Difference between revisions of "Aspergillosis"
Jump to navigation
Jump to search
BaraStudent (talk | contribs) (→Birds) |
|||
| (75 intermediate revisions by 6 users not shown) | |||
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
| − | + | Caused by [[Aspergillus spp.]] | |
| − | |||
| − | + | *Avians: | |
| − | + | **Diffuse infection of the [[Avian Respiration - Anatomy & Physiology#Air Sacs|air sacs]] | |
| + | **Diffuse pneumonic form | ||
| + | **Nodular form involving the [[Avian Respiration - Anatomy & Physiology#Avian Lungs|lungs]] | ||
| + | **Spores are inhaled | ||
| + | **Yellow nodules in the [[Avian Respiration - Anatomy & Physiology#Avian Lungs|lungs]] and [[Avian Respiration - Anatomy & Physiology#Air Sacs|air sacs]] | ||
| + | **The acute form usually affects young birds and is rapidly fatal (within 24-48 hours) | ||
| + | ***Signs include [[Diarrhoea|diarrhoea]], listlessness, pyrexia, loss of appetite and loss of condition | ||
| + | ***Sometimes convulsions may occur | ||
| + | ***Resembles Pullorum disease | ||
| + | **The chronic form usually occurs in adult birds and is sporadic, presenting with milder clinical signs | ||
| + | {| align="right" | ||
| + | |<gallery>Image:Aspergillus swan.jpg|<center><p>'''Aspergillus in a swan'''</p><sup>Copyright Professor Andrew N. Rycroft, BSc, PHD, C. Biol.F.I.Biol., FRCPath</sup></center></gallery> | ||
| + | |} | ||
| + | *Cattle: | ||
| + | **Infection can cause abortion and ocular infections | ||
| + | **Infections involve the [[Female Reproductive Tract -The Uterus - Anatomy & Physiology|uterus]], [[Foetal Membranes - Anatomy & Physiology|fetal membranes]] and fetal skin | ||
| + | **Lesions are usually up to 2mm in diameter and contain asteroid bodies with a germinated spore in the centre | ||
| + | ***Acute infection causes miliary lesions | ||
| + | ***Chronic infections causes granulomatous and calcified lesions | ||
| − | + | *Horses: | |
| − | + | **[[Guttural Pouches Inflammatory - Pathology|Guttural pouch mycosis]] common | |
| + | **Infection can cause abortion | ||
| + | **May cause [[Bronchi and Bronchioles Inflammatory - Pathology#Chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (COPD)|COPD]] | ||
| − | + | *Dogs, cats and sheep: | |
| + | **Infections occur, but infrequently | ||
| + | **[[Lungs - Anatomy & Physiology|lungs]] and [[Nasal cavity - Anatomy & Physiology|nasal cavity]] most usually affected | ||
| + | **Disseminated form with granulomas and infarcts can occur in dogs | ||
| + | **Pulmonary and intersitital forms can occur in cats | ||
| + | {| align="right" | ||
| + | |<gallery>Image:Aspergillus in vivo.jpg|<center><p>'''Aspergillus in vivo'''</p><sup>Copyright Professor Andrew N. Rycroft, BSc, PHD, C. Biol.F.I.Biol., FRCPath</sup></center></gallery> | ||
| + | |} | ||
| + | *Humans: | ||
| + | **Primary and secondary infections | ||
| + | **[[Lungs - Anatomy & Physiology|lungs]], [[Skin - Anatomy & Physiology|skin]], [[Nasal cavity - Anatomy & Physiology|nasal sinuses]], [[Ear - Anatomy & Physiology#Outer Ear|external ear]], [[Bronchi and bronchioles - Anatomy & Physiology|bronchi]], [[Bones and Cartilage - Anatomy & Physiology|bones]] and meninges all affected | ||
| + | **Infection occurs most frequently in immunocompromised patients | ||
| − | + | *Grows on Sabauraud's Dextrose and Blood agar | |
| − | + | **White colonies intitially which turn green, then dark green, flat and velvety | |
| − | + | **Colony colour varies with species | |
| − | + | *Also grows on Czapek-Dox agar and 2% malt extract agar supplemented with antibacterial antibiotics | |
| − | + | *Microscopically: | |
| − | + | **Conidiophores with large terminal vesicles (only visible in the [[Lungs - Anatomy & Physiology|lungs]] and air sacs where there is access to oxygen) | |
| + | ***Vesicle shape varies depending on the species | ||
| + | **Is a common contaminant so repeated tests should be done for a definitive diagnosis | ||
| − | + | *Serology: | |
| − | + | **Gel immunodiffusion for canine nasal asper | |
| − | + | *Treatment: | |
| − | + | **Surgery | |
| + | **Antifungal drugs | ||
| + | ***[[Antifungal Drugs#The Azoles|Ketoconazole]], [[Antifungal Drugs#Polyene Antifungals|Nystatin]], [[Antifungal Drugs#Polyene Antifungals|Amphotericin B]], [[Antifungal Drugs#Flucytosine|5-fluorocytosine]], [[Antifungal Drugs#The Azoles|Thiabendazole]] | ||
| − | + | *Pathology: | |
| − | + | **''Aspergillus fumigatus'' causes [[Nasal Cavity Inflammatory - Pathology#Infectious causes of rhinitis|rhinitis]], [[Respiratory Fungal Infections - Pathology#|respiratory tract inflammation]] and [[Paranasal Sinuses Inflammatory - Pathology#Infectious causes of sinusitis|sinusitis]] | |
| − | ''' | + | **Sometimes appears on [[Nasal Cavity Hyperplastic and Neoplastic - Pathology#Progressive ethmoidal haematoma|lesions of ethmoidal haematoma]] |
| − | + | {| align="center" | |
| − | + | |<gallery>Image:Aspergillus sporing heads.jpg|<center><p>'''Aspergillus sporing heads'''</p><sup>Copyright Professor Andrew N. Rycroft, BSc, PHD, C. Biol.F.I.Biol., FRCPath</sup></center> | |
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | { | ||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | | | ||
| − | | | ||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | <gallery> | ||
| − | |||
| − | Image:Aspergillus sporing heads.jpg|<center><p>'''Aspergillus sporing heads'''</p><sup>Copyright Professor Andrew N. Rycroft, BSc, PHD, C. Biol.F.I.Biol., FRCPath</sup></center> | ||
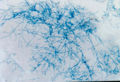
Image:Mycelium aspergillus quink.jpg|<center><p>'''Aspergillus mycelium stained with blue/black Quink'''</p><sup>Copyright Professor Andrew N. Rycroft, BSc, PHD, C. Biol.F.I.Biol., FRCPath</sup></center> | Image:Mycelium aspergillus quink.jpg|<center><p>'''Aspergillus mycelium stained with blue/black Quink'''</p><sup>Copyright Professor Andrew N. Rycroft, BSc, PHD, C. Biol.F.I.Biol., FRCPath</sup></center> | ||
Image:Mycotic abortion asper 1.jpg|<center><p>'''Mycotic Abortion caused by Aspergillus'''</p><sup>Copyright Professor Andrew N. Rycroft, BSc, PHD, C. Biol.F.I.Biol., FRCPath</sup></center> | Image:Mycotic abortion asper 1.jpg|<center><p>'''Mycotic Abortion caused by Aspergillus'''</p><sup>Copyright Professor Andrew N. Rycroft, BSc, PHD, C. Biol.F.I.Biol., FRCPath</sup></center> | ||
| Line 72: | Line 70: | ||
Image:Mycotic abortion asper 3.jpg|<center><p>'''Mycotic Abortion caused by Aspergillus'''</p><sup>Copyright Professor Andrew N. Rycroft, BSc, PHD, C. Biol.F.I.Biol., FRCPath</sup></center> | Image:Mycotic abortion asper 3.jpg|<center><p>'''Mycotic Abortion caused by Aspergillus'''</p><sup>Copyright Professor Andrew N. Rycroft, BSc, PHD, C. Biol.F.I.Biol., FRCPath</sup></center> | ||
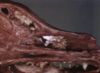
Image:Nasal Aspergillus.jpg|<center><p>'''Nasal Aspergillus'''</p><sup>Copyright Professor Andrew N. Rycroft, BSc, PHD, C. Biol.F.I.Biol., FRCPath</sup></center> | Image:Nasal Aspergillus.jpg|<center><p>'''Nasal Aspergillus'''</p><sup>Copyright Professor Andrew N. Rycroft, BSc, PHD, C. Biol.F.I.Biol., FRCPath</sup></center> | ||
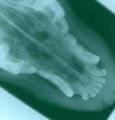
| − | Image: | + | Image:Canine nasal asper radiograph.jpg|<center><p>'''Canine nasal aspergillus radiograph'''</p><sup>Copyright Professor Andrew N. Rycroft, BSc, PHD, C. Biol.F.I.Biol., FRCPath</sup></center></gallery> |
| − | Image:Aspergillus | + | |} |
| − | </ | + | |
| + | ===''Aspergillus fumigatus''=== | ||
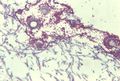
| + | [[Image:Aspergillus pneumonia of cattle.jpg|right|thumb|100px|<small><center>Aspergillus hyphae in cattle lung (Image sourced from Bristol Biomed Image Archive with permission)</center></small>]] | ||
| + | [[Image:Aspergillosis in nasal cavity.jpg|right|thumb|100px|<small><center>Nasal aspergillosis (Image sourced from Bristol Biomed Image Archive with permission)</center></small>]] | ||
| − | + | *[[Aspergillus spp.|''Aspergillus fumigatus'']] | |
| − | * | + | *Most commonly in dogs but also other species |
| − | * | + | *Causes [[Nasal Cavity Inflammatory - Pathology#Infectious causes of rhinitis|rhinitis]], often also involves the [[Paranasal Sinuses Inflammatory - Pathology#Infectious causes of sinusitis|frontal sinus]] |
| − | * | + | *Chronic necrotising inflammation with friable exudate containing necrotic tissue and fungal hyphae |
| − | * | + | * Result in severe neutrophilic [[Nasal Cavity Inflammatory - Pathology|rhinitis]]/[[Paranasal Sinuses Inflammatory - Pathology|sinusitis]] |
| − | * | + | *These lesions can be aggressive causing destruction of turbinates and nasal septum |
| − | * | + | *Can occur secondary to areas of mucosal compromise eg: adjacent to a space-occupying lesion |
| + | *Can cause pulmonary aspergillosis especially in '''birds''', but also other animals | ||
| + | **Initiated by inhalation of spores,the most likely source of which is mouldy feed and bedding | ||
| + | **Given the wide exposure that occurs, it is thought that immunodeficiency may contribute to colonisation with this organism | ||
| + | **Gross lesions : | ||
| + | ***Multiple discrete grey/ white nodules which develop around fungal colonies | ||
| + | ***Blood vessels can become involved in the lesions -> invasion, haemorrhage or thrombosis | ||
| + | **Histologically: | ||
| + | ***Granulomatous chronic lesions | ||
| + | ***Macrophages and epithelioid cells | ||
| + | ***Fibrous capsule | ||
| + | *In horses: | ||
| + | **[[Nasal Cavity Inflammatory - Pathology#Infectious causes of rhinitis|Nasal aspergillosis]] | ||
| + | **[[Guttural Pouches Inflammatory - Pathology|Guttural pouch infections]] in horses - fungal plaques form on the adventitia of the carotid arteries can lead to catastrophic haemorrhage following erosion of carotid arteries! | ||
| + | **Often present with [[Respiratory System Clinical Signs - Pathology#Epistaxis|epistaxis]] | ||
| + | **May present with neurological dysfunction | ||
| + | **Rarely extends to other resions: cranium, middle ear, atlanto-occipital joint | ||
| + | **May extend to [[Paranasal Sinuses Inflammatory - Pathology#Infectious causes of sinusitis|sinuses]] | ||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | [[Category: | + | [[Category:To_Do_-_Clinical]] |
| − | |||
Revision as of 14:29, 30 June 2010
Caused by Aspergillus spp.
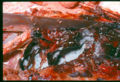
- Avians:
- Diffuse infection of the air sacs
- Diffuse pneumonic form
- Nodular form involving the lungs
- Spores are inhaled
- Yellow nodules in the lungs and air sacs
- The acute form usually affects young birds and is rapidly fatal (within 24-48 hours)
- Signs include diarrhoea, listlessness, pyrexia, loss of appetite and loss of condition
- Sometimes convulsions may occur
- Resembles Pullorum disease
- The chronic form usually occurs in adult birds and is sporadic, presenting with milder clinical signs
- Cattle:
- Infection can cause abortion and ocular infections
- Infections involve the uterus, fetal membranes and fetal skin
- Lesions are usually up to 2mm in diameter and contain asteroid bodies with a germinated spore in the centre
- Acute infection causes miliary lesions
- Chronic infections causes granulomatous and calcified lesions
- Horses:
- Guttural pouch mycosis common
- Infection can cause abortion
- May cause COPD
- Dogs, cats and sheep:
- Infections occur, but infrequently
- lungs and nasal cavity most usually affected
- Disseminated form with granulomas and infarcts can occur in dogs
- Pulmonary and intersitital forms can occur in cats
- Humans:
- Primary and secondary infections
- lungs, skin, nasal sinuses, external ear, bronchi, bones and meninges all affected
- Infection occurs most frequently in immunocompromised patients
- Grows on Sabauraud's Dextrose and Blood agar
- White colonies intitially which turn green, then dark green, flat and velvety
- Colony colour varies with species
- Also grows on Czapek-Dox agar and 2% malt extract agar supplemented with antibacterial antibiotics
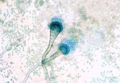
- Microscopically:
- Conidiophores with large terminal vesicles (only visible in the lungs and air sacs where there is access to oxygen)
- Vesicle shape varies depending on the species
- Is a common contaminant so repeated tests should be done for a definitive diagnosis
- Conidiophores with large terminal vesicles (only visible in the lungs and air sacs where there is access to oxygen)
- Serology:
- Gel immunodiffusion for canine nasal asper
- Treatment:
- Surgery
- Antifungal drugs
- Pathology:
- Aspergillus fumigatus causes rhinitis, respiratory tract inflammation and sinusitis
- Sometimes appears on lesions of ethmoidal haematoma
Aspergillus fumigatus
- Aspergillus fumigatus
- Most commonly in dogs but also other species
- Causes rhinitis, often also involves the frontal sinus
- Chronic necrotising inflammation with friable exudate containing necrotic tissue and fungal hyphae
- Result in severe neutrophilic rhinitis/sinusitis
- These lesions can be aggressive causing destruction of turbinates and nasal septum
- Can occur secondary to areas of mucosal compromise eg: adjacent to a space-occupying lesion
- Can cause pulmonary aspergillosis especially in birds, but also other animals
- Initiated by inhalation of spores,the most likely source of which is mouldy feed and bedding
- Given the wide exposure that occurs, it is thought that immunodeficiency may contribute to colonisation with this organism
- Gross lesions :
- Multiple discrete grey/ white nodules which develop around fungal colonies
- Blood vessels can become involved in the lesions -> invasion, haemorrhage or thrombosis
- Histologically:
- Granulomatous chronic lesions
- Macrophages and epithelioid cells
- Fibrous capsule
- In horses:
- Nasal aspergillosis
- Guttural pouch infections in horses - fungal plaques form on the adventitia of the carotid arteries can lead to catastrophic haemorrhage following erosion of carotid arteries!
- Often present with epistaxis
- May present with neurological dysfunction
- Rarely extends to other resions: cranium, middle ear, atlanto-occipital joint
- May extend to sinuses