Difference between revisions of "Immune Responses to Viral Infections"
Rjfrancisrvc (talk | contribs) |
|||
| (8 intermediate revisions by the same user not shown) | |||
| Line 3: | Line 3: | ||
==Innate immunity== | ==Innate immunity== | ||
This becomes active during the early stages of infection. Defences include: | This becomes active during the early stages of infection. Defences include: | ||
| − | *Interferon (IFN)- typically stimulates the inhibition of viral replication. There are three known types: | + | *[[Cytokines|Interferon (IFN)]] - typically stimulates the inhibition of viral replication. There are three known types: |
| − | **Infection of a cell by a virus stimulates production of IFN- | + | **Infection of a cell by a virus stimulates production of IFN-α and IFN-β, which activate genes in neighbouring cells. One of these genes, for example, codes for a protein kinase that blocks translation of proteins. Another activates an endonuclease that degrades viral RNA. |
**IFN-γ increases the expression of MHC I and II, enhancing the function of the adaptive immune response. It also activates macrophages and NK cells. | **IFN-γ increases the expression of MHC I and II, enhancing the function of the adaptive immune response. It also activates macrophages and NK cells. | ||
| − | *Natural killer (NK) cells- one of the main mediators of antibody-dependent cell-mediated cytotoxicity | + | *[[Natural Killer cells|Natural killer (NK) cells]] - one of the main mediators of antibody-dependent cell-mediated cytotoxicity |
*For more on [[Innate Immunity to Viruses|Innate immunity to viruses]], see here. | *For more on [[Innate Immunity to Viruses|Innate immunity to viruses]], see here. | ||
| Line 13: | Line 13: | ||
[[Image:B Cell viral response.jpg|thumb|right|200px|B Cell Immunity to Viruses - B. Catchpole, RVC 2008]] | [[Image:B Cell viral response.jpg|thumb|right|200px|B Cell Immunity to Viruses - B. Catchpole, RVC 2008]] | ||
| − | *Antibodies- these are particularly important in preventing the spread of the virus in the bloodstream | + | *[[Immunoglobulins|Antibodies]] - these are particularly important in preventing the spread of the virus in the bloodstream |
**[[IgA]] production is increased at mucosal surfaces- helps prevent reinfection | **[[IgA]] production is increased at mucosal surfaces- helps prevent reinfection | ||
**Although antibodies that target any viral protein can be produced, only those directed against proteins found in the virion envelope or infected cell membrane will be effective | **Although antibodies that target any viral protein can be produced, only those directed against proteins found in the virion envelope or infected cell membrane will be effective | ||
**When targeted against free virus particles, antibodies are effective at preventing them binding and entering the cell and uncoating. | **When targeted against free virus particles, antibodies are effective at preventing them binding and entering the cell and uncoating. | ||
| − | **When targeting virus-infected cells, they aid antibody-dependent cell-mediated cytotoxicity by NK cells, macrophages and [[Neutrophils|neutrophils]] | + | **When targeting virus-infected cells, they aid antibody-dependent cell-mediated cytotoxicity by NK cells, [[Macrophages|macrophages]] and [[Neutrophils|neutrophils]] |
| − | *Complement- although not considered a major factor in defence against viruses, complement is able to damage the virion envelope (virolysis) | + | *[[Complement]] - although not considered a major factor in defence against viruses, complement is able to damage the virion envelope (virolysis) |
**Coupled with antibody, complement is also able to: | **Coupled with antibody, complement is also able to: | ||
***block the virus receptor | ***block the virus receptor | ||
| Line 25: | Line 25: | ||
***aid opsonisation of free virus or infected cells for phagocytosis | ***aid opsonisation of free virus or infected cells for phagocytosis | ||
[[Image:T Cell viral response.jpg|thumb|right|200px|T Cell Immunity to Viruses - B. Catchpole, RVC 2008]] | [[Image:T Cell viral response.jpg|thumb|right|200px|T Cell Immunity to Viruses - B. Catchpole, RVC 2008]] | ||
| − | *T cells | + | *[[T cells]] |
| − | **CD8+ cytotoxic T cells are particularly important as nearly all the cells in the body express MHC class I. They tend to focus at the site of viral replication and destroy virus-infected cells. | + | **CD8<sup>+</sup> cytotoxic T cells are particularly important as nearly all the cells in the body express MHC class I. They tend to focus at the site of viral replication and destroy virus-infected cells. |
| − | **CD4+ T cells are important in the recruitment of macrophages, using cytokines such as IFN-γ and TNF, and the induction of CD8+ cytotoxic T cells | + | **CD4<sup>+</sup> T cells are important in the recruitment of macrophages, using cytokines such as IFN-γ and TNF, and the induction of CD8<sup>+</sup> cytotoxic T cells |
| − | **The presence of CD4+ T cells is also vital for the antibody response, i.e. class-switching and affinity development | + | **The presence of CD4<sup>+</sup> T cells is also vital for the antibody response, i.e. class-switching and affinity development |
*For more on the adaptive response to viruses, see [[Adaptive Immunity to Viruses]] | *For more on the adaptive response to viruses, see [[Adaptive Immunity to Viruses]] | ||
Latest revision as of 09:40, 24 May 2012
Introduction
Innate immunity
This becomes active during the early stages of infection. Defences include:
- Interferon (IFN) - typically stimulates the inhibition of viral replication. There are three known types:
- Infection of a cell by a virus stimulates production of IFN-α and IFN-β, which activate genes in neighbouring cells. One of these genes, for example, codes for a protein kinase that blocks translation of proteins. Another activates an endonuclease that degrades viral RNA.
- IFN-γ increases the expression of MHC I and II, enhancing the function of the adaptive immune response. It also activates macrophages and NK cells.
- Natural killer (NK) cells - one of the main mediators of antibody-dependent cell-mediated cytotoxicity
- For more on Innate immunity to viruses, see here.
Adaptive immunity
The importance of the adaptive immune system in responding to viral infections can be demonstrated using athymic 'nude' mice, which lack mature T cells. These mice show particular vulnerability to the herpes simplex virus, resulting in death when infection reaches the CNS. However transfer of antigen-specific T cells to the mice shortly after infection leads to recovery.
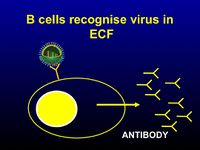
- Antibodies - these are particularly important in preventing the spread of the virus in the bloodstream
- IgA production is increased at mucosal surfaces- helps prevent reinfection
- Although antibodies that target any viral protein can be produced, only those directed against proteins found in the virion envelope or infected cell membrane will be effective
- When targeted against free virus particles, antibodies are effective at preventing them binding and entering the cell and uncoating.
- When targeting virus-infected cells, they aid antibody-dependent cell-mediated cytotoxicity by NK cells, macrophages and neutrophils
- Complement - although not considered a major factor in defence against viruses, complement is able to damage the virion envelope (virolysis)
- Coupled with antibody, complement is also able to:
- block the virus receptor
- aid lysis of infected cells
- aid opsonisation of free virus or infected cells for phagocytosis
- Coupled with antibody, complement is also able to:
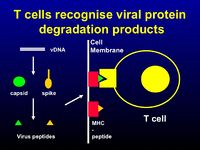
- T cells
- CD8+ cytotoxic T cells are particularly important as nearly all the cells in the body express MHC class I. They tend to focus at the site of viral replication and destroy virus-infected cells.
- CD4+ T cells are important in the recruitment of macrophages, using cytokines such as IFN-γ and TNF, and the induction of CD8+ cytotoxic T cells
- The presence of CD4+ T cells is also vital for the antibody response, i.e. class-switching and affinity development
- For more on the adaptive response to viruses, see Adaptive Immunity to Viruses
Immunopathology
Tissue damage can result from the response to viral infection:
- Immune complexes, such as those formed during chronic infections (e.g. hepatitis B), can be deposited in the kidneys or blood vessels. Here they can induce an inflammatory response, such as glomerulonephritis
- In a process mediated by the high-affinity Fc receptor, complexes can be taken up by macrophages, enhancing viral infectivity. This phenomenon is seen in Dengue virus infections (implicated as the cause of Dengue haemorrhagic fever)
- The activity of cytotoxic T cells can cause widespread damage resulting in death, e.g. the response to lymphocytic choriomeningitis (LCM) virus in the CNS
- Viruses can infect cells of the immune system, where they may persist indefinitely. Occasionally, this infection may cause pathology, e.g. the death of T cells and macrophages in HIV, or neoplasia of B cells caused by the Epstein-Barr virus
- Viruses may also induce autoimmunity:
- Damage to tissues caused by viruses may expose 'hidden' self-antigens that provoke an inflammatory response, e.g. murine Theiler's virus, in which myelin in the CNS is targeted
- Viral antigens that are very similar to self-antigens are recognised and both proteins are targeted
Viral Evasion of Immune Defence Mechanisms
- Antigenic variation- by mutating regions of the proteins that are normally targeted by antibodies, viruses can produce new strains that avoid immune recognition, e.g. antigenic drift and shift seen in influenza
- The herpes simplex viruses encode glycoproteins with IgG-Fc binding sites, interfering with complement activation
- Some viruses inhibit the transport of MHC class I to the cell surface, avoiding cytotoxic T cell responses, e.g. adenovirus
- By producing small strands of RNA, viruses such as the Epstein-Barr virus are able to inhibit the action of interferon by blocking protein kinase activation
Prevention and control
Antibiotics cannot treat viral infection. While anti-viral therapies do exist, they are costly and often ineffective. The alternatives, therefore, include vaccination (priming the immune response to create memory lymphocytes for a particular virus) or eradication.