Difference between revisions of "Leishmania"
Mariapavlou (talk | contribs) |
|||
| (57 intermediate revisions by 14 users not shown) | |||
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
| − | {{ | + | {{OpenPagesTop}} |
| − | + | Causes: '''''Leishmaniasis''''' | |
| − | {{ | + | {{Taxobox |
| − | | | + | |name =''Leishmania spp.'' |
| − | | | + | |kingdom =Eukaryota |
| − | | | + | |sub-kingdom = |
| − | | | + | |phylum =Euglenozoa |
| − | | | + | |super-class = |
| − | | | + | |class =Kinetoplastea |
| + | |sub-class = | ||
| + | |super-order = | ||
| + | |order =Trypanosomatida | ||
| + | |sub-order = | ||
| + | |super-family = | ||
| + | |family =Trypanosomatidae | ||
| + | |sub-family = | ||
| + | |genus =Leishmania | ||
| + | |species =''L. infantum'', ''L. donovani'', ''L.chagasi'' | ||
}} | }} | ||
| − | + | ==Overview== | |
| − | == | ||
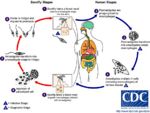
[[Image:Leishmania Life Cycle.jpg|thumb|right|150px|Leishmania Life Cycle - Wikimedia Commons]] | [[Image:Leishmania Life Cycle.jpg|thumb|right|150px|Leishmania Life Cycle - Wikimedia Commons]] | ||
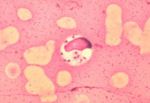
[[Image:Leishmania donovani.jpg|thumb|right|150px|''Leishmania donovani'' in bone marrow cell - Dr. L.L. Moore, Jr.]] | [[Image:Leishmania donovani.jpg|thumb|right|150px|''Leishmania donovani'' in bone marrow cell - Dr. L.L. Moore, Jr.]] | ||
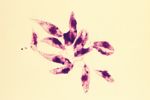
| − | [[Image:Leishmania tropica.jpg|right|thumb|150px|''L. tropica'' | + | [[Image:Leishmania tropica.jpg|right|thumb|150px|''L. tropica'' <p> Yutaka TsutsumiWikiMedia Commons]] |
| − | + | ''Leishmania spp.'' are intracellular parasites of [[Macrophage|macrophages]] from the same family as ''[[Trypanosoma]] spp.''. These organisms parasitise human, dogs and wild animals throughout southern Europe, Africa, Asia and South America. The infection is transmitted by [[Psychodidae|sandflies]]. Infection can cause both cutaneous and visceral disease. Clinical disease cause by ''Leishmania'' is termed Leishmaniasis. Three types of ''Leishmania spp.'' are described; | |
| + | # '''Hypopylaria''' - found in lizards that ingest the sandfly intermediate host. Development occurs in the hindgut of the fly. | ||
| + | # '''Peripylaria''' - found in mammals and lizards, development occurs in the fore- and hindgut of the fly. | ||
| + | # '''Suprapylaria''' - found only in mammals transmitted by the bite of a sandfly, development occurs in the fore- and midgut of the fly. | ||
| − | + | ==Recognition== | |
| + | ''Leishmania spp.'' are ovoid shaped parasites containing a rod shaped 'kinetoplast'. The kinetoplast is associated with a rudimentary flagellum that does not extened beyond the cell margin. The position of the kinetoplast changes as the parasite changes between life stages. Once ingested by a sand fly the parasite takes the promastigote form and the kinetoplast moves to the posterior of the cell. | ||
| − | + | ==Life Cycle== | |
| + | The life cycle of ''Leishamania spp.'' requires transmission between mammalian (and occasionally reptile) hosts by a blood sucking fly. The [[Psychodidae|sand flies]] is the intermediate host, in the Old World the flies are of the genus ''Phlebotomus'' and in the New World they are of the genus ''Lutzomyia''. | ||
| − | + | The promastigote form which lacks a flagella is found in the vertebrate hosts [[Macrophage|macrophages]]. The amistgote is ingested by the sand fly whilst it feeds on the host, once ingested the ''Leishamnia'' will transform into the flagellated promastigote form in the insect gut. Replication by binary fission occurs in the insects gut followed by migration to the proboscis of the insect. The presence of ''Leishamnia'' in the insects proboscis allows inoculation of the next host on which the fly feeds with the ''Leishmania'' parasite. Crushing the sand fly on the skin of a mammal can allow percutaneous transmission. | |
| − | + | Once inside the vertebrate host the ''Leishmania'' will invade the hosts [[Macrophage|macrophages]] and having done this revert to the amastigote form. | |
| − | ''' | + | ==Pathogenesis== |
| − | + | Infection with ''Leishmania'' can produce either cutaneous or visceral disease as the infected macrophages proliferate in foci. The cutaneous form of the disease produces areas of ulceration on the pinnae of the [[Ear - Anatomy & Physiology|ears]], eyelids or on the [[Lips|lips]]. These ulcerations can also be seen between the digits of the dogs paw. This is a parasitic infection of the [[Protozoal Dermatosis|skin]]. The visceral form causes a chronic wasting condition where generalised excema can be seen. Hair is lost from around the eyes giving the animal a 'spectacled' appearance. These symptoms are accompanied by an intermittent fever and some generalized lymphadenopathy. | |
| − | + | There is a very long incubation period from infection to pathology, which can take years and therefore many infected dogs either never become symptomatic or remain so for a long period of time. Even once an animal has been treated for leishmaniasis it is not uncommon for clinical symptoms to recur after a lengthy period of remission. | |
| − | + | ==Epidemiology== | |
| + | The spread of the disease relies on the presence of the [[Psychodidae|sand fly]] as a vector. Therfore the regions in which it is found commonly are those in which conditions are suitable for the flies such as the Mediteranean coast, southern Europe as well as in central America and northern Africa. As these flies are very common in these regions, controlling their numbers has limited success, however due to control of [[Culicidae|mosquitos]] to prevent the spread of malaria, the number of sand flies has also been reduced and a reduction in the number of cases of leishmania has been noted. Although this parasite is of primary veterinary importance in dogs, large reservoirs exist in wild animals and stray dogs. This reservoir is easily accessed by the sand fly vector and compounds the issue of controlling the spread of the disease. | ||
| − | + | Although the UK is not home to any species of sand fly, leishmaniasis is being observed more frequently in the domestic dog population. This has largely been attributed to the increase in the number of animals that travel to areas of Europe and north Africa where the disease is endemic. These animals often acquire the disease whilst abroad but may not show clinical signs until they have been back in the UK for a considerable length of time. There has however been some evidence to show that close contact between dogs can spread the disease, though this method of transmission is much less common. | |
| − | ''' | + | ==Diagnosis== |
| − | + | Definitive diagnosis of Leishmaniasis requires combining observation of the clinical signs and the demonstration of ''Leishmania'' organisms in the animal. In the cutaneous disease this may be done by microscopic analysis of skin scrapings from the animals. For diagnosis of the visceral disease samples of joint fluid, [[Lymph Nodes - Anatomy & Physiology|lymph node]] or [[Bone Marrow - Anatomy & Physiology|bone marrow]] biopsies may all contain macrophages that have been infected by the organisms. | |
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | + | Cytological examination of fine needle aspirates should show evidence of [[Lymph Node Abnormalities|reactive hyperplasia]] in the lymph nodes, with increased numbers of lymphoblasts and [[B cell differentiation|plasma cells]]. [[Lymph Node Abnormalities|Reactive hyperplasia]] of [[B cell differentiation|plasma cells]] is especially common in Leishmaniasis cases as it causes chronic antigen stimulation. [[B cell differentiation|Mott cells]], which are [[B cell differentiation|plasma cells]] containing vesicles of accumulated [[Immunoglobulins - Overview|immunoglobulins]] (Russell bodies) may also be evident. They are also the result of a chronic disease process, such as Leishmaniasis. | |
| + | As mentioned above, the parasite itself can be identified cytologically within [[Macrophage|macrophages]] to confirm disease. | ||
| − | + | ==Treatment and Control== | |
| − | + | Control of ''Leishmania'' is difficult due to the large environmental pool and the sand flies that transmit the disease. One method is to prevent the sand flies from biting dogs by using collars impregnated with [[Ectoparasiticides|insecticides]] or repellents. These have a limited effect and do not guarantee the safety of the animal. Destruction of infected and stray dogs will decrease the pool from which sand flies may obtain the parasite but this is often morally difficult and due to the infection of wildlife does not stop spread completely. | |
| − | + | Chemotherapy can be used to treat dogs with leishmaniasis; however this will not eliminate the infection completely. It may appear to resolve the infection, but it is not uncommon for clinical sign to return later in the dog's life. It is important to factor in the risks involved with chemotherapy, such as suppression of the immune system, and the expense of prolonged treatment. | |
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | + | {{Learning | |
| + | |Vetstream = [https://www.vetstream.com/canis/Content/Disease/dis00998.asp Canine leishmaniosis]<br>[https://www.vetstream.com/canis/Content/Freeform/fre00654.asp PET passport travel scheme] | ||
| + | |flashcards = [[Protozoa_Flashcards#Tropical_Protozoa|Tropical Protozoa Flashcards]] | ||
| + | [[Cytology Q&A 08]] | ||
| + | |full text = [http://www.cabi.org/cabdirect/FullTextPDF/2005/20053201552.pdf ''' Canine visceral leishmaniasis.''' Gaskin, A.; Seward, R. L.; Knight, D. H.; American Heartworm Society, Batavia, USA, Recent advances in heartworm disease: Symposium 01, San Antonio, Texas, USA, 20-22 April, 2001, 2001, pp 63-65, 35 ref.] | ||
| + | }} | ||
| − | |||
| − | + | {{review}} | |
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | + | {{OpenPages}} | |
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | + | [[Category:Tropical Protozoa]] | |
| − | + | [[Category:Dermatological Diseases - Dog]] | |
| − | + | [[Category:Expert Review]] | |
Latest revision as of 10:32, 18 January 2017
Causes: Leishmaniasis
| Leishmania spp. | |
|---|---|
| Kingdom | Eukaryota |
| Phylum | Euglenozoa |
| Class | Kinetoplastea |
| Order | Trypanosomatida |
| Family | Trypanosomatidae |
| Genus | Leishmania |
| Species | L. infantum, L. donovani, L.chagasi |
Overview
Leishmania spp. are intracellular parasites of macrophages from the same family as Trypanosoma spp.. These organisms parasitise human, dogs and wild animals throughout southern Europe, Africa, Asia and South America. The infection is transmitted by sandflies. Infection can cause both cutaneous and visceral disease. Clinical disease cause by Leishmania is termed Leishmaniasis. Three types of Leishmania spp. are described;
- Hypopylaria - found in lizards that ingest the sandfly intermediate host. Development occurs in the hindgut of the fly.
- Peripylaria - found in mammals and lizards, development occurs in the fore- and hindgut of the fly.
- Suprapylaria - found only in mammals transmitted by the bite of a sandfly, development occurs in the fore- and midgut of the fly.
Recognition
Leishmania spp. are ovoid shaped parasites containing a rod shaped 'kinetoplast'. The kinetoplast is associated with a rudimentary flagellum that does not extened beyond the cell margin. The position of the kinetoplast changes as the parasite changes between life stages. Once ingested by a sand fly the parasite takes the promastigote form and the kinetoplast moves to the posterior of the cell.
Life Cycle
The life cycle of Leishamania spp. requires transmission between mammalian (and occasionally reptile) hosts by a blood sucking fly. The sand flies is the intermediate host, in the Old World the flies are of the genus Phlebotomus and in the New World they are of the genus Lutzomyia.
The promastigote form which lacks a flagella is found in the vertebrate hosts macrophages. The amistgote is ingested by the sand fly whilst it feeds on the host, once ingested the Leishamnia will transform into the flagellated promastigote form in the insect gut. Replication by binary fission occurs in the insects gut followed by migration to the proboscis of the insect. The presence of Leishamnia in the insects proboscis allows inoculation of the next host on which the fly feeds with the Leishmania parasite. Crushing the sand fly on the skin of a mammal can allow percutaneous transmission.
Once inside the vertebrate host the Leishmania will invade the hosts macrophages and having done this revert to the amastigote form.
Pathogenesis
Infection with Leishmania can produce either cutaneous or visceral disease as the infected macrophages proliferate in foci. The cutaneous form of the disease produces areas of ulceration on the pinnae of the ears, eyelids or on the lips. These ulcerations can also be seen between the digits of the dogs paw. This is a parasitic infection of the skin. The visceral form causes a chronic wasting condition where generalised excema can be seen. Hair is lost from around the eyes giving the animal a 'spectacled' appearance. These symptoms are accompanied by an intermittent fever and some generalized lymphadenopathy.
There is a very long incubation period from infection to pathology, which can take years and therefore many infected dogs either never become symptomatic or remain so for a long period of time. Even once an animal has been treated for leishmaniasis it is not uncommon for clinical symptoms to recur after a lengthy period of remission.
Epidemiology
The spread of the disease relies on the presence of the sand fly as a vector. Therfore the regions in which it is found commonly are those in which conditions are suitable for the flies such as the Mediteranean coast, southern Europe as well as in central America and northern Africa. As these flies are very common in these regions, controlling their numbers has limited success, however due to control of mosquitos to prevent the spread of malaria, the number of sand flies has also been reduced and a reduction in the number of cases of leishmania has been noted. Although this parasite is of primary veterinary importance in dogs, large reservoirs exist in wild animals and stray dogs. This reservoir is easily accessed by the sand fly vector and compounds the issue of controlling the spread of the disease.
Although the UK is not home to any species of sand fly, leishmaniasis is being observed more frequently in the domestic dog population. This has largely been attributed to the increase in the number of animals that travel to areas of Europe and north Africa where the disease is endemic. These animals often acquire the disease whilst abroad but may not show clinical signs until they have been back in the UK for a considerable length of time. There has however been some evidence to show that close contact between dogs can spread the disease, though this method of transmission is much less common.
Diagnosis
Definitive diagnosis of Leishmaniasis requires combining observation of the clinical signs and the demonstration of Leishmania organisms in the animal. In the cutaneous disease this may be done by microscopic analysis of skin scrapings from the animals. For diagnosis of the visceral disease samples of joint fluid, lymph node or bone marrow biopsies may all contain macrophages that have been infected by the organisms.
Cytological examination of fine needle aspirates should show evidence of reactive hyperplasia in the lymph nodes, with increased numbers of lymphoblasts and plasma cells. Reactive hyperplasia of plasma cells is especially common in Leishmaniasis cases as it causes chronic antigen stimulation. Mott cells, which are plasma cells containing vesicles of accumulated immunoglobulins (Russell bodies) may also be evident. They are also the result of a chronic disease process, such as Leishmaniasis. As mentioned above, the parasite itself can be identified cytologically within macrophages to confirm disease.
Treatment and Control
Control of Leishmania is difficult due to the large environmental pool and the sand flies that transmit the disease. One method is to prevent the sand flies from biting dogs by using collars impregnated with insecticides or repellents. These have a limited effect and do not guarantee the safety of the animal. Destruction of infected and stray dogs will decrease the pool from which sand flies may obtain the parasite but this is often morally difficult and due to the infection of wildlife does not stop spread completely.
Chemotherapy can be used to treat dogs with leishmaniasis; however this will not eliminate the infection completely. It may appear to resolve the infection, but it is not uncommon for clinical sign to return later in the dog's life. It is important to factor in the risks involved with chemotherapy, such as suppression of the immune system, and the expense of prolonged treatment.
| Leishmania Learning Resources | |
|---|---|
To reach the Vetstream content, please select |
Canis, Felis, Lapis or Equis |
 Test your knowledge using flashcard type questions |
Tropical Protozoa Flashcards |
 Full text articles available from CAB Abstract (CABI log in required) |
Canine visceral leishmaniasis. Gaskin, A.; Seward, R. L.; Knight, D. H.; American Heartworm Society, Batavia, USA, Recent advances in heartworm disease: Symposium 01, San Antonio, Texas, USA, 20-22 April, 2001, 2001, pp 63-65, 35 ref. |
| This article has been peer reviewed but is awaiting expert review. If you would like to help with this, please see more information about expert reviewing. |
Error in widget FBRecommend: unable to write file /var/www/wikivet.net/extensions/Widgets/compiled_templates/wrt69863efc6c31f1_62208482 Error in widget google+: unable to write file /var/www/wikivet.net/extensions/Widgets/compiled_templates/wrt69863efc75cef8_02902308 Error in widget TwitterTweet: unable to write file /var/www/wikivet.net/extensions/Widgets/compiled_templates/wrt69863efc7ae688_42160079
|
| WikiVet® Introduction - Help WikiVet - Report a Problem |