Snake Cardiovascular System
| This article has been peer reviewed but is awaiting expert review. If you would like to help with this, please see more information about expert reviewing. |
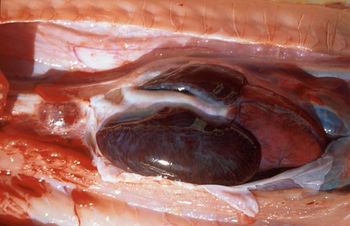
The cardiovascular system of snakes is similar to other non-crocodilian reptiles but is modified for their linear shape.
Systemic venous return
Snakes have both renal and hepatic portal circluations. Jugulars are located anterior to the heart near the trachea and may be cannulated by a cutdown procedure. The right jugular is larger than the left. Blood returns to the heart from the systemic circulation through the sinus venosus.
- Find out more about the snake respiratory system.
- Find out more about the reptile haemopoietic system.
Heart
The position of the heart varies among species and, as there is no diaphragm, it is mobile within the ribcage. Heart position varies slightly with its ecological niche and phylogenetic position, and its mobility may facilitate the passage of relatively large prey (see snake feeding). The heart has three chambers: right and left atria and one ventricle. The right atrium receives deoxygenated blood from the systemic circulation and the left receives oxygenated blood from lungs via the left and right pulmonary veins. The ventricle has internal ridges that enable a considerable functional separation between the oxygenated and deoxygenated blood. It is divided into three subchambers: the cavum pulmonale, cavum venosum and cavum arteriosum.
Snakes can control arterial pressure reflexly, but this is diminished when the body temperature is outside the preferred optimum temperature zone (POTZ). Oxygen dissociation curves of snake blood are also influenced by temperature.
Systemic arteries
There are two aortae that leave the heart - the right aorta exits from the left side of the ventricle and the left aorta from the right side. The aortae join caudal to the heart to form the abdominal aorta that extends caudally through the coelomic cavity. The left systemic arch is larger than the right, the opposite to most tetrapods.
Carotids extend cranially from the heart and adjacent to the trachea. The jugulars may be easily cannulated by a cutdown for placement of an IV catheter.
- Sites to collect blood from a snake include a ventral tail vein and cannulated jugular vein, and via cardiocentesis.
For information on blood sample collection methods, see snake blood collection.
For information on reptile surgery, see snake surgery.
Haemocrit
The normal packed cell volume of a snake ranges between 20% and 30%. The blood volume (based on the black ratsnake, Elaphe sp.) is equivalent to approximately 6% of the animal's body weight.
- For more information on reptile blood, see the relevant section on haematology or biochemistry.
References
Mader, D.R. (2005). Reptile Medicine and Surgery. Saunders. pp. 47. ISBN 072169327X