Difference between revisions of "Lungs Inflammatory - Pathology"
Jump to navigation
Jump to search
(Redirected page to Category:Pneumonia) |
|||
| (6 intermediate revisions by the same user not shown) | |||
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
| − | # | + | [[Pneumonia Overview]] |
| + | |||
| + | ==Pneumonia - Introduction and Classification== | ||
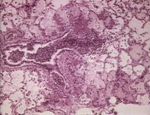
| + | [[Image:Acute fibrinous pneumonia.jpg|right|thumb|150px|<small><center>Acute fibrinous pneumonia (Image sourced from Bristol Biomed Image Archive with permission)</center></small>]] | ||
| + | *Pneumonia | ||
| + | **Inflammation that takes place in the '''alveoli and their walls''' | ||
| + | **Can be grouped either according to | ||
| + | ***Nature of the inflammatory process | ||
| + | ***Aetiological agent | ||
| + | ***Pattern of the lesion | ||
| + | |||
| + | *Patterns of lung inflammation vary depending on the aetiology, route and method of exposure and multiple host factors including age, general health, and immune status | ||
| + | **There are five general patterns of pneumonia: | ||
| + | ***[[Bronchopneumonia]] | ||
| + | ***[[Bronchointerstitial Pneumonia]] | ||
| + | ***[[Lobar Pneumonia]] | ||
| + | ***[[Interstitial Pneumonia]] | ||
| + | ***[[Embolic Pneumonia]] | ||
| + | |||
| + | |||
| + | ==='''[[Bronchopneumonia]]'''=== | ||
| + | |||
| + | ==='''[[Bronchointerstitial Pneumonia]]'''=== | ||
| + | |||
| + | ==='''[[Lobar Pneumonia]]'''=== | ||
| + | |||
| + | ==='''[[Interstitial Pneumonia]]'''=== | ||
| + | |||
| + | ==='''[[Embolic Pneumonia]]'''=== | ||
| + | |||
| + | ==='''[[Granulomatous Pneumonia]]'''=== | ||
| + | |||
| + | ==='''[[Verminous Pneumonia]]'''=== | ||
| + | |||
| + | ==Stages of pneumonia== | ||
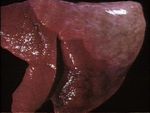
| + | [[Image:Acute exudative pneumonia.jpg|right|thumb|150px|<small><center>Acute exudative pneumonia (Image sourced from Bristol Biomed Image Archive with permission)</center></small>]] | ||
| + | [[Image:Acute exudative pneumonia - gross.jpg|right|thumb|150px|<small><center>Acute exudative pneumonia (Image sourced from Bristol Biomed Image Archive with permission)</center></small>]] | ||
| + | *Regardless of the pattern, all pneumonias pass through three stages: | ||
| + | **'''Exudative phase''' | ||
| + | ***In this initial stage inflammatory exudate pours into alveolar spaces and alveolar capillaries are congested | ||
| + | ***Type I alveolar epithelial cells are highly sensitive to injury and cannot proliferate in response to injury | ||
| + | ***Necrosis and sloughing of injured type I cells, denuding alveolar spaces of lining epithelium | ||
| + | ***[[Neutrophils|Neutrophils]] begin to enter alveolar spaces distended with inflammatory oedema | ||
| + | **'''Proliferative phase''' | ||
| + | ***Type II alveolar cells (less sensitive to and can proliferate in response to injury) begin to proliferate within 24 hours and eventually line the alveolar walls denuded of type I cells ***By 6 days cuboidal type II cells can completely line the alveoli | ||
| + | ***Proliferation of type II cells marks the shift from the exudative to the proliferative stage of pneumonia, also heralded by decreased blood flow in alveolar capillaries | ||
| + | ***Because the original squamous type I cells have been replaced by cuboidal type II cells, the microscopic appearance of pneumonic lungs at about 1 week has been described as “alveolar epithelialization”, “alveolar adenomatosis”, or “bronchiolisation of alveoli” | ||
| + | **'''Repair phase''' | ||
| + | ***Resolution of pneumonia is accomplished by transformation of type II cells to type I cells | ||
| + | |||
| + | |||
| + | ==[[Pulmonary abscesses]]== | ||
| + | |||
| + | =='''Infectious causes of pneumonia'''== | ||
| + | {| cellpadding="5" cellspacing="0" border="1" | ||
| + | | . | ||
| + | | [[:Category:Respiratory Viral Infections|'''VIRAL''']] | ||
| + | | [[:Category:Respiratory Bacterial Infections|'''BACTERIAL''']] | ||
| + | | [[:Category:Respiratory Fungal Infections|'''FUNGAL''']] | ||
| + | | [[:Category:Respiratory Parasitic Infections|'''PARASITIC''']] | ||
| + | |- | ||
| + | | '''Dogs''' | ||
| + | | [[Canine Distemper Virus|Canine distemper]] | ||
| + | | usually secondary | ||
| + | | [[Blastomycosis|''Blastomyces dermatitidis'']] | ||
| + | | [[Angiostrongylus vasorum|''Angiostrongylus vasorum'']] | ||
| + | |- | ||
| + | | . | ||
| + | | [[Canine Infectious Tracheobronchitis|Infectious canine tracheitis]] | ||
| + | | bronchopneumonia: ''[[Bordetella bronchiseptica]], [[:Category:Staphylococcus species|Staphylococci]], [[:Category:Streptococcus species|Streptococci]], Coliforms'' | ||
| + | | [[Histoplasmosis|''Histoplasma capsulatum'']] | ||
| + | | ''[[Toxoplasma gondii]]'' | ||
| + | |- | ||
| + | | . | ||
| + | | [[Canine Herpesvirus 1|Herpes virus]] | ||
| + | | . | ||
| + | | . | ||
| + | | . | ||
| + | |- | ||
| + | | '''Cats''' | ||
| + | | [[Feline Calicivirus|Feline calicivirus]] | ||
| + | | bronchopneumonia: ''[[:Category:Pasteurella and Mannheimia species|Pasteurella sp.]], [[:Category:Streptococcus species|Streptococcus spp.]]'' | ||
| + | | . | ||
| + | | ''[[Aelurostrongylus abstrusus]]'' | ||
| + | |- | ||
| + | | . | ||
| + | | . | ||
| + | | [[Chlamydiosis, Feline|Feline chlamydiosis]] | ||
| + | | . | ||
| + | | . | ||
| + | |- | ||
| + | | '''Horses''' | ||
| + | | [[Equine Rhinopneumonitis|Equine rhinopneumonitis]] | ||
| + | | [[Strangles|Strangles]] | ||
| + | | [[Pneumocystis carinii|''Pneumocystis carinii'']] | ||
| + | | ''[[Parascaris equorum]]'' | ||
| + | |- | ||
| + | | . | ||
| + | | [[Equine Influenza|Equine influenza]] | ||
| + | | [[Glanders|Glanders]] | ||
| + | | . | ||
| + | | . | ||
| + | |- | ||
| + | | . | ||
| + | | [[Equine Viral Arteritis|Equine viral arteritis]] | ||
| + | | [[Rhodococcus equi|''Rhodococcus equi'']] | ||
| + | | . | ||
| + | | . | ||
| + | |- | ||
| + | | '''Cattle''' | ||
| + | | [[Bovine Parainfluenza - 3|Parainfluenza- 3]] | ||
| + | | [[Necrotic Laryngitis]] | ||
| + | | . | ||
| + | | ''[[Dictyocaulus viviparus]]'' | ||
| + | |- | ||
| + | | . | ||
| + | | . | ||
| + | | [[Pneumonic Pasteurellosis|Pneumonic pasteurellosis]] | ||
| + | | . | ||
| + | | . | ||
| + | |- | ||
| + | | . | ||
| + | | . | ||
| + | | [[Contagious Bovine Pleuropneumonia|Contagious bovine pleuropneumonia]] | ||
| + | | . | ||
| + | | . | ||
| + | |- | ||
| + | | . | ||
| + | | . | ||
| + | | [[Enzootic Pneumonia - Calves|Enzootic pneumonia of calves]] | ||
| + | | . | ||
| + | | . | ||
| + | |- | ||
| + | | . | ||
| + | | . | ||
| + | | [[Acute Exudative Pneumonia|Acute exudative pneumonia]] | ||
| + | | . | ||
| + | | . | ||
| + | |- | ||
| + | | . | ||
| + | | . | ||
| + | | [[Enzootic Pneumonia - Calves|''Mycoplasmal'' pneumonia]] | ||
| + | | . | ||
| + | | . | ||
| + | |- | ||
| + | | . | ||
| + | | . | ||
| + | | [[Tuberculosis - Cattle|''Mycobacterium bovis'' - tuberculosis]] | ||
| + | | . | ||
| + | | . | ||
| + | |- | ||
| + | | . | ||
| + | | . | ||
| + | | bronchopneumonia: [[:Category:Pasteurella and Mannheimia species|''Pasteurella sp.'']], ''[[Corynebacterium pyogenes]]'' | ||
| + | | . | ||
| + | | . | ||
| + | |- | ||
| + | | '''Sheep''' | ||
| + | | [[Visna-Maedi Virus|Maedi Visna]] | ||
| + | | bronchopneumonia: ''[[Corynebacterium pyogenes]]'' | ||
| + | | . | ||
| + | | [[Muellerius|''Muellerius capillaris'']] | ||
| + | |- | ||
| + | | . | ||
| + | | [[Bovine Parainfluenza - 3|Parainfluenza- 3]] | ||
| + | | [[Enzootic Pneumonia - Lambs|Enzootic pneumonia of lambs]] | ||
| + | | . | ||
| + | | . | ||
| + | |- | ||
| + | | . | ||
| + | | [[Sheep Pulmonary Adenomatosis]] | ||
| + | | [[Melioidosis|''Pseudomonas (Malleomyces) pseudomallei'']] | ||
| + | | . | ||
| + | | . | ||
| + | |- | ||
| + | | '''Pigs''' | ||
| + | | [[Porcine Cytomegalovirus|Inclusion body rhinitis]] | ||
| + | | [[Enzootic Pneumonia - Pigs|Enzootic pneumonia of pigs]] | ||
| + | | . | ||
| + | | [[Ascaris suum|''Ascaris suum'']] | ||
| + | |- | ||
| + | | . | ||
| + | | [[Swine Influenza|Swine influenza]] | ||
| + | | [[Actinobacillus pleuropneumoniae|''Actinobacillus pleuropneumoniae'']] | ||
| + | | . | ||
| + | | . | ||
| + | |- | ||
| + | | . | ||
| + | | [[Porcine Reproductive and Respiratory Syndrome|Porcine reproductive and respiratory syndrome]] | ||
| + | | [[Necrotic Laryngitis]] | ||
| + | | . | ||
| + | | . | ||
| + | |- | ||
| + | | . | ||
| + | | [[Porcine Circoviruses|Postweaning multisystemic wasting syndrome]] | ||
| + | | [[Pasteurellosis - Pigs|''Pasteurella multocida'']] | ||
| + | | . | ||
| + | | . | ||
| + | |- | ||
| + | | . | ||
| + | | [[Porcine Respiratory Coronavirus|Porcine respiratory coronavirus]] | ||
| + | | [[Contagious Porcine Pleuropneumonia|Contagious porcine pleuropneumonia]] | ||
| + | | . | ||
| + | | . | ||
| + | |- | ||
| + | | . | ||
| + | | . | ||
| + | | [[Glasser's Disease|Glasser's disease]] | ||
| + | | . | ||
| + | | . | ||
| + | |- | ||
| + | | . | ||
| + | | . | ||
| + | | [[Atrophic Rhinitis|''Bordetella bronchiseptica'']] | ||
| + | | . | ||
| + | | . | ||
| + | |- | ||
| + | | . | ||
| + | | . | ||
| + | | bronchopneumonia: [[:Category:Pasteurella and Mannheimia species|''Pasteurella'' spp.]], ''[[Corynebacterium pyogenes]]'', also [[:Category:Streptococcus species |''Streptococcus'' spp.]], [[Tuberculosis - Pigs|Tuberculosis]] | ||
| + | | . | ||
| + | | . | ||
| + | |- | ||
| + | |} | ||
| + | |||
| + | |||
| + | |||
| + | =='''Other forms of pneumonia'''== | ||
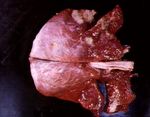
| + | [[Image:Acute necrotising pneumonia.jpg|right|thumb|150px|<small><center>Acute necrotising pneumonia (Image sourced from Bristol Biomed Image Archive with permission)</center></small>]] | ||
| + | |||
| + | ===[[Aspiration Pneumonia]]=== | ||
| + | |||
| + | |||
| + | ===[[Gangrenous pneumonia]]=== | ||
| + | |||
| + | |||
| + | ===Lipid pneumonia=== | ||
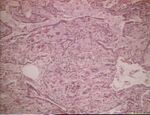
| + | [[Image:Lipid pneumonia.jpg|right|thumb|150px|<small><center>Lipid pneumonia (Image sourced from Bristol Biomed Image Archive with permission)</center></small>]] | ||
| + | *Associated with inhalation of oil, paraffin, etc. | ||
| + | *Reaction dominated by macrophages which fill the alveoli and interstitial thickening (mononuclear cells and fibrosis) | ||
| + | *Tends to acumulate in ventral regions bilterally | ||
| + | *Occurs subclinically in cats, sometimes dogs, unrelated to aspiration | ||
| + | *Gross lesion: | ||
| + | **Multifocal, firm, white nodules | ||
| + | *Microscopic lesions: | ||
| + | **Macrophages full of lipid forming foam within alveoli | ||
| + | **Interstitial lymphocyte and plasma cell infiltration, fibrosis | ||
| + | |||
| + | |||
| + | [[Category:Pneumonia]] | ||
| + | |||
| + | |||
| + | ===Uraemic pneumonia=== | ||
| + | *Severe uraemia causes increased permeability of the blood-air barrier and therefore can cause [[Pulmonary Oedema|pulmonary oedema]] | ||
| + | *In addition to the oedema, there may also be degeneration and calcification of smooth muscle and connective tissue fibres | ||
| + | *Lungs do not collapse on opening the thorax in severe cases | ||
| + | |||
| + | |||
| + | [[Category:Pneumonia]] | ||
| + | |||
| + | |||
| + | ===Foetal pneumonia=== | ||
| + | *Especially foals and farm species | ||
| + | *Due to aspiration of amniotic fluid contaminated with meconium and bacteria | ||
| + | **Secondary to fetal distress | ||
| + | **Microscopic lesions of [[Lungs Inflammatory - Pathology#Bronchopneumonia|bronchopneumonia]] | ||
| + | **Involves all lobes (versus postnatal bronchopneumonia) | ||
| + | *Haematogenous spread | ||
| + | **Causes [[Lungs Inflammatory - Pathology#Interstitial pneumonia|interstitial pneumonia]] | ||
| + | **Often caused by ''Listeria monocytogenes'', ''Salmonella'' spp. or ''Chlamydia psittaci'' | ||
| + | *In viral abortions | ||
| + | **Cause [[Lungs Inflammatory - Pathology#Bronchointerstitial pneumonia|bronchointerstitial pneumonia]] | ||
| + | **E.g.: [[Infectious Bovine Rhinotracheitis|IBR]], [[Bovine Parainfluenza - 3|PI-3]] and [[Equine Rhinopneumonitis|equine viral rhinopneumonitis]] | ||
| + | |||
| + | |||
| + | [[Category:Pneumonia]] | ||
| + | |||
| + | =Test yourself with the Lungs Pathology Flashcards= | ||
| + | |||
| + | [[Lungs_Flashcards_-_Pathology|Lungs Pathology Flashcards]] | ||
Revision as of 18:20, 19 February 2011
Pneumonia - Introduction and Classification
- Pneumonia
- Inflammation that takes place in the alveoli and their walls
- Can be grouped either according to
- Nature of the inflammatory process
- Aetiological agent
- Pattern of the lesion
- Patterns of lung inflammation vary depending on the aetiology, route and method of exposure and multiple host factors including age, general health, and immune status
- There are five general patterns of pneumonia:
Bronchopneumonia
Bronchointerstitial Pneumonia
Lobar Pneumonia
Interstitial Pneumonia
Embolic Pneumonia
Granulomatous Pneumonia
Verminous Pneumonia
Stages of pneumonia
- Regardless of the pattern, all pneumonias pass through three stages:
- Exudative phase
- In this initial stage inflammatory exudate pours into alveolar spaces and alveolar capillaries are congested
- Type I alveolar epithelial cells are highly sensitive to injury and cannot proliferate in response to injury
- Necrosis and sloughing of injured type I cells, denuding alveolar spaces of lining epithelium
- Neutrophils begin to enter alveolar spaces distended with inflammatory oedema
- Proliferative phase
- Type II alveolar cells (less sensitive to and can proliferate in response to injury) begin to proliferate within 24 hours and eventually line the alveolar walls denuded of type I cells ***By 6 days cuboidal type II cells can completely line the alveoli
- Proliferation of type II cells marks the shift from the exudative to the proliferative stage of pneumonia, also heralded by decreased blood flow in alveolar capillaries
- Because the original squamous type I cells have been replaced by cuboidal type II cells, the microscopic appearance of pneumonic lungs at about 1 week has been described as “alveolar epithelialization”, “alveolar adenomatosis”, or “bronchiolisation of alveoli”
- Repair phase
- Resolution of pneumonia is accomplished by transformation of type II cells to type I cells
- Exudative phase
Pulmonary abscesses
Infectious causes of pneumonia
Other forms of pneumonia
Aspiration Pneumonia
Gangrenous pneumonia
Lipid pneumonia
- Associated with inhalation of oil, paraffin, etc.
- Reaction dominated by macrophages which fill the alveoli and interstitial thickening (mononuclear cells and fibrosis)
- Tends to acumulate in ventral regions bilterally
- Occurs subclinically in cats, sometimes dogs, unrelated to aspiration
- Gross lesion:
- Multifocal, firm, white nodules
- Microscopic lesions:
- Macrophages full of lipid forming foam within alveoli
- Interstitial lymphocyte and plasma cell infiltration, fibrosis
Uraemic pneumonia
- Severe uraemia causes increased permeability of the blood-air barrier and therefore can cause pulmonary oedema
- In addition to the oedema, there may also be degeneration and calcification of smooth muscle and connective tissue fibres
- Lungs do not collapse on opening the thorax in severe cases
Foetal pneumonia
- Especially foals and farm species
- Due to aspiration of amniotic fluid contaminated with meconium and bacteria
- Secondary to fetal distress
- Microscopic lesions of bronchopneumonia
- Involves all lobes (versus postnatal bronchopneumonia)
- Haematogenous spread
- Causes interstitial pneumonia
- Often caused by Listeria monocytogenes, Salmonella spp. or Chlamydia psittaci
- In viral abortions
- Cause bronchointerstitial pneumonia
- E.g.: IBR, PI-3 and equine viral rhinopneumonitis