Difference between revisions of "Respiratory Bacterial Infections - Pathology"
Jump to navigation
Jump to search
| Line 141: | Line 141: | ||
*Synonym: '''Shipping fever''' | *Synonym: '''Shipping fever''' | ||
| − | *Caused by [[ | + | *Caused by [[Mannheimia haemolytica|''Manheimia haemolytica'' biotype A serotype 1 (90%)]] and ''[[Pasteurella multocida]]'' |
*In young, growing cattle | *In young, growing cattle | ||
*In clinically normal cattle ''Mann. haemolytica'' serotype 2 is present in low numbers, only in nasal cavity and tonsils | *In clinically normal cattle ''Mann. haemolytica'' serotype 2 is present in low numbers, only in nasal cavity and tonsils | ||
| Line 217: | Line 217: | ||
***[[Respiratory Viral Infections - Pathology#Infectious bovine rhinotracheitis (IBR)|Bovine herpes viruses]] | ***[[Respiratory Viral Infections - Pathology#Infectious bovine rhinotracheitis (IBR)|Bovine herpes viruses]] | ||
**Bacteria | **Bacteria | ||
| − | ***[[ | + | ***[[Mannheimia haemolytica|''Manheimia (Pasteurella) haemolytica'' serotype A1]] |
| − | ***[[Pasteurella | + | ***[[Pasteurella multocida|''Pasteurella multocida'']] |
***[[Arcanobacter pyogenes|''Arcanobacter pyogenes'']] | ***[[Arcanobacter pyogenes|''Arcanobacter pyogenes'']] | ||
***''[[Haemophilus somnus]]'' | ***''[[Haemophilus somnus]]'' | ||
| Line 258: | Line 258: | ||
===Enzootic pneumonia of lambs=== | ===Enzootic pneumonia of lambs=== | ||
| − | *Caused by [[ | + | *Caused by [[Mannheimia haemolytica|''Pasteurella (Manheimia) haemolytica'']], possibly together with [[:Category:Mycoplasmas|''Mycoplasma ovipneumoniae'']] |
*Mainly in late spring/early summer after environmental stress i.e. handling or moving | *Mainly in late spring/early summer after environmental stress i.e. handling or moving | ||
*May be acute with producing a fibrinonecrotic [[Bronchi and Bronchioles Inflammatory - Pathology#Infectious causes of bronchitis or bronchiolitis|broncho]][[Lungs Inflammatory - Pathology#Infectious causes of pneumonia|pneumonia]] and associated [[Pleural Cavity & Membranes Inflammatory - Pathology|pleuritis]] | *May be acute with producing a fibrinonecrotic [[Bronchi and Bronchioles Inflammatory - Pathology#Infectious causes of bronchitis or bronchiolitis|broncho]][[Lungs Inflammatory - Pathology#Infectious causes of pneumonia|pneumonia]] and associated [[Pleural Cavity & Membranes Inflammatory - Pathology|pleuritis]] | ||
| Line 283: | Line 283: | ||
**''[[Bordetella bronchiseptica]]'' | **''[[Bordetella bronchiseptica]]'' | ||
***Appears to facilitate colonisation of nasal epithelium by the toxigenic ''Pasteurella'' | ***Appears to facilitate colonisation of nasal epithelium by the toxigenic ''Pasteurella'' | ||
| − | **Toxin-producing strain of [[Pasteurella | + | **Toxin-producing strain of [[Pasteurella multocida|''Pasteurella multocida'']] capsular type D (or sometimes A) |
| − | ''Pasteurella multocida'']] capsular type D (or sometimes A) | ||
***Experimental evidence shows that the toxin acts directly on bone cells of the nasal turbinates to cause bone loss, each pathogen can cause atrophy itself but greater damage when together | ***Experimental evidence shows that the toxin acts directly on bone cells of the nasal turbinates to cause bone loss, each pathogen can cause atrophy itself but greater damage when together | ||
*Exacerbated by adverse dietary and managemental factors | *Exacerbated by adverse dietary and managemental factors | ||
| Line 306: | Line 305: | ||
*2 forms of the disease | *2 forms of the disease | ||
**''''Progressive' atrophic rhinitis''' | **''''Progressive' atrophic rhinitis''' | ||
| − | ***Due to infection of the nasal turbinates by P.multocida strains carrying the toxA gene that encodes for an osteolytic toxin. [[Pasteurella | + | ***Due to infection of the nasal turbinates by P.multocida strains carrying the toxA gene that encodes for an osteolytic toxin. [[Pasteurella multocida|''P.multocida'']] adheres poorly to mucous membranes, and therefore requires a predisposing nasal insult to assist colonisation eg: co-infection with [[Bordetella bronchiseptica|''B.bronchiseptica'']] or [[Cytomegalovirus|Porcine cytomegalovirus (inclusion body rhinitis)]] |
***Turbinate bone atrophy is permanent and progressive | ***Turbinate bone atrophy is permanent and progressive | ||
**''''Non-progressive' atrophic rhinitis''' | **''''Non-progressive' atrophic rhinitis''' | ||
| Line 327: | Line 326: | ||
*Cough, reduced growth rate | *Cough, reduced growth rate | ||
*Attached to cilia - no [[Respiratory System General Introduction - Pathology#Mucociliary escalator|mucociliary clearance]] | *Attached to cilia - no [[Respiratory System General Introduction - Pathology#Mucociliary escalator|mucociliary clearance]] | ||
| − | *Usually non-fatal unless there is secondary infection (e.g. [[Pasteurella | + | *Usually non-fatal unless there is secondary infection (e.g. [[Pasteurella multocida|''Pasteurella multocida'']]) |
*Gross pathology: | *Gross pathology: | ||
**Confluent consolidation of the cranioventral lung lobes | **Confluent consolidation of the cranioventral lung lobes | ||
| Line 348: | Line 347: | ||
===Pasteurellosis in pigs=== | ===Pasteurellosis in pigs=== | ||
| − | *[[Pasteurella | + | *[[Pasteurella multocida|''Pasteurella multocida'']] can cause a severe acute fibrinous [[Bronchi and Bronchioles Inflammatory - Pathology#Infectious causes of bronchitis or bronchiolitis|broncho]][[Lungs Inflammatory - Pathology#Infectious causes of pneumonia|pneumonia]] in pigs |
*The most significant disease here is that caused by ''P. multocida'' secondary to underlying [[:Category:Mycoplasmas|''mycoplasma'' pneumonia]], see above [[Respiratory Bacterial Infections - Pathology#Enzootic pneumonia of pigs|enzootic pneumonia of pigs]] | *The most significant disease here is that caused by ''P. multocida'' secondary to underlying [[:Category:Mycoplasmas|''mycoplasma'' pneumonia]], see above [[Respiratory Bacterial Infections - Pathology#Enzootic pneumonia of pigs|enzootic pneumonia of pigs]] | ||
**This results in chronic suppurative [[Bronchi and Bronchioles Inflammatory - Pathology#Infectious causes of bronchitis or bronchiolitis|bronchopneumonia]] with abscessation and [[Pleural Cavity & Membranes Inflammatory - Pathology|pleuritis]] | **This results in chronic suppurative [[Bronchi and Bronchioles Inflammatory - Pathology#Infectious causes of bronchitis or bronchiolitis|bronchopneumonia]] with abscessation and [[Pleural Cavity & Membranes Inflammatory - Pathology|pleuritis]] | ||
| Line 385: | Line 384: | ||
===Snuffles=== | ===Snuffles=== | ||
| − | *Caused by [[Pasteurella | + | *Caused by [[Pasteurella multocida|''Pasteurella multocida'']], less commonly and/or ''[[Bordetella bronchiseptica]]'' |
*Clinical signs (nasal discharge, sneezing) result from an acute to chronic [[Nasal Cavity Inflammatory - Pathology|rhinitis]] | *Clinical signs (nasal discharge, sneezing) result from an acute to chronic [[Nasal Cavity Inflammatory - Pathology|rhinitis]] | ||
Revision as of 12:40, 14 May 2010
| This article has been peer reviewed but is awaiting expert review. If you would like to help with this, please see more information about expert reviewing. |
|
|
In general
- Main clinical expression is as secondary invaders of previously damaged lung tissue due to viral or parasitic involvement or environmental stress
- Some are initial pathogens in their own right while others can damage the tract allowing invasion by more pathogenic types
In Dogs
Infectious canine tracheitis
- See Infectious canine tracheitis
- Synonym: Kennel cough
- Multiple agents implicated
Tuberculosis in dogs
- Dogs are rarely susceptible to Mycobacterium spp. causing tuberculosis in cattle, usually either from human or farm animal source
- Gross pathology:
- Multifocal nodules, firm, calcified with necrotic centres
- Usually caudal lung lobes
- Also granulomatous pleuritis and haemothorax
Nocardiosis
- Caused by Nocardia
- Grossly:
- Haemorrhagic purulent exudate in pleural cavity
- Yellow granules on pleural surface
- Possibly caused by penetrating awns of grass
- Mainly in sporting breeds
In Cats
Feline Chlamydiosis
- Persistent respiratory infection caused by Chlamydia psittaci (felis)
- Mild conjunctivitis, serous purulent rhinitis and conjunctivitis, in severe cases mild bronchointerstitial pneumonia - feline pneumonitis
Mycoplasma felis
- Can also cause mild respiratory infection
In Horses
- Overview of equine respiratory disease by N Chanter of the Animal Health Trust, taken from Equine respiratory diseases edited by P Lekeux. Chapters of this book are published by the International Veterinary Information Service (IVIS)
Strangles
- Caused by very pathogenic Streptococcus equi subsp. equi
- Haemolytic streptococci of Lancefield group C are common inhabitants of the equine nasopharynx
- Streptococcus zooepidemicus and S. equisimilis are usually non-pathogenic
- Typically suppurative rhinitis, pharyngitis and lymphadenitis of the lymph nodes of the head and neck that drain the upper respiratory tract, these lymph nodes often rupture and discharge pus 2-3 weeks after the onset of infection
- Infection with Streptococcus equi occurs after contact with contaminated feed, water bowls or an infected carrier horse
- Organism remains viable in environment for months
- Possibility of other sources of infection - in pharynx of in-contact dogs?, guttural pouches of persistently infected horses
- Attaches to nasopharyngeal epithelial cells, then mucosa, lymphatics and lymph nodes
- Multiplies extra-cellularly
- Gross pathology
- Initial bilateral nasal discharge, serous becoming purulent
- Catarrhal conjunctivitis may be present
- Less frequently, complications can occur as follows :
- Purulent inflammation may extent to guttural pouches or lungs, sinusitis
- Bacteraemia with metastatic abscesses - most often to the mesenteric and mediastinal lymph nodes, less frequently, other organs such as liver, kidney and brain can be involved - Bastard strangles
- Retropharyngeal abscesses can rupture onto the skin of neck or into the guttural pouch resulting in guttural pouch empyema or chondroid formation - carrier state
- Purpura haemorrhagica: an acute vasculitis causing urticaria and extensive oedema of ventrum, head and distal limbs
- Laryngeal hemiplegia due to enlarged retropharyngeal lymph nodes
- Compression of cranial nerves
- Interview with Professors Josh Slater and Ken Smith providing an interesting insight into the pathogenesis, prevalence and possible prevention of Streptococcus equi infections in horses - listen to Strangles podcast
Streptococcus equi subsp. zooepidemicus
- Causative agent Streptococcus equi subsp. zooepidemicus
- Can infect the respiratory tract (nasal cavity, paranasal sinuses, trachea and bronchi/bronchioles)
- URT infection can be indistinguishable clinically from Strangles, but does not cause suppurative lymphadenitis (cf: S.equi subsp. equi)
Glanders
- Caused by Burkholderia (Pseudomonas) mallei
- Exists in eastern Europe and Asia
- Notifiable in UK
- Characterised by multiple small submucosal nasal nodules which liquefy and ulcerate
- Cores of neutrophils surrounded by a rim of macrophages and granulation tissue
- In addition may have similar nodules in lungs, lymph nodes and cutaneous lymphatics
- Clinical signs: fever and head/ neck lymphadenitis, rhinitis
Rhodococcus equi
- Causative agent Rhodococcus (Corynebacterium) equi
- Important cause of sever, often fatal granulomatous pneumonia in foals
- Clinical signs include depression, cough, weight loss, respiratory distress, diarrhoea, arthritis, subcutaneous abscesses
- Bacterium survives phagocytosis and multiplies
- Bacterial toxins -> caseous necrosis in lungs -> attracts inflammatory cells -> pyogranulomatous pneumonia
- Grossly:
- Multiple firm nodules, usually no encapsulation
- Partial atelectasis
- Histologically:
- Pyogranulomatous lesions
- Macrophages with ingested microorganisms in the alveoli
- Necrosis spreading through parenchyma
In Cattle
Necrotic laryngitis
- Synonyms: laryngeal diphtheria, calf diphtheria
- Common disease in cattle, and can occur in swine
- Caused by infection with Fusobacterium necrophorum
- Lesions may also be found in other parts of the oropharynx
- The bacterium usually gains entry through damaged mucosal surfaces e.g. after viral infections or injury following (poor!) use of dosing guns, coarse poor quality roughage
- Results in severe acute neutrophilic laryngitis
- Extensive accumulation of fibrin and necrotic cellular debris on the ulcerated mucosal surface
- Lesions appear as dry plaques of fibrinonecrotic exudate and ulceration on the laryngeal mucosa
- Inhalation of exudate and bacterial organisms may cause bronchopneumonia
- Death may result from toxaemia or asphyxiation
- Also may occur in pigs
CAR bacillus
- Causative agent: Cillia-associated respiratory bacillus
- An unclassified bacteria that can't be grown in culture
- Colonises ciliated epithelium in rodents and ruminants
- Associated with chronic lymphocytic rhinitis, tracheitis and bronchitis
- Clinical disease in rabbits and rodents
- Subclinical disease in ruminants
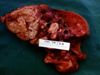
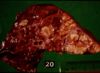
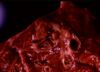
Pneumonic pasteurellosis
- Synonym: Shipping fever
- Caused by Manheimia haemolytica biotype A serotype 1 (90%) and Pasteurella multocida
- In young, growing cattle
- In clinically normal cattle Mann. haemolytica serotype 2 is present in low numbers, only in nasal cavity and tonsils
- Clinical signs: depression, anorexia, rapid shallow respiration, crusty nose with mucopurulent discharge, serous ocular discharge
- Acute bronchopneumonia and may progress to lobar pneumonia with toxaemia
- Pathology
- Lobar, cranioventral exudative pneumonia with fibrin, fibrinous pleuritis, areas of coagulative necrosis
- Histology
- Large numbers of bacteria are usually associated with necrotic lesions
Tuberculosis
- Caused by Mycobacterium bovis and M. tuberculosis
- Reside primarily within macrophages where they multiply and result in characteristic granulomatous inflammation (macrophages and giant cells, epithelioid cells)
- Cattle can be infected by inhalation of the organism or through milk
- The primary complex
- Describes the initial focus of infection at the portal of entry (lungs) plus involvement of regional lymph nodes
- 90% of cases exhibit the pulmonary form
- Grossly:
- Small tubercles in dorsocaudal subpleural areas which progress to larger confluent areas of caseous necrosis
- Usually start at bronchio-alveolar junction an progress to the alveoli
- Caseous lesions, may calcify or be encapsulated
- Multiple foci may coalesce
- Ulcers in trachea and bronchi due to coughed up bacteria
- Spreads into pleura
- Microscopically:
- Typical granulomatous inflammation
- Epitheliod and giant cells at centre of tubercles
- Macrophages with ingested bacteria, forming epithelioid cells - large vesicular nuclei, abundant pale cytoplasm
- Giant cells, formed by fusion of macrophages, with multiple nuclei
- Narrow layer of lymphocytes, mononuclear cells and plasma cells at the periphery of the tubercle
- With time, peripheral fibroplasia and central necrosis develop
- If the infection is not contained in the primary complex described above, the mycobacteria can disseminate via lymphatics to other organs and lymph nodes
- This can allow the development of miliary tuberculosis, i.e. numerous small foci of infection in many organs/ tissues
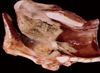
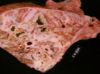
Contagious bovine pleuropneumonia (CBPP)
- Caused by Mycoplasma mycoides, small colony variant
- Causes a fibrinonecrotic pneumonia and fibrinous pleuritis
- Also affects caudodorsal areas
- Bronchopneumonia -> lobar pneumonia
- Sequestra are common
- NB: similarity to pneumonic pasteurellosis but CBPP has more pronounced marbled effect
- Interstitial septa are markedly widened by fibrinous exudate and the necrotic areas may have a fibrous capsule
- Large colony variant will cause a similar disease in goats
Enzootic pneumonia of calves
- Range of infectious agents together with managemental and environmental stress cause damage to the respiratory tract
- Causes unthriftiness in animals < 6 months old
- Usually the primary pathogen is a virus, secondary pathogens are bacteria and mycoplasmas
- Pathogens:
- Mycoplasmas
- Mycoplasmal bronchitis and pneumonia of calves is an important component of the syndrome of enzootic pneumonia
- On its own causes Mycoplasmal ("Cuffing") pneumonia responsible for bronchitis and bronchiolitis and bronchointerstitial pneumonia
- It is thought to pick up host antigens in order to prevent recognition by the body defences as foreign
- In uncomplicated mycoplasma infection, the lesions are generally mild and consist of patchy red/purple areas of atelectasis in the cranio-ventral lung lobes
- More confluent areas can develop with an underlying bronchointestitial pneumonia and resulting atelectasis
- M. bovis
- Most pathogenic
- Widespread lymphofollicular accumulations which contain germinal centres develop more slowly
- These lesions can result in narrowing of the bronchiolar lumina - this is the classical lesion of ‘cuffing pneumonia’
- M. dispar
- Ureaplasma sp.
- Viruses
- Bovine respiratory syncytial virus (BRSV) - can be primary, causes suppression of pulmonary immune response
- Parainfluenza- 3 (PI3) - can be primary, causes suppression of pulmonary immune response
- Bovine viral diarrhoea virus (BVDV) - suppression of pulmonary immune response
- Adenoviruses
- Calf coronavirus
- Bovine herpes viruses
- Bacteria
- Mycoplasmas
- All transmitted by aerosol and direct contact
- Gross pathology:
- Consolidation of the cranioventral areas which increases in volume with duration
- On cut surface, exudate in the main airway of affected lobules with thickening of the surrounding connective tissue
- Micro pathology:
- Substantial lymphoid tissue around the airways
- Even to proper follicle formation, some of which may be large enough to compress the lumen
- Mixed cell exudate in the airway lumen
- Partial alveolar collapse distal to the compression
- Alveolar exudate contains a mixture of inflammatory cells
- Slight thickening of the alveolar walls with lymphocytes
Acute exudative pneumonia
- Pneumonia in very young calves
- Arcanobacter pyogenes is most frequently isolated
- Cranio-ventral distribution
In Sheep
Laryngeal chondritis
- Caused by Fusobacterium necrophorum
- Infection of laryngeal cartilages
- Can be seen in short-necked breed, e.g. Texels, East Friesians and Southdowns
- Leads to extreme respiratory distress
- Laryngeal mucosa is necrotic and ulcerated
- Associated with laryngeal oedema
- Also may occur in young horses and calves
CAR bacillus
- As in cattle
Enzootic pneumonia of lambs
- Caused by Pasteurella (Manheimia) haemolytica, possibly together with Mycoplasma ovipneumoniae
- Mainly in late spring/early summer after environmental stress i.e. handling or moving
- May be acute with producing a fibrinonecrotic bronchopneumonia and associated pleuritis
- Or tending towards chronicity with abscessation and fibrous pleural adhesions
- A septicaemic form (mortality 5%) is reported to follow the stress of movement to new pasture in the autumn in weaned lambs.
- Foci of necrosis containing many bacteria are seen at the site of initial invasion in the pharynx and in the liver
- Meningitis in young lambs and mastitis in ewes are other expressions
Melioidosis (Pseudoglanders)
- Caused by Pseudomonas (Malleomyces) pseudomallei, Closely related to P. mallei in horses
- Causes disease in sheep, goats and pigs, occasionally other species
- Starts as a pyemia and localises in varius tissues, including the lung as abscessation
- Encapsulated abscesses contain yellow, caseous or creamy pus
- Pneumonia and arthritis are the most common presentation
In Pigs
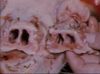
Atrophic Rhinitis
- Atrophy of nasal turbinates and distortion and shortening of the snout
- Caused by co-infection of the nasal mucosa with
- Bordetella bronchiseptica
- Appears to facilitate colonisation of nasal epithelium by the toxigenic Pasteurella
- Toxin-producing strain of Pasteurella multocida capsular type D (or sometimes A)
- Experimental evidence shows that the toxin acts directly on bone cells of the nasal turbinates to cause bone loss, each pathogen can cause atrophy itself but greater damage when together
- Bordetella bronchiseptica
- Exacerbated by adverse dietary and managemental factors
- In rapidly growing young pigs (4-12 weeks old)
- Clinical signs
- Progressive facial deformity with rhinitis, catarrhal nasal discharge
- Sneezing, coughing, can progress to dyspnoea and anorexia
- Gross pathology
- Overlying skin on shortened snout is thrown into folds
- Deviation of the snout to most affected side
- Various loss of turbinate bone, ventral usually more affected
- Deviation of nasal septum away from affected chamber
- Inflammatory, haemorrhagic and ulcerative lesions in the nasal mucosa
- Micro pathology
- Reduction in the amount of bone in the turbinates
- No osteoid laid down between osteoblasts and existing bone
- Increased fibrous tissue
- Non-specific mucosal inflammation
- 2 forms of the disease
- 'Progressive' atrophic rhinitis
- Due to infection of the nasal turbinates by P.multocida strains carrying the toxA gene that encodes for an osteolytic toxin. P.multocida adheres poorly to mucous membranes, and therefore requires a predisposing nasal insult to assist colonisation eg: co-infection with B.bronchiseptica or Porcine cytomegalovirus (inclusion body rhinitis)
- Turbinate bone atrophy is permanent and progressive
- 'Non-progressive' atrophic rhinitis
- Due to infection of the nasal turbinates by Bordetella bronchiseptica strains alone, that carry a gene that encodes for a dermonecrotic toxin.
- Turbinate bone can regenerate by the time of slaughter
- 'Progressive' atrophic rhinitis
- Bordetella bronchiseptica also causes bronchopneumonia
Necrotic laryngitis in pigs
- As in cattle
- Caused by infection with Fusobacterium necrophorum
Enzootic pneumonia of pigs
- Caused by Mycoplasma hyopneumoniae and Mycoplasma hyorhinis
- Also called mycoplasmal pneumonia
- Major cause of unthriftiness in young pigs
- Pneumonia in weaned pigs
- Cough, reduced growth rate
- Attached to cilia - no mucociliary clearance
- Usually non-fatal unless there is secondary infection (e.g. Pasteurella multocida)
- Gross pathology:
- Confluent consolidation of the cranioventral lung lobes
- In other areas there may be small red to grey focal lesions evident which indicate the bronchiolar orientation of the inflammatory process
- Histologically
- Changes result from a catarrhal bronchointerstitial pneumonia
- In chronic cases, prominent accumulations of lymphoid cells can be seen around airways and blood vessels
Actinobacillus pleuropneumoniae
- Causative agent: Actinobacillus pleuropneumoniae
- Expolsive outbreaks of pneumonia
- Spread by direct contact and aerosol
- Lesions
- Largely from toxin produced
- In diphragmatic lobes of the lungs
- Haemorrhage with fibrinous pleuritis
- Usually localised, sometimes generalised
Pasteurellosis in pigs
- Pasteurella multocida can cause a severe acute fibrinous bronchopneumonia in pigs
- The most significant disease here is that caused by P. multocida secondary to underlying mycoplasma pneumonia, see above enzootic pneumonia of pigs
- This results in chronic suppurative bronchopneumonia with abscessation and pleuritis
- If there is considerable pleural involvement, it may be indistinguishable from lesions caused by Haemophilus pleuropneumonia (below)
- Also isolated from cases of meningitis and septicaemia in piglets
Contagious porcine pleuropneumonia
- Caused by Haemophilus (Actinobacillus) pleuropneumonia
- Seen mainly between 6wks-6mths of age but will affect any age
- Highly pathogenic strains are capable of initiating disease on their own with high mortality in young pigs
- A fibrinonecrotic bronchopneumonia with pleurisy
- Foci of haemorrhagic consolidation or necrosis, mainly around major bronchi, tend to sequestrate
- Tending to spread throughout all lung lobes: therefore a cranioventral distribution may not be particularly evident
Glasser's disease
- Caused by Haemophilus parasuis
- May cause suppurative bronchopneumonia and pleuritis (as part of polyserositis)
- Stress of mixing, weaning and adverse environmental conditions are predisposing to the disease
Streptococcal pneumonia
- Caused by Streptococcus suis type II
- Zoonotic
- Carried in nasal cavity and lymph nodes of healthy pigs
- Some serotypes may cause embolic pneumonia, others suppurative or fibrinous bronchopneumonia, often in combination with other bacteria
Tuberculosis in pigs
- Pigs are susceptible to the Mycobacterium spp. causing tuberculosis in cattle
- Rarely extends to lungs after haematogenous spread from ingested bacteria causing tubercles with various degrees of calcification, encapsulation and caseation
In Rabbits
Snuffles
- Caused by Pasteurella multocida, less commonly and/or Bordetella bronchiseptica
- Clinical signs (nasal discharge, sneezing) result from an acute to chronic rhinitis
CAR bacillus
- As in cattle