Spleen - Anatomy & Physiology
| ||||||||||||||
Introduction
The spleen is a major lymphoid and blood filtration organ and is located in the left cranial abdomen. It is responsible for storing and removing erythrocytes from the blood as well as antigen surveillance of the blood and antibody production.
Development
The spleen develops in association with the digestive system in the dorsal mesogastrium, and as the stomach rotates during development the spleen comes to occupy the left cranial abdomen. Haematopoietic cells in the spleen are derived from the AGM (aorta-gonad-mesonephros) and yolk sac and as the primary lymphoid organs become established it becomes populated with T and B lymphocytes.
Structure
|
|
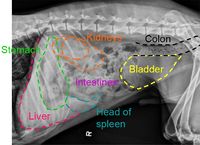
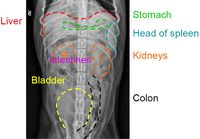
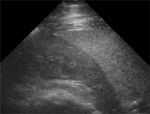
Normal Ultrasound (Equine) |
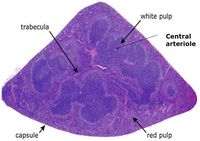
Histological section |
|---|---|
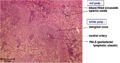
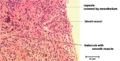
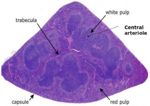
The spleen lies vertically on the left side of the cranial abdomen. It is attached to the greater curvature of the stomach by the gastrosplenic ligament. The spleen is enclosed in a capsule of fibrous and elastic tissue that extends into the parenchyma as trabeculae.
The parenchyma is supported by a fine mesh of reticular fibres and is divided into two types of tissue, the red and the white pulp, which are separated by the marginal sinus.
Red Pulp
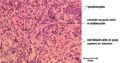
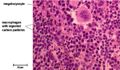
The red pulp makes up the majority of the spleen and is composed of a network of cell cords in series with vascular sinuses. The splenic cords contain macrophages, plasma cells, lymphocytes and other mature blood cells e.g. granulocytes and erythrocytes. While the vascular sinuses are wide vascular channels lined with endothelial cells. Blood cells and fluid can pass into the splenic cords through fenestrations in the sinus walls.
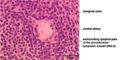
White Pulp
White pulp is organised in relation to the splenic arterioles and consists of discrete lymphoid tissue surrounding a central arteriole. There is a sheath of T cells directly around the arteriole, the periarteriolar lymphoid sheath (PALS), which is surrounded by a marginal sinus, and then a zone of B cells and macrophages (the marginal zone). B cell follicles are associated with the marginal zone and expand and develop germinal centres after antigen activation. The marginal sinuses are linked to the red pulp sinuses.
White pulp stains basophilic in a H&E stain
Species Differences
 |
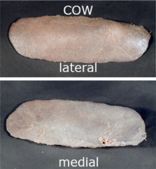 |
| Equine | Bovine |
|---|---|
 |
 |
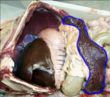
| Canine | Ovine |
The capsule and trabeculae are much more muscular in carnivores and horses than ruminants
- Carnivores
- Is elongated and dumb-bell shaped (larger ventrally)
- Ruminants
- Is flat and oblong shaped
- Horses
- Lies under the last three ribs. Dorsally it is broad but narrows as it extends cranially and ventrally
- On rectal palpation it is located against the body wall and feels smooth with a sharp border
- Pigs
- Elongated and strap-like under the last few ribs
- Birds (Picture here)
- Lies alongside, to the right, of the proventriculus and is found caudodorsally to the liver
- Spherical in chickens, triangular in ducks & oval in pigeons
Vasculature
The splenic artery, a branch of the celiac artery, supplies the spleen. The artery branches into arterioles and capillaries, which may either:
- Connect with the venous sinuses, or
- Terminate with open ends in the splenic cords
Blood released into the splenic cords, either from the sinuses or capillaries, eventually filters back into the sinus network. The sinuses converge and empty into trabecular veins, which then merge into a single splenic vein which then empties into the portal vein.
Lymphocytes in the arterial blood migrate from the red pulp sinuses, through the splenic cords and through the white pulp. T cells specifically migrate through the PALS and B cells specifically migrate through the follicles. Antigen in the blood is filtered by the large numbers of macrophages in the splenic cords and white pulp.
Species Differences
The splenic artery:
- Passes through the spleen without dividing in ruminants
- Branches regularly as it passes through the spleen in horses and pigs
- Branches before it reaches the spleen in dogs and cats
Innervation
Innervation is purely sympathetic[1] and nerve fibres travel with the artery into the spleen.
Histology
Functions
The spleen has a number of functions:
- It filters the blood removing ageing erythrocytes and antigens
- It stores erythrocytes and platelets
- Secondary lymphoid organ
Erythrocytes & Platelets
In the foetus the spleen also has a role in haematopoiesis when it becomes the main erythrocyte producing organ during the haematopoietic transitional phase.
In the developed animal the red pulp is involved in the removal of aged, damaged or abnormal erythrocytes (along with the liver and bone marrow). As erythrocytes age they become less supple and this causes them to become damaged when they pass through the very narrow capillaries of the spleen, after which they are phagocytised by splenic macrophages. If a splenectomy is performed the number of aged erythrocytes in circulation increases.
The red pulp also acts as a storage site for erythrocytes. The degree of storage is variable between species but is particularly notable in horses which, during exercise under sympathetic activity, can contract their spleen to increase the concentration of circulating erythrocytes. In some species such as cats and rodents the red pulp acts as a storage site for platelets and contains megakaryocytes.
Lymphoid
Blood flows through the marginal sinus. This means that most antigens present in the blood come into contact with the B lymphocytes and dendritic cells in the spleen. Dendritic cells in the marginal sinus and red pulp take up antigens from the blood and transport them to the primary follicles in the white pulp. If the antigen activates the B lymphocytes then a germinal centre will form in the primary follicle and this is called a splenic nodule. Antibody producing cells then migrate to the red pulp and marginal zone.
Following splenectomy this doesn’t occur and animals are predisposed to septicaemia and infection with blood protozoa.
| Spleen - Anatomy & Physiology Learning Resources | |
|---|---|
 Selection of relevant videos |
Equine thoracic cavity dissection Feline Abdomen Foal gastrointestinal tract potcast Ruminant abdomen potcast Video: Lateral view of the feline thorax and abdomen potcast Abdominal viscera of the horse dissection |
Anatomy Museum Resources |
Spleen Histology - Low Power 1 Spleen Histology - Low Power 2 Spleen Histology - High Power Rodent Spleen Histology |
| Sample Book Chapters | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
In pathology
Direct pathology
- Specific spleen pathology can be found here
- Acute undifferentiated leukaemia and lymphoid neoplasms
Changed or affected by
References
- ↑ Nance, D.M. and Sanders, V.M. (2007) Autonomic innervation and regulation of the immune system (1987-2007). Brain, Behavior, and Immunity 21(6): pp.736-745.
| Originally funded by the RVC Jim Bee Award 2007 |
Error in widget FBRecommend: unable to write file /var/www/wikivet.net/extensions/Widgets/compiled_templates/wrt69a1f4a414a9b8_77159983 Error in widget google+: unable to write file /var/www/wikivet.net/extensions/Widgets/compiled_templates/wrt69a1f4a4191ff4_86595985 Error in widget TwitterTweet: unable to write file /var/www/wikivet.net/extensions/Widgets/compiled_templates/wrt69a1f4a41d4190_31951727
|
| WikiVet® Introduction - Help WikiVet - Report a Problem |