Difference between revisions of "Avian Vent and Cloaca - Anatomy & Physiology"
(→Links) |
Fiorecastro (talk | contribs) |
||
| (15 intermediate revisions by 3 users not shown) | |||
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
| − | == | + | {{OpenPagesTop}} |
| + | ==Overview== | ||
| + | |||
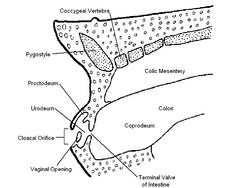
| + | The hindgut of the avian digestive system terminates in the '''cloaca'''. The external opening through which faecal matter and uric acid is excreted is called the '''vent'''. The shape of the vent varies depending on species. | ||
| + | [[Image:Avian Cloaca Diagram.jpg|thumb|right|250px|Avian Cloaca Diagram - Copyright RVC 2008]] | ||
| − | |||
| − | |||
==The Cloaca== | ==The Cloaca== | ||
| − | + | The '''[[Colon - Anatomy & Physiology|colon]]''', '''[[Ureters - Anatomy & Physiology|ureters]]''' and '''deferent ducts'''/'''left [[Avian Female Reproductive System#Oviduct|oviduct]]''' enter at various levels. It can be divided into the '''coprodeum''', '''urodeum''' and '''proctodeum''' by complete annular folds. Some urinary excretions arriving in the cloaca become incorporated with the ingesta and move in a retrograde fashion to the [[Caecum - Anatomy & Physiology|caeca]], increasing the absorption of water and electrolytes from the urinary waste. | |
| − | + | The '''coprodeum''' is the most cranial division of the cloaca. It is the continuation of the colon where faeces are stored. It is bounded by the '''coprourodeal fold'''. It can be stretched by the faecal pressure so the central opening is everted through the vent. | |
| − | + | The '''urodeum''' is the middle part of the cloaca. It is caudal to the '''proctodeum fold'''. It has the ureteric opening in the dorsolateral wall above the papilla of the deferent duct/[[Avian Female Reproductive System#Oviduct|oviduct]] opening. | |
| − | + | [[Image:Bursa of Fabricus.jpg|thumb|right|250px|Bursa of Fabricus - Copyright Nottingham 2008]] | |
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | + | The '''proctodeum''' is the caudal segment. It is short and ends at the vent. The opening in the dorsal wall leads to the cloacal '''bursa of Fabricus'''. | |
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
==The Vent== | ==The Vent== | ||
| − | + | The vent is a horizontal slit. It has the [[Avian Male Reproductive Tract - Anatomy & Physiology#Phallus|phallus]] of males on the internal surface of the ventral lip. During insemination, the vent is inverted. | |
| − | + | ==Histology== | |
| − | + | The avian vent and cloaca consist of columnar epithelium. Stratified squamous epithelium are present at the external opening of the vent and in the '''caudal proctodeum'''. There are broad folds of mucous membrane forming crypts, which branch near their base. Lymphoid tissue is present in the submucosa. The fold of mucous membrane covering the entrance to the bursa is composed of columnar epithelium, muscle, connective tissue and goblet cells. There are two layers of tunica muscularis; '''inner circular''' and '''outer longitudinal'''. | |
| − | |||
| − | |||
==Species Differences== | ==Species Differences== | ||
| − | + | '''Galliformes''' (turkeys and chickens) can move urates from the urinary tract into the [[Colon - Anatomy & Physiology|colon]] and [[Caecum - Anatomy & Physiology|caeca]] where ammonia is released for protein synthesis. A small membrane covers the opening of the [[Avian Female Reproductive System #Oviduct|oviduct]] into the cloaca in '''ducks''', '''geese''' and '''swans''' until sexual maturity. | |
| − | + | ==Links== | |
| − | |||
| − | == | ||
| − | [[ | + | '''Click here for information on the [[Bursa of Fabricius - Anatomy & Physiology|Bursa of Fabricus]]''' |
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | [[ | + | {{Template:Learning |
| + | |flashcards = [[The Avian Alimentary Tract - Anatomy & Physiology - Flashcards|Avian Alimentary Tract]] | ||
| + | }} | ||
| + | ==Webinars== | ||
| + | <rss max="10" highlight="none">https://www.thewebinarvet.com/internal-medicine/webinars/feed</rss> | ||
[[Category:Avian Alimentary System - Anatomy & Physiology]] | [[Category:Avian Alimentary System - Anatomy & Physiology]] | ||
| + | [[Category:Avian Reproduction]] | ||
| + | [[Category:A&P Done]] | ||
Latest revision as of 20:02, 2 November 2022
Overview
The hindgut of the avian digestive system terminates in the cloaca. The external opening through which faecal matter and uric acid is excreted is called the vent. The shape of the vent varies depending on species.
The Cloaca
The colon, ureters and deferent ducts/left oviduct enter at various levels. It can be divided into the coprodeum, urodeum and proctodeum by complete annular folds. Some urinary excretions arriving in the cloaca become incorporated with the ingesta and move in a retrograde fashion to the caeca, increasing the absorption of water and electrolytes from the urinary waste.
The coprodeum is the most cranial division of the cloaca. It is the continuation of the colon where faeces are stored. It is bounded by the coprourodeal fold. It can be stretched by the faecal pressure so the central opening is everted through the vent.
The urodeum is the middle part of the cloaca. It is caudal to the proctodeum fold. It has the ureteric opening in the dorsolateral wall above the papilla of the deferent duct/oviduct opening.
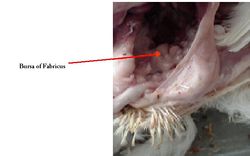
The proctodeum is the caudal segment. It is short and ends at the vent. The opening in the dorsal wall leads to the cloacal bursa of Fabricus.
The Vent
The vent is a horizontal slit. It has the phallus of males on the internal surface of the ventral lip. During insemination, the vent is inverted.
Histology
The avian vent and cloaca consist of columnar epithelium. Stratified squamous epithelium are present at the external opening of the vent and in the caudal proctodeum. There are broad folds of mucous membrane forming crypts, which branch near their base. Lymphoid tissue is present in the submucosa. The fold of mucous membrane covering the entrance to the bursa is composed of columnar epithelium, muscle, connective tissue and goblet cells. There are two layers of tunica muscularis; inner circular and outer longitudinal.
Species Differences
Galliformes (turkeys and chickens) can move urates from the urinary tract into the colon and caeca where ammonia is released for protein synthesis. A small membrane covers the opening of the oviduct into the cloaca in ducks, geese and swans until sexual maturity.
Links
Click here for information on the Bursa of Fabricus
| Avian Vent and Cloaca - Anatomy & Physiology Learning Resources | |
|---|---|
 Test your knowledge using flashcard type questions |
Avian Alimentary Tract |
Webinars
Failed to load RSS feed from https://www.thewebinarvet.com/internal-medicine/webinars/feed: Error parsing XML for RSS