Difference between revisions of "Immunoglobulin M"
Rjfrancisrvc (talk | contribs) |
Rjfrancisrvc (talk | contribs) |
||
| Line 3: | Line 3: | ||
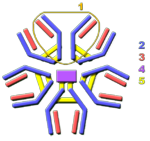
[[Image:LH IgM.png|thumb|150px|right|'''IgM'''<p>1 = IgM monomer</p><p>2 = Heavy chains</p><p>3 = Light chains</p><p>4 =J chain</p><p>5 = Disulfide bonds</p>]] | [[Image:LH IgM.png|thumb|150px|right|'''IgM'''<p>1 = IgM monomer</p><p>2 = Heavy chains</p><p>3 = Light chains</p><p>4 =J chain</p><p>5 = Disulfide bonds</p>]] | ||
[[Image:IgM.jpg|thumb|right|150px|IgM - B. Catchpole, RVC 2008]] | [[Image:IgM.jpg|thumb|right|150px|IgM - B. Catchpole, RVC 2008]] | ||
| − | <p>Is found in high concentrations in blood plasma (below [[IgG]] conc.) and is the major Ig produced during primary immune response</p> | + | ==Overview== |
| + | <p>Is found in high concentrations in blood plasma (below [[IgG]] conc.) and is the major Ig produced, by [[B cell differentiation|plasma cells]], during the primary immune response</p> | ||
| + | |||
==Structure== | ==Structure== | ||
<p>IgM is the primordial antibody and, although a monomer, is secreted as a pentamer (five monomers joined by disulphide bonds with two monomers joined by a J chain). This gives it ten identical antigen binding sites although IgM usually has relatively low affinity for its antigen. Its heavy chain is type mu (µ).</p> | <p>IgM is the primordial antibody and, although a monomer, is secreted as a pentamer (five monomers joined by disulphide bonds with two monomers joined by a J chain). This gives it ten identical antigen binding sites although IgM usually has relatively low affinity for its antigen. Its heavy chain is type mu (µ).</p> | ||
==Production== | ==Production== | ||
| − | <p>Produced by plasma cells in the spleen, bone marrow and lymph nodes. Since it is around five times larger than "normal" antibody it does not diffuse quickly or enter tissues readily and as such its concentration in extracellular fluid and lymph is very low. | + | <p>Produced by plasma cells in the spleen, bone marrow and lymph nodes. Since it is around five times larger than "normal" antibody it does not diffuse quickly or enter tissues readily and as such its concentration in extracellular fluid and lymph is very low. It does not cross the placenta even in animals with haemochorial placentas e.g. apes. </p> |
| − | It does not cross the placenta even in animals with haemochorial placentas e.g. apes. </p> | + | <p>IgM is the first class of antibody produced by plasma cells, with production replaced by either [[IgG]] or [[IgE]] in a process known as '''[[Immunoglogulin Overview|class-switching]]''' once the secondary immune response is initiated </p> |
==Function== | ==Function== | ||
<p> | <p> | ||
| − | IgM mainly functions as a target for [[Complement|complement]] activation as well as roles in agglutination, opsonisation and virus | + | IgM mainly functions as a target for [[Complement|complement]] activation as well as roles in agglutination, opsonisation and virus neutralisation.</p> |
<br> | <br> | ||
---- | ---- | ||
Revision as of 10:09, 25 May 2012
| This article has been peer reviewed but is awaiting expert review. If you would like to help with this, please see more information about expert reviewing. |
Shortened to IgM
Overview
Is found in high concentrations in blood plasma (below IgG conc.) and is the major Ig produced, by plasma cells, during the primary immune response
Structure
IgM is the primordial antibody and, although a monomer, is secreted as a pentamer (five monomers joined by disulphide bonds with two monomers joined by a J chain). This gives it ten identical antigen binding sites although IgM usually has relatively low affinity for its antigen. Its heavy chain is type mu (µ).
Production
Produced by plasma cells in the spleen, bone marrow and lymph nodes. Since it is around five times larger than "normal" antibody it does not diffuse quickly or enter tissues readily and as such its concentration in extracellular fluid and lymph is very low. It does not cross the placenta even in animals with haemochorial placentas e.g. apes.
IgM is the first class of antibody produced by plasma cells, with production replaced by either IgG or IgE in a process known as class-switching once the secondary immune response is initiated
Function
IgM mainly functions as a target for complement activation as well as roles in agglutination, opsonisation and virus neutralisation.
| Originally funded by the RVC Jim Bee Award 2007 |