== | ===Abdominal Palpation=== | ||
| Line 35: | Line 23: | ||
===Laboratory Tests=== | ===Laboratory Tests=== | ||
| − | Clinical pathology such as haematology and biochemistry can be used to rule out conditions such as uraemia, diabetic ketoacidosis, hypoadrenocorticism, hepatic disease, hypercalcaemia and pancreatitis. | + | Clinical pathology such as haematology and biochemistry can be used to rule out conditions such as [[Uraemia|uraemia]],[[Diabetes Mellitus#Diabetic Ketoacidosis| diabetic ketoacidosis]], hypoadrenocorticism], hepatic disease, hypercalcaemia and [[Pancreatitis|pancreatitis]]. |
===Radiography=== | ===Radiography=== | ||
| Line 44: | Line 32: | ||
==Treatment== | ==Treatment== | ||
| − | Many different techniques of treating acute gastritis have been described | + | Many different techniques of treating acute gastritis have been described. In general, therapy is designed to rest the stomach by witholding food and maintaining the animal's fluid , electrolyte and acid/base balance. |
| − | + | ||
| − | + | Witholding food and water for 24 hours is usually sufficient to control vomiting in combination with parenteral fluid therapy to avoid dehydration. | |
| − | + | Small amounts of a bland diet such as boiled chicken and potato can be offered once the animal has not vomited for at least 12 hours. | |
| − | + | Gut protectants should be considered if the animal presents with haematemesis. Some examples of [[Gastroprotective Drugs|gastroprotective drugs]] include sucralfate which forms a protective barrier over the mucosal surface and also stimulates bicarbonate and mucus secretion and omeprazole which is a proton pump inhibitor that reduces gastric acid secretion. | |
| + | [[Emetics and Anti-Emetic Drugs#Anti-Emetics|Anti-emetics]] can be used but only if vomiting is causing pain or if unsustainable fluid and electrolyte losses occur. | ||
==Prognosis== | ==Prognosis== | ||
| + | The prognosis is excellent if fluid and electrolyte balance is maintained. | ||
| + | |||
| + | {{Learning | ||
| + | |Vetstream = [https://www.vetstream.com/canis/Content/Disease/dis02679.asp, Acute gastritis] | ||
| + | |literature search = [http://www.cabdirect.org/search.html?q=title%3A%28%22gastritis%22%29+AND+title%3A%28acute%29&fq=sc%3A%22ve%22 Acute gastritis publications] | ||
| + | }} | ||
==References== | ==References== | ||
| + | |||
| + | Hall, E.J, Simpson, J.W. and Williams, D.A. (2005) '''BSAVA Manual of Canine and Feline Gastroenterology (2nd Edition)''' ''BSAVA'' | ||
| + | |||
| + | Merck & Co (2008) '''The Merck Veterinary Manual (Eighth Edition)''' ''Merial'' | ||
| + | |||
| + | |||
| + | {{review}} | ||
| + | |||
| + | {{OpenPages}} | ||
| + | |||
| + | [[Category:Stomach_and_Abomasum_-_Inflammatory_Pathology]] | ||
| + | [[Category:Expert_Review - Small Animal]][[Category:Gastric Diseases - Dog]][[Category:Gastric Diseases - Cat]] | ||
Latest revision as of 16:43, 2 September 2015
Introduction
Acute inflammation of the stomach is not uncommon, especially in the dog. The cause is usually the ingestion of substances including foreign bodies, spoiled or contaminated food, toxic plants ,chemicals and drugs (especially non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs). Infectious, viral and bacterial causes are thought to exist in cats and dogs but have not yet been identified.
Ingestion of these substances causes disruption of the gastric mucosal barrier. This results in increased permeability, with hydrogen ions and pepsin penetrating the mucosa. An inflammatory response subsequently occurs that may damage blood vessels, resulting in the extravasation of blood and plasma into the gastric lumen. Mucosal erosions can develop due to necrosis of the mucosal epithelial cells.
Gastritis can cause contraction of gastric smooth muscle which causes spasms and pain. Vomiting is also a symptom following stimulation of nerve endings that connect with the vomiting centre.
Signalment
Dogs are more commonly affected than cats due to their less selective eating habits.
Diagnosis
Acute gastritis is a diagnosis of exclusion based on physical examination findings, history of ingestion of causative substances and diagnostic tests.
Clinical Signs
Include acute vomiting (food, bile together with small amounts of blood may be present in the vomitus), anorexia, polydipsia, lethargy, depression and if severely affected dehydration.
Abdominal Palpation
Severely affected animals may show signs of discomfort on palpation of the cranial abdomen.
Laboratory Tests
Clinical pathology such as haematology and biochemistry can be used to rule out conditions such as uraemia, diabetic ketoacidosis, hypoadrenocorticism], hepatic disease, hypercalcaemia and pancreatitis.
Radiography
Abdominal radiographs may be taken if the animal is severely ill and to rule out other causes such as an alimentary foreign body or obstruction.
Endoscopy
Gastroscopy may be used to visualise gastric erosions/ulcers and hyperaemia.
Treatment
Many different techniques of treating acute gastritis have been described. In general, therapy is designed to rest the stomach by witholding food and maintaining the animal's fluid , electrolyte and acid/base balance.
Witholding food and water for 24 hours is usually sufficient to control vomiting in combination with parenteral fluid therapy to avoid dehydration. Small amounts of a bland diet such as boiled chicken and potato can be offered once the animal has not vomited for at least 12 hours. Gut protectants should be considered if the animal presents with haematemesis. Some examples of gastroprotective drugs include sucralfate which forms a protective barrier over the mucosal surface and also stimulates bicarbonate and mucus secretion and omeprazole which is a proton pump inhibitor that reduces gastric acid secretion.
Anti-emetics can be used but only if vomiting is causing pain or if unsustainable fluid and electrolyte losses occur.
Prognosis
The prognosis is excellent if fluid and electrolyte balance is maintained.
| Gastritis, Acute Learning Resources | |
|---|---|
To reach the Vetstream content, please select |
Canis, Felis, Lapis or Equis |
 Search for recent publications via CAB Abstract (CABI log in required) |
Acute gastritis publications |
References
Hall, E.J, Simpson, J.W. and Williams, D.A. (2005) BSAVA Manual of Canine and Feline Gastroenterology (2nd Edition) BSAVA
Merck & Co (2008) The Merck Veterinary Manual (Eighth Edition) Merial
| This article has been peer reviewed but is awaiting expert review. If you would like to help with this, please see more information about expert reviewing. |
Error in widget FBRecommend: unable to write file /var/www/wikivet.net/extensions/Widgets/compiled_templates/wrt69a234797c0606_46777620 Error in widget google+: unable to write file /var/www/wikivet.net/extensions/Widgets/compiled_templates/wrt69a23479820ac6_60753012 Error in widget TwitterTweet: unable to write file /var/www/wikivet.net/extensions/Widgets/compiled_templates/wrt69a23479903ad0_92659963
|
| WikiVet® Introduction - Help WikiVet - Report a Problem |