Difference between revisions of "Nervous and Special Senses - Anatomy & Physiology"
| (23 intermediate revisions by 4 users not shown) | |||
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
| − | {{ | + | {{toplink |
| + | |pagetype=Anatomy | ||
| + | |thispagenormal= {{PAGENAME}} | ||
| + | |thispagemap= Nervous System and Special Senses (Content Map) - Anatomy & Physiology | ||
| + | }} | ||
| + | <br> | ||
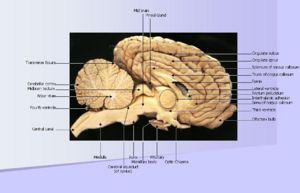
[[Image:mainpagecnsbrain.jpg|thumb|right|300px|Saggital section of equine brain - © RVC]] | [[Image:mainpagecnsbrain.jpg|thumb|right|300px|Saggital section of equine brain - © RVC]] | ||
| + | |||
==Nervous System== | ==Nervous System== | ||
| − | + | ||
| + | * [[Neurones - Anatomy & Physiology|Neurones]] | ||
| + | * [[Neurotransmitters - Anatomy & Physiology|Neurotransmitters]] | ||
| + | * [[Action Potentials - Anatomy & Physiology|Action Potentials]] | ||
===Central Nervous System (CNS)=== | ===Central Nervous System (CNS)=== | ||
---- | ---- | ||
| − | The central nervous system is comprised of the '''brain and spinal cord'''. The brain is contained within the skull, and the spinal cord is contained within the spinal vertebral canal. The brain is covered and protected by the meninges. The meninges are comprised of three layers: the dura mater (the outermost layer), the arachnoid mater (the middle layer), and the pia mater (the innermost layer). [[Cerebral Spinal Fluid - Anatomy & Physiology|Cerebral Spinal Fluid]] (CSF) is the fluid surrounding the brain as well as the central canal of the spinal cord which helps cushion the CNS, acts as a chemical buffer, provides immunological protection and transports waste products and nutrients. Nerves arising from the brain and brain stem are the [[#Innervation - cranial nerves| cranial nerves]] whilst those arising from the spinal cord are the [[PNS Structure - Anatomy & Physiology| | + | The central nervous system is comprised of the '''brain and spinal cord'''. The brain is contained within the skull, and the spinal cord is contained within the spinal vertebral canal. The brain is covered, and protected, by the meninges. The meninges are comprised of three layers: the dura mater (the outermost layer), the arachnoid mater (the middle layer), and the pia mater (the innermost layer).[[Cerebral Spinal Fluid - Anatomy & Physiology|Cerebral Spinal Fluid]] (CSF) is the fluid surrounding the brain as well as the central canal of the spinal cord which helps cushion the CNS, acts as a chemical buffer, provides immunological protection and transports waste products and nutrients. Nerves arising from the brain and brain stem are the [[#Innervation - cranial nerves| cranial nerves]] whilst those arising from the spinal cord are the [[PNS Structure - Anatomy & Physiology|perhipheral nerves]]. |
*[[CNS Development - Anatomy & Physiology|Development]] | *[[CNS Development - Anatomy & Physiology|Development]] | ||
| Line 13: | Line 22: | ||
*[[Hindbrain - Anatomy & Physiology|Hindbrain]] | *[[Hindbrain - Anatomy & Physiology|Hindbrain]] | ||
*[[Spinal Cord - Anatomy & Physiology|Spinal Cord]] | *[[Spinal Cord - Anatomy & Physiology|Spinal Cord]] | ||
| − | *[[Meninges - Anatomy & Physiology|Meninges]] | + | *[[CNS Meninges - Anatomy & Physiology|Meninges]] |
*[[CNS Vasculature - Anatomy & Physiology|Vasculature]] | *[[CNS Vasculature - Anatomy & Physiology|Vasculature]] | ||
| − | *[[ | + | *[[CNS Histology - Anatomy & Physiology|Histology]] |
===Peripheral Nervous System (PNS)=== | ===Peripheral Nervous System (PNS)=== | ||
---- | ---- | ||
| − | The Peripheral Nervous System includes both [[#Innervation - cranial nerves| cranial nerves]] and [[#Innervation - spinal nerves| spinal nerves]], and is commonly divided into the somatic nervous system and the autonomic nervous system. The somatic nervous system co-ordinates body movements and also receives external stimuli. It basically regulates activities that are under conscious control. | + | The Peripheral Nervous System includes both [[#Innervation - cranial nerves| cranial nerves]] and [[#Innervation - spinal nerves| spinal nerves]], and is commonly divided into the somatic nervous system and the autonomic nervous system. The [[Somatic Nervous System - Anatomy & Physiology|somatic nervous system]] co-ordinates body movements and also receives external stimuli. It basically regulates activities that are under conscious control. |
| − | The autonomic nervous system contains the sympathetic nervous system and the parasympathetic nervous system as well as an enteric division. The sympathetic nervous system is the ‘fight or flight’ system which | + | The [[Autonomic Nervous System - Anatomy & Physiology|autonomic nervous system]] contains the [[Sympathetic Nervous System - Anatomy & Physiology|sympathetic nervous system]] and the [[Parasympathetic Nervous System - Anatomy & Physiology|parasympathetic nervous system]] as well as an enteric division. The sympathetic nervous system is the ‘fight or flight’ system which comes into role when an animal is under threat, it's main neurotransmitter is adrenaline. The parasympathetic nervous system is the ‘rest and digest’ system which is responsible for digestion; the primary neurotransmitter is acetylcholine. Further information on the structure, physiology and pathology of the PNS is available from the following links: |
*[[PNS Structure - Anatomy & Physiology|Structure]] | *[[PNS Structure - Anatomy & Physiology|Structure]] | ||
*[[Reflex Arcs - Anatomy & Physiology|Reflex Arc]] | *[[Reflex Arcs - Anatomy & Physiology|Reflex Arc]] | ||
| − | *[[PNS | + | *[[PNS Vasculature - Anatomy & Physiology|Vasculature]] |
| − | *[[ | + | *[[PNS Histology - Anatomy & Physiology |Histology]] |
===Information Pathways=== | ===Information Pathways=== | ||
---- | ---- | ||
| − | + | *[[Sensory Pathways - Anatomy & Physiology|Sensory Pathways]] | |
| + | |||
| + | *[[Motor Pathways - Anatomy & Physiology|Motor Pathways]] | ||
==Special Senses== | ==Special Senses== | ||
| − | In anatomy, there are four major senses which have specialised organs assocated with them. They are the [[Eye - Anatomy & Physiology|eye | + | In anatomy, there are four major senses which have specialised organs assocated with them. They are the [[Eye - Anatomy & Physiology|eye],the [[Ear - Anatomy & Physiology|ear]], the [[Nose - Anatomy & Physiology|nose]] and the [[Tongue - Anatomy & Physiology|tongue]]. These organs detect visual, auditory, olfactory and taste respectively. |
| − | |||
| − | + | ==Test yourself - Nervous System and Special Senses flashcards== | |
| − | + | *'''[[Sensory_Pathways_Flashcards_-_Anatomy_%26_Physiology|Sensory pathways flashcards]]''' | |
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | ==References== | + | ==References for Nervous and Special Senses== |
'''BOOKS''' | '''BOOKS''' | ||
*''Textbook of Veterinary Anatomy'' by Dyce, Sack and Wensing. 3rd Edition | *''Textbook of Veterinary Anatomy'' by Dyce, Sack and Wensing. 3rd Edition | ||
*''Veterinary Anatomy of Domestic Mammals'' by König and Liebich. 3rd Edition | *''Veterinary Anatomy of Domestic Mammals'' by König and Liebich. 3rd Edition | ||
| + | |||
'''IMAGES''' | '''IMAGES''' | ||
*''Royal Veterinary College'' Histology Department | *''Royal Veterinary College'' Histology Department | ||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
Revision as of 15:12, 12 June 2010
|
|
Nervous System
Central Nervous System (CNS)
The central nervous system is comprised of the brain and spinal cord. The brain is contained within the skull, and the spinal cord is contained within the spinal vertebral canal. The brain is covered, and protected, by the meninges. The meninges are comprised of three layers: the dura mater (the outermost layer), the arachnoid mater (the middle layer), and the pia mater (the innermost layer).Cerebral Spinal Fluid (CSF) is the fluid surrounding the brain as well as the central canal of the spinal cord which helps cushion the CNS, acts as a chemical buffer, provides immunological protection and transports waste products and nutrients. Nerves arising from the brain and brain stem are the cranial nerves whilst those arising from the spinal cord are the perhipheral nerves.
Peripheral Nervous System (PNS)
The Peripheral Nervous System includes both cranial nerves and spinal nerves, and is commonly divided into the somatic nervous system and the autonomic nervous system. The somatic nervous system co-ordinates body movements and also receives external stimuli. It basically regulates activities that are under conscious control. The autonomic nervous system contains the sympathetic nervous system and the parasympathetic nervous system as well as an enteric division. The sympathetic nervous system is the ‘fight or flight’ system which comes into role when an animal is under threat, it's main neurotransmitter is adrenaline. The parasympathetic nervous system is the ‘rest and digest’ system which is responsible for digestion; the primary neurotransmitter is acetylcholine. Further information on the structure, physiology and pathology of the PNS is available from the following links:
Information Pathways
Special Senses
In anatomy, there are four major senses which have specialised organs assocated with them. They are the [[Eye - Anatomy & Physiology|eye],the ear, the nose and the tongue. These organs detect visual, auditory, olfactory and taste respectively.
Test yourself - Nervous System and Special Senses flashcards
References for Nervous and Special Senses
BOOKS
- Textbook of Veterinary Anatomy by Dyce, Sack and Wensing. 3rd Edition
- Veterinary Anatomy of Domestic Mammals by König and Liebich. 3rd Edition
IMAGES
- Royal Veterinary College Histology Department